NILOTINIB

WO 2016024289, NILOTINIB, New Patent by SUN
SUN PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LTD [IN/IN]; 17/B, Mahal Industrial Estate, Off Mahakali Caves Road, Andheri (east), Mumbai 400093 (IN)
THENNATI, Rajamannar; (IN).
KILARU, Srinivasu; (IN).
VALANCE SURENDRAKUMAR, Macwan; (IN).
SHRIPRAKASH DHAR, Dwivedi; (IN)
The present invention provides novel salts of nilotinib and polymorphs thereof. The acid addition salts of nilotinib with benzenesulfonic acid, butanedisulfonic acid, 1-5- naphthalenedisulfonic acid, naphthalene-1-sulfonic acid and 1-hydroxynaphthoic acid; hydrates and anhydrates thereof.
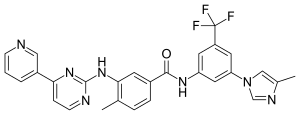
Nilotinib, 4-methyl-N-[3-(4-methyl-lH-imidazol-l-yl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl] amino] -benzamide, having the following formula

is marketed under the name Tasigna® in US and Europe. Tasigna contains nilotinib monohydrate monohydrochloride salt and is available as capsules for the treatment of adult patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) in chronic phase. Tasigna is also indicated for the treatment of chronic phase and accelerated phase Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (Ph+ CML) in adult patients resistant or intolerant to prior therapy that included imatinib.
Nilotinib is considered a low solubility/low permeability (class IV) compound in the Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS). Therefore, dissolution of nilotinib can potentially be rate limiting step for in-vivo absorption. It is soluble in acidic media; being practically insoluble in buffer solutions of pH 4.5 and higher.
WIPO publication 2014059518A1 discloses crystalline forms of nilotinib hydrochloride and methods of the preparation of various crystalline solvates of nilotinib hydrochloride including benzyl alcohol, acetic acid and propylene glycol.
WIPO publication 2011033307A1 discloses nilotinib dihydrochloride and its hydrates and method for their preparation.
WIPO publication 2011163222A1 discloses the preparation of nilotinib salts and crystalline forms thereof. The salts of nilotinib disclosed are hydrochloride, fumarate, 2-chloromandelate, succinate, adipate, L-tartrate, glutarate, p-toluenesulfonate, camphorsulfonate, glutamate, palmitate, quinate, citrate, maleate, acetate, L-malate, L-aspartate, formate, hydrobromide, oxalate and malonate.
WIPO publication number 2011086541A1 discloses a nilotinib monohydrochloride monohydrate salt and methods for preparing.
WIPO publication number 2010054056A2 describes several crystalline forms of nilotinib hydrochloride.
WIPO publication number 2007/015871A1 discloses the preparation of nilotinib salts and crystalline forms thereof. The salts are mixtures of nilotinib and one acid wherein the acids are selected from the group consisting of hydrochloric acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid, sulfonic acid, methane sulfonic acid, ethane sulfonic acid, benzene sulfonic acid, p-toluene sul- fonic acid, citric acid, fumaric acid, gentisic acid, malonic acid, maleic acid, and tartaric acid.
WIPO publication number 2007015870A2 discloses several nilotinib salts including amorphous and crystalline forms of nilotinib free base, nilotinib HC1 and nilotinib sulfate along with their hydrate and solvates.
EXAMPLES:
Example 1: Preparation of nilotinib benzenesulfonate crystalline Form I
Nilotinib base (1 g) was suspended in water (20 ml). A solution of benzenesulfonic acid (0.4 g) in water (3ml) was added and the content was heated at 60 °C for 2-3 h. The mixture was cooled to 25-30 °C, filtered, washed with water (3 x 5 ml) and dried under vacuum for 2 h at 50-55 °C.
1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 2.40 (s,3H), 2.42 (s,3H), 7.35-7.37 (m,3H), 7.51-7.66 (m,5H),7.83 (d,lH), 7.96 (s,lH),8.08 (s,lH),8.30 (s,lH) 8.39 (s,lH),8.54 (d,lH), 8.61 (d,lH), 8.64 (s,lH), 8.75 (d,lH), 9.25 (s,lH), 9.34 (d,lH), 9.61 (s,lH), 10.84 (s,lH).
The salt provides an XRPD pattern substantially same as set forth in FIG. 1.
Example 2: Preparation of nilotinib butanedisulfonate (2: 1) crystalline Form II
Nilotinib base (100 g) was dissolved in 20 % water in THF solution (2000 ml) at 60-65 °C and insoluble matter was filtered. The filtrate was concentrated under vacuum below 60 °C. Filtered water (1000 ml) was added to the reaction mixture and it was heated at 50-55 °C, followed by addition of 1,4-butanedisulfonic acid -60% aqueous solution (28.6 ml) at same temperature. The content was stirred at 50-55 °C for 2-3h. Reaction mixture as cooled to 25-30 °C and product was filtered, washed with water (200 ml x 2) and dried in air oven at 50-55 °C (yield: 115 g).

