
BMS-262084
CAS 253174-92-4
- Molecular FormulaC18H31N7O5
- Average mass425.483 Da
NII-I0IR71971G
I0IR71971G
(2S,3R)-1-[4-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)piperazine-1-carbonyl]-3-[3-(diaminomethylideneamino)propyl]-4-oxoazetidine-2-carboxylic acid(2S,3R)-1-{[4-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)piperazin-1-yl]carbonyl}-3-{3-[(diaminomethylidene)amino]propyl}-4-oxoazetidine-2-carboxylic acid
(2S,3R)-3-{3-[(Diaminomethylene)amino]propyl}-1-({4-[(2-methyl-2-propanyl)carbamoyl]-1-piperazinyl}carbonyl)-4-oxo-2-azetidinecarboxylic acid253174-92-4[RN]2-Azetidinecarboxylic acid, 3-[3-[(diaminomethylene)amino]propyl]-1-[[4-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-1-piperazinyl]carbonyl]-4-oxo-, (2S,3R)-
Factor XIa inhibitors (thrombosis), BMS; Factor XIa inhibitors (thrombosis), Bristol-Myers Squibb; BMS-654457; Factor XIa inhibitors (cardiovascular diseases), BMS; BMS-724296
Novel crystalline forms of BMS-262084 as Factor XIa antagonist useful for treating cardiovascular diseases.
PHASE 2

PAPER
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters (2002), 12(21), 3229-3233.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960894X02006881
Abstract
A series of N1-activated C4-carboxy azetidinones was prepared and tested as inhibitors of human tryptase. The key stereochemical and functional features required for potency, serine protease specificity and aqueous stability were determined. From these studies compound 2, BMS-262084, was identified as a potent and selective tryptase inhibitor which, when dosed intratracheally in ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs, reduced allergen-induced bronchoconstriction and inflammatory cell infiltration into the lung.
BMS-262084 was identified as a potent and selective tryptase inhibitor that, when dosed intratracheally in ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs, reduced allergen-induced bronchoconstriction and inflammatory cell infiltration into the lung.

PAPER
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jo010757o
Journal of Organic Chemistry (2002), 67(11), 3595-3600.

A highly stereoselective synthesis of the novel tryptase inhibitor BMS-262084 was developed. Key to this synthesis was the discovery and development of a highly diastereoselective demethoxycarbonylation of diester 12 to form the trans-azetidinone 13. BMS-262084 was prepared in 10 steps from d-ornithine in 30% overall yield.
1 as a white powder (3.18 g, 99% yield). Mp: 213-215 °C dec. [α]25D = −65.9 (c 0.99, MeOH). 1H NMR (CD3OD): δ 4.17 (d, J = 3.29 Hz, 1H), 3.61−3.11 (m, 11H), 1.94−1.75 (m, 4H), 1.32 (s, 9H). 13C NMR (CD3OD): δ 176.6, 168.7, 159.4, 158.7, 152.3, 58.7, 53.2, 51.8, 46.5, 45.0, 41.8, 29.6, 27.4, 26.3. HRMS: calcd for C18H32N7O5(M+ + H) 426.2465, found 426.2470. IR (KBr): 3385, 3184, 1775, 1657, 1535, 1395, 1259, 1207, 996, 763 cm–1. Anal. Calcd for C18H31N7O5: C, 50.81, H, 7.34, N, 23.04. Found: C, 50.65, H, 7.42, N, 22.72. Chiral HPLC: ee 99.6%; Chiralpak OD column, 250 × 4.6 mm, 10 μm; mobile phase hexane/EtOH (85:15, v/v); isocratic at ambient temperature, 1.0 mL/min, 220 nm; concentration 0.25 mg/mL, 10 μL injection; RT = 18.6 min (enantiomer, RT = 15.7 min).


PATENT
WO2018133793
claiming macrocyclic compounds.
