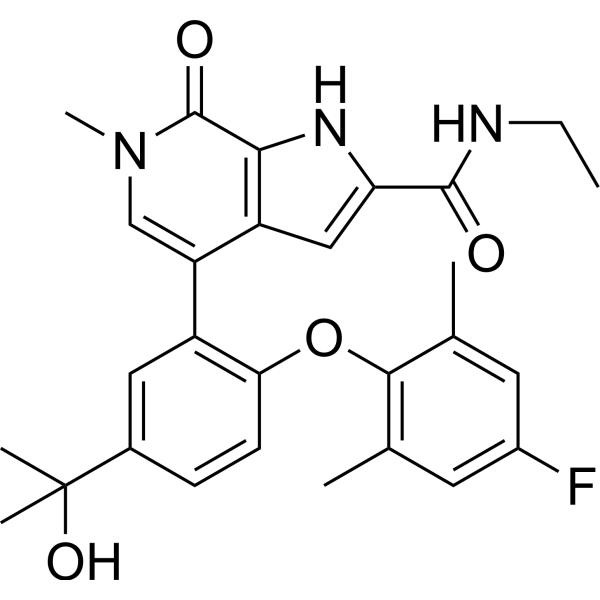
ABBV 744
N-Ethyl-4-[2-(4-fluoro-2,6-dimethylphenoxy)-5-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)phenyl]-6,7-dihydro-6-methyl-7-oxo-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridine-2-carboxamide
1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridine-2-carboxamide, N-ethyl-4-[2-(4-fluoro-2,6-dimethylphenoxy)-5-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)phenyl]-6,7-dihydro-6-methyl-7-oxo-
| Molecular Weight |
491.55 |
|---|---|
| Formula |
C₂₈H₃₀FN₃O₄ |
| CAS No. |
2138861-99-9 |
ABBV-744 is a highly BDII-selective BET bromodomain inhibitor, used in the research of inflammatory diseases, cancer, and AIDS.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Phase I, AbbVie is evaluating oral agent ABBV-744 in early clinical trials for the treatment of metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and for the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML).


PATENT
WO 2017177955
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2017177955&tab=FULLTEXT
Bromodomains refer to conserved protein structural folds which bind to N-acetylated lysine residues that are found in some proteins. The BET family of bromodomain containing proteins comprises four members (BRD2, BRD3, BRD4 and BRDt) . Each member of the BET family employs two bromodomains to recognize N-acetylated lysine residues typically, but not exclusively those found on transcription factors (Shi, J., et al. Cancer Cell 25 (2) : 210-225 (2014) ) or on the amino-terminal tails of histone proteins. Numbering from the N-terminal end of each BET protein the tandem bromodomains are typically labelled Binding Domain I (BDI) and Binding Domain II (BDII) . These interactions modulate gene expression by recruiting transcription factors to specific genome locations within chromatin. For example, histone-bound BRD4 recruits the transcription factor P-TEFb to promoters, resulting in the expression of a subset of genes involved in cell cycle progression (Yang et al., Mol. Cell. Biol. 28: 967-976 (2008) ) . BRD2 and BRD3 also function as transcriptional regulators of growth promoting genes (LeRoy et al., Mol. Cell 30: 51-60 (2008) ) . BET family members were recently established as being important for the maintenance of several cancer types (Zuber et al., Nature 478: 524-528 (2011) ; Mertz et al; Proc. Nat’l. Acad. Sci. 108: 16669-16674 (2011) ; Delmore et al., Cell 146: 1-14, (2011) ; Dawson et al., Nature 478: 529-533 (2011) ) . BET family members have also been implicated in mediating acute inflammatory responses through the canonical NF-KB pathway (Huang et al., Mol. Cell. Biol. 29: 1375-1387 (2009) ) resulting in the upregulation of genes associated with the production of cytokines (Nicodeme et al., Nature 468: 1119-1123, (2010) ) . Suppression of cytokine induction by BET bromodomain inhibitors has been shown to be an effective approach to treat inflammation-mediated kidney disease in an animal model (Zhang, et al., J. Biol. Chem. 287: 28840-28851 (2012) ) . BRD2 function has been linked to pre-disposition for dyslipidemia or improper regulation of adipogenesis, elevated inflammatory profiles and increased susceptibility to autoimmune diseases (Denis, Discovery Medicine 10: 489-499 (2010) ) . The human immunodeficiency virus utilizes BRD4 to initiate transcription of viral RNA from stably integrated viral DNA (Jang et al., Mol. Cell, 19: 523-534 (2005) ) . BET bromodomain inhibitors have also been shown to reactivate HIV transcription in models of latent T cell infection and latent monocyte infection (Banerjee, et al, J. Leukocyte Biol. doi: 10.1189/jlb. 0312165) . BRDt has an important role in spermatogenesis that is blocked by BET bromodomain inhibitors (Matzuk, et al., Cell 150: 673-684 (2012) ) . Thus, compounds that inhibit the binding of BET family bromodomains to their cognate acetylated lysine proteins are being pursued for the treatment of cancer, inflammatory diseases, kidney diseases, diseases involving metabolism or fat accumulation, and some viral infections, as well as for providing a method for male contraception. Accordingly, there is an ongoing medical need to develop new drugs to treat these indications.
FIDANZE, Steven D., et al. BROMODOMAIN INHIBITORS. WO 2017177955 A1.
////////////ABBV 744, Acute Myeloid Leukemia, AML, Phase 1 , AbbVie
CC(O)(C)C1=CC(C(C2=C3NC(C(NCC)=O)=C2)=CN(C)C3=O)=C(OC4=C(C)C=C(F)C=C4C)C=C1