Sun Pharma managing director Dilip Shanghvi.
Purity (by HPLC):99.76%
1H NMR (400 MHz,DMSO-d6) δ 1.63-1.66(m,2H), 2.40(d,3H),2.42(s,3H),2.43-2.47(m,2H), 7.51-7.62(m,3H),7.85(dd,lH),7.96(s,lH),8.08(s,lH),8.34(s,lH),8.38(d,lH),8.52-8.55(m,lH), 8.60-8.62 (m,2H), 8.75(d,lH), 9.25(S,1H),9.34(S,1H),9.59(S,1H),10.86(S,1H)
Water content: 7.95 %.
The salt has a XRPD pattern substantially same as set forth in FIG. 2.
Example 3: Preparation of nilotinib butanedisulfonate (2: 1) crystalline Form II
Nilotinib base (300 g) was suspended in methanol (3000 ml) and aqueous hydrochloric acid was added to get pH less than 2. Reaction contents were heated at reflux and was filtered and washed with methanol (100 ml). 5% (w/w) NaOH (1200 ml) solution was added at 40-45 °C within 15 min, reaction mixture was stirred for 2h. Product was filtered, washed with water
(300 ml x 3) and dried for lh. Wet material was suspended in water (3000 ml), heated at 50- 55 °C followed by addition of 1,4-butanedisulfonic acid -60% aqueous solution. The reaction mixture was stirred at 50-55°C for 2hrs. Product was filtered at room temperature, washed with water (500 ml x 2) and dried in air oven at 50-55 °C (yield: 293 g).
Purity (by HPLC): 99.88 %
1H NMR (400 MHz,DMSO-d6+TFA-dl) δ 1.75-1.78(m,2H), 2.36(d,3H),2.38(s,3H),2.69- 2.72(m,2H),7.45(d,lH),7.68(d,lH),7.83(s,lH),7.88(dd,lH),7.97(s,lH),8.16-8.19(m,lH), 8.35
(s,2H), 8.63(d,lH),8.68(d,lH),9.04(d,lH),9.21(d,lH),9.53(br s,lH),9.69(d,lH)10.80 (s,lH)
Water content: 6.44 %
Example 4: Preparation of nilotinib butanedisulfonate (2: 1) crystalline Form III
Nilotinib butanedisulfonate (210g) was dissolved in acetic acid water mixture (50:50) (2520 ml) at 75-80 °C and was filtered to remove insoluble matter and washed with acetic acid water mixture (50:50) (210 ml). Water (3150ml) was added to the filtrate and stirred first at room temperature and then at 0-5 °C. Product was filtered and washed with water. Material was dried in air oven at 70-75 °C. Dried material was leached with methanol (3438 ml) at reflux temperature, filtered and dried in air oven 70-75°C (yield: 152.6 g)
Purity (by HPLC): 99.89 %
1H NMR (400 MHz,DMSO-d6+TFA-dl) δ 1.73-1.77(m,2H), 2.40(s,6H),2.67-2.70(m,2H), 7.50 (d,lH), 7.70(d,lH), 7.88-7.92(m,2H), 8.07(s,lH),8.23 (dd,lH), 8.34(s,2H), 8.67 (d,lH), 8.72 (d,lH), 9.09(d,lH), 9.23 (s,lH), 9.54(d,lH), 9.74(d,lH), 10.86(s,lH).
Water content: 0.61 %
The salt provides an XRPD pattern substantially same as set forth in FIG. 3.
Example 5: Preparation of crystalline form of nilotinib butanedisulfonate (2: 1)
Crystalline Nilotinib butanedisulfonate (1 g) of Example 2 was suspended in methanol (20 ml) and was stirred at reflux for 60 min. The mixture was cooled to room temperature. Solid was filtered, washed with methanol (2 ml x 3) and dried in air oven at 70-75°C (yield: 0.8 g)
Example 6: Preparation of nilotinib butanedisulfonate (1: 1) crystalline Form IV
Nilotinib base (20 g) was suspended in methanol (800 ml) and 1,4-butanedisulfonic acid -60
% aqueous solution (6 ml) was added at 50-55 °C, and was filtered to remove insoluble matter. Filtrate was stirred at room temperature for 2-3 h. Product formed was filtered, washed with methanol (20 ml x 2) and dried the product in air oven at 70-75 °C (yield: 18.4 g).
Purity (by HPLC):99.86 %
1H NMR (400 MHz,DMSO-d6) δ 1.64-1.68(m,4H), 2.47-2.5 l(m,4H), 2.41(s,3H), 2.42(d,3H), 7.52(d,lH), 7.83-7.89(m,2H), 7.99(s,lH), 8.15(s,lH), 8.36 (d,lH), 8.39(s,lH), 8.65-8.66(m,2H), 8.79(d,lH), 8.89(br s,lH), 9.36(s,lH), 9.41(br s,lH), 9.74(d,lH), 10.91(s,lH).
The salt has XRPD pattern substantially same as set forth in FIG. 4.