PATENT
WO-2020259366
Novel crystalline and solid forms of BMS-262084 (designates as monohydrate or 1.5 hydrate), processes for their preparation and compositions comprising them are claimed. BMS-262084 is disclosed to be Factor XIa antagonist, useful for treating cardiovascular diseases.MS-262084 (CAS number: 253174-92-4), the chemical name is (2S,3R)-1-[4-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)piperazine-1-carbonoyl]-3-[3- (Diaminomethylamino)propyl]-4-cyclopropanamide-2-carboxylic acid, also called compound (1) in the present invention, is developed by BMS (Bristol-Myers-Squibb) to treat cardiovascular diseases The drug, as an oral coagulation factor XIa inhibitor for thrombus, has the advantage of significantly reducing the risk of bleeding, and its structure is shown in formula (1):
Patent application WO 9967215A1 discloses the BMS-262084 compound, but the specific molecular formula of the solid substance obtained by the disclosed preparation process is C 18 H 31 N 7 O 5 ·1.56H 2 O, which is similar to the crystal of BMS-262084 described in this application. Type and amorphous water have different molecular weights.
“A stereoselective synthesis of BMS-262084 an azetidinone-based tryptase inhibitor” (Source: Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2002,67(11):3595-3600; Journal of Organic Chemistry,2002,67(11):3595-3600) It is mentioned that the preparation method of BMS-262084 is that hydrogenolysis under neutral conditions eliminates the benzene and Cbz protection groups, and obtains BMS-262084 (melting point 213-215℃). The inventors conducted experiments based on part of the contents disclosed in the document, and the test results obtained crystal form A and crystal form B. The X-ray powder diffraction patterns are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 respectively.Example 1
“A stereoselective synthesis of BMS-262084 an azetidinone-based tryptase inhibitor” (Source: Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2002,67(11):3595-3600; Journal of Organic Chemistry,2002,67(11):3595-3600) Only ethanol solvents are mentioned in the literature. Since no specific crystal refining process was provided, only part of the experiment was performed using ethanol solvent.
1) Ethanol solvent volatilization at room temperature: 50mg of BMS-262084 (amorphous) was added to 1.0 mL of ethanol solvent and completely dissolved at room temperature (about 25°C). After volatilizing at room temperature for two days, the solid product was obtained and its crystal form was tested. It is crystal form A, as shown in Figure 1. It is considered that it contains a small amount of amorphous form; but it is unstable and will undergo crystal transformation at room temperature. After standing for one day, the XRPD was tested, and it was found that it was converted to a mixture containing crystal form A, other crystal forms and amorphous forms.
2) Ethanol solvent high-temperature volatilization: 50mg BMS-262084 is added to 1.0mL ethanol solvent, completely dissolved at high temperature (about 60℃), and high-temperature volatilization is carried out in the open to obtain a solid product. The crystal form of the solid product is detected, and the crystal form is B (contains a lot of amorphous), see Figure 2.
