Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.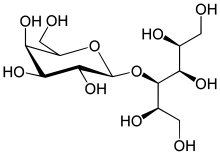
Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.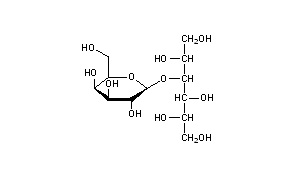
Lactitol
ラクチトール;
| Formula |
C12H24O11
|
|---|---|
| CAS |
585-86-4
|
| Mol weight |
344.3124
|
To treat chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) in adults
FDA 2/12/2020, APPROVED, Pizensy
Lactitol, NS-4, Portolac, Importal
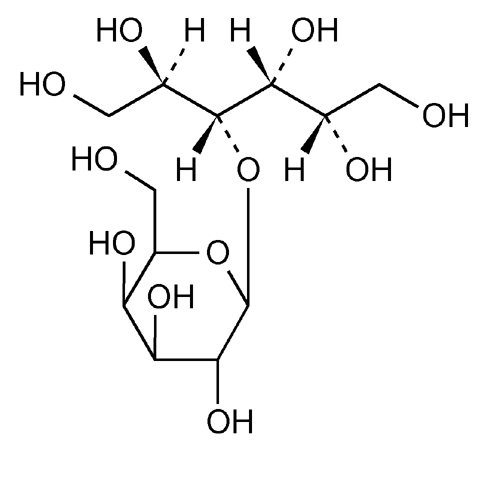
Lactitol is a sugar alcohol used as a replacement bulk sweetener for low calorie foods with approximately 40% of the sweetness of sugar. It is also used medically as a laxative. Lactitol is produced by two manufacturers, Danisco and Purac Biochem.
Applications
MedicalLactitol is used in a variety of low food energy or low fat foods. High stability makes it popular for baking. It is used in sugar-freecandies, cookies (biscuits), chocolate, and ice cream. Lactitol also promotes colon health as a prebiotic. Because of poor absorption, lactitol only has 2.4 kilocalories (9 kilojoules) per gram, compared to 4 kilocalories (17 kJ) per gram for typical saccharides. Hence, lactitol is about 60% as caloric as typical saccharides.
Lactitol is listed as an excipient in some prescription drugs.[1][2]
Lactitol is a laxative and is used to prevent or treat constipation,[3] e.g., under the trade name Importal.[4][5]
In February 2020, Lactitol was approved for use in the United States as an osmotic laxative for the treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) in adults.[6][7][8]
Lactitol in combination with Ispaghula husk is an approved combination for idiopathic constipation as a laxative and is used to prevent or treat constipation.[medical citation needed]
Safety and health
Lactitol, erythritol, sorbitol, xylitol, mannitol, and maltitol are all sugar alcohols.[medical citation needed] The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies sugar alcohols as “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS). They are approved as food additives, and are recognized as not contributing to tooth decay or causing increases in blood glucose.Lactitol is also approved for use in foods in most countries around the world.
Like other sugar alcohols, lactitol causes cramping, flatulence, and diarrhea in some individuals who consume it. This is because humans lack a suitable beta-galactosidase in the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and a majority of ingested lactitol reaches the large intestine,[9] where it then becomes fermentable to gut microbes (prebiotic) and can pull water into the gut by osmosis.{[medical citation needed] Those with health conditions should consult their GP or dietician prior to consumption.{[medical citation needed]
History
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Pizensy based on evidence from a clinical trial (Trial 1/ NCT02819297) of 594 patients with CIC conducted in the United States.[8] The FDA also considered other supportive evidence including data from Trial