Example 7: Preparation of nilotinib 1,5-napthalenedisulfonic acid salt (2: 1) crystalline Form V
Nilotinib base (1 g) was suspended in water (20 ml). A solution of 1,5-napthalenedisulfonic acid (0.4 g; 0.6 eq.) in water (5ml) was added and the content was heated at 50-55 °C for lh. The mixture was cooled to 25-30 °C, filtered and washed with water (10 ml). The product was dried in air oven at 50-55°C (yield: 1.2 g).
1H NMR (400 MHz,DMSO-d6) δ 2.39 (s,3H), 2.42 (s,3H), 7.45-7.61 (m,4H),7.84 (d,lH), 7.97(s,2H),8.08 (m,lH),8.31 (s,lH) 8.38 (s,lH),8.55 (d,lH), 8.63 (s,2H), 8.75 (s,lH), 8.92 (d,lH), 9.26 (s, 1H), 9.34 (s,lH),9.62 (s,lH), 10.85 (s,lH).
The salt has a XRPD pattern substantially same as set forth in FIG. 5.
Example 8: Preparation of nilotinib 1,5-napthalenedisulfonic acid salt (1: 1) crystalline Form VI
Nilotinib base (1 g) was suspended in water (20 ml). A solution of 1,5-napthalenedisulfonic acid (0.8 g; 1.2eq) in water (5 ml) was added and the content was heated at 50-55 °C for 1 h. The mixture was cooled to 25-30 °C, filtered, washed with water (10 ml) and dried in air oven at 50-55 °C (yield: 1.4g).
1H NMR(400 MHz,DMSO-d6) δ 2.40 (s,3H),2.41 (s,3H), 7.43-7.52 (m,3H),7.61 (d,lH), 7.85-7.99(m,5H),8.11 (s,lH),8.34 (s,2H), 8.64-8.67 (m,2H), 8.89-8.92 (m,4H),9.40(d,2H), 9.72 (s,lH), 10.87 (s,lH).
The salt has a XRPD pattern substantially same as set forth in FIG. 6.
Example 9: Preparation of nilotinib napthalene-1- sulfonic acid salt crystalline Form VII Nilotinib base (1 g) was suspended in water (10 ml) and heated to 50-55 °C. A solution of napthelene-1 -sulfonic acid and methanol (10 ml) was added to it and heated at 70-75 °C for 30 min. The mixture was cooled to 25-30 °C and stirred for 10 min. The product was filtered, washed with water (2 x 2 ml) and dried under vacuum for 1-2 h at 50-55 °C.
1H NMR (400 MHz,DMSO-d6) δ 2.41 (s,3H),2.42 (s,3H), 7.46-7.58 (m,5H), 7.70-8.00 (m,7H)8.11(s,lH)8.31(s,lH),8.37(s,lH),8.63-8.66 (m,3H), 8.81-8.89 (m,2H), 9.31 (s,lH), 9.37 (d,lH), 9.71 (d,lH), 10.86 (s,lH)
The salt has a XRPD pattern substantially same as set forth in FIG. 7.
Example 10: Preparation of nilotinib l-hydroxy-2-napthoic acid salt crystalline Form VIII Nilotinib base (1 g) was suspended in water (20 ml) and heated to 50-55 °C. l-Hydroxy-2-napthoic acid was added to it and the content was heated at 50-55 °C for 1 h. Methanol (5 ml) was added to the mixture and stirred for 30 min. The content was filtered, washed with water (2 x 2 ml) and dried under vacuum for 1 h at 50-55 °C.
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 2.25 (s,3H), 2.41 (s,3H), 7.40-7.92 (m,l lH), 8.23-8.73 (m,8H), 9.24 (s,lH), 9.34(s,lH), 10.70 (s,lH).
The salt has a XRPD pattern substantially same as set forth in FIG. 8.
 |
|
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
4-methyl-N-[3-(4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)- 5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3- [(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl) amino]benzamide
|
|
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Tasigna |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608002 |
| Licence data | EMA:Link, US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Legal status | |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 30%[1] |
| Protein binding | 98%[1] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (mostly CYP3A4-mediated)[1] |
| Biological half-life | 15-17 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Faeces (93%)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 641571-10-0(base)  |
| ATC code | L01XE08 |
| PubChem | CID 644241 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 5697 |
| DrugBank | DB04868  |
| ChemSpider | 559260  |
| UNII | F41401512X  |
| KEGG | D08953  |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:52172  |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL255863  |
| PDB ligand ID | NIL (PDBe, RCSB PDB) |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C28H22F3N7O |
| Molar mass | 529.5245 g/mol |
//////////////WO 2016024289, WO-2016024289, NILOTINIB, New Patent, SUN
Cc1ccc(cc1Nc2nccc(n2)c3cccnc3)C(=O)Nc4cc(cc(c4)n5cc(nc5)C)C(F)(F)F
Filed under: PATENT, PATENTS, Uncategorized Tagged: NEW PATENT, NILOTINIB, Sun, sun pharma, WO 2016024289





