SYN1
WO 9967215
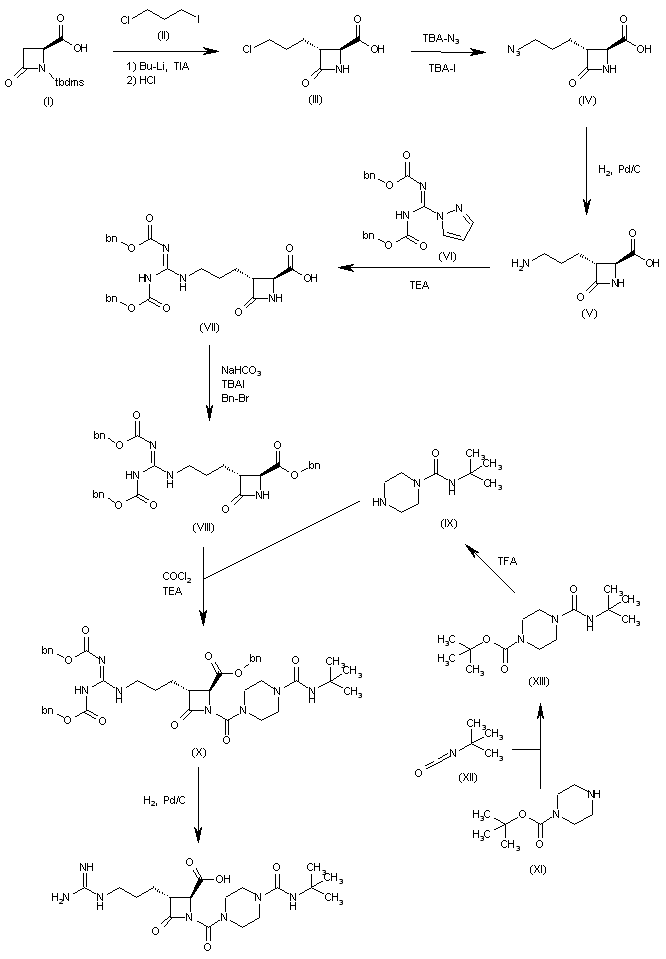
The condensation of N-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-4-oxoazetidine-2(S)-carboxylic acid (I) with 1-chloro-3-iodopropane (II) by means of BuLi and triisopropylamine (TIA) in THF, followed by treatment with HCl, gives the 3(R)-(3-chloropropyl) derivative (III), which is treated with tetrabutylammonium azide and tetrabutylammonium iodide in DMF to yield the 3-azidopropyl derivative (IV). The reduction of (IV) with H2 over Pd/C in DMF affords the 3-aminopropyl compound (V), which is treated with 1-[N,N’-bis(benzyloxycarbonyl)-1H-pyrazole] (VI) in the same solvent to provide the protected 3-guanidinopropyl compound (VII). The esterification of (VII) with NaHCO3, tetrabutylammonium iodide and Bn-Br in DMF gives the benzyl ester (VIII), which is condensed with N-tert-butylpiperazine-1-carboxamide (IX) and phosgene by means of TEA in toluene to yield the protected precursor (X). Finally, this compound is debenzylated by hydrogenation with H2 over Pd/C in dioxane to give the target azetidine-carboxylic acid.
SYN 2
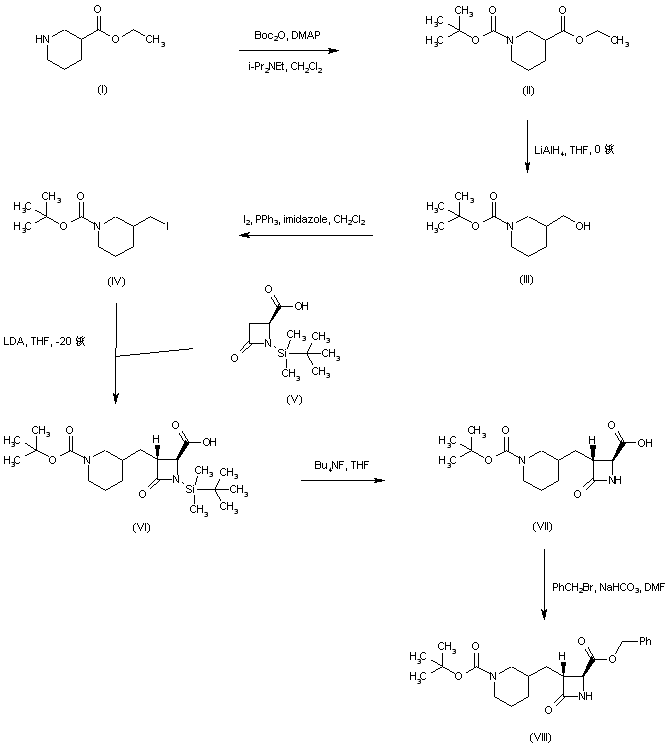
Ethyl nipecotate (I) was protected as the N-Boc derivative (II) and subsequently reduced to alcohol (III) by means of LiAlH4. Conversion of alcohol (III) into iodide (IV) was achieved by treatment with iodine and triphenylphosphine. The dianion of the chiral azetidinecarboxylic acid (V) was alkylated with iodide (IV) to furnish adduct (VI) as a diastereomeric mixture that was desilylated to (VII) using tetrabutylammonium fluoride. Benzyl ester (VIII) was then obtained by reaction of carboxylic acid (VII) with benzyl bromide and NaHCO3.
SYN 3
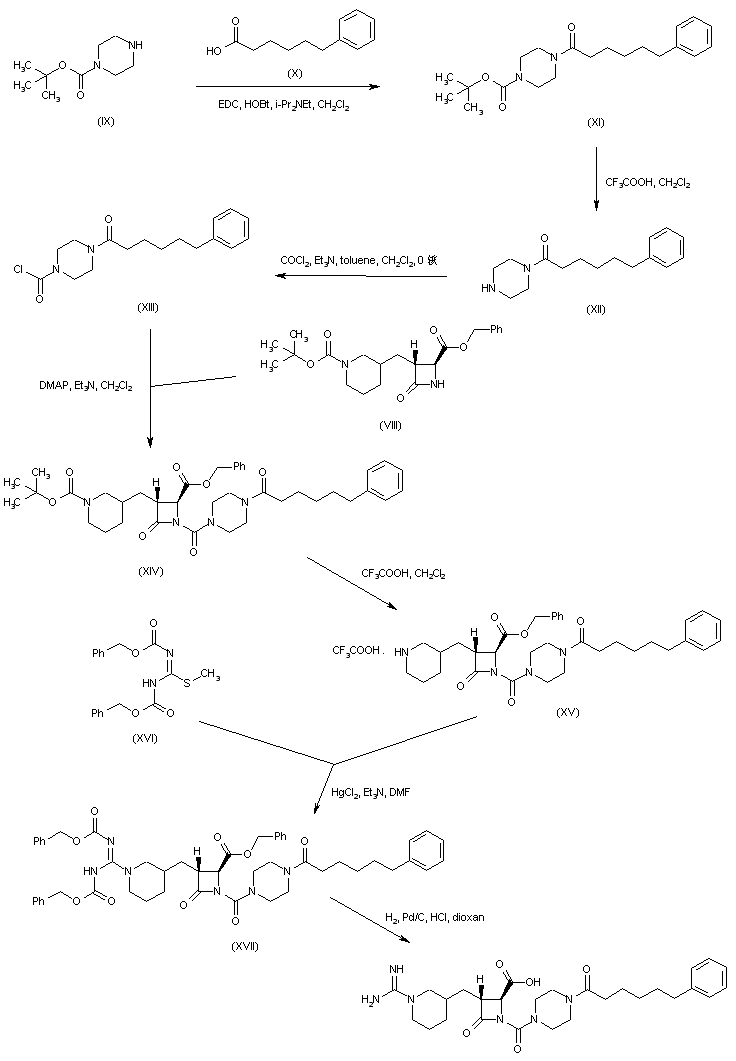
Coupling of 6-phenylhexanoic acid (X) with N-Boc-piperazine (IX) to give (XI), followed by acid deprotection of the Boc group of (XI), provided (6-phenylhexanoyl)piperazine (XII). This was converted to the carbamoyl chloride (XIII) upon treatment with phosgene. The condensation of carbamoyl chloride (XIII) with azetidinone (VIII) gave rise to the urea derivative (XIV). After acid cleavage of the Boc protecting group of (XIV), the resulting piperidine (XV) was condensed with N,N’-dicarbobenzoxy-S-methylisothiourea (XVI) in the presence of HgCl2, yielding the protected guanidine (XVII). This was finally deprotected by catalytic hydrogenolysis over Pd/C.
////////////////////////BMS-262084, BMS 262084, BMS 724296, Factor XIa inhibitors, thrombosis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, BMS 654457, PHASE 2
CC(C)(C)NC(=O)N1CCN(CC1)C(=O)N2C(C(C2=O)CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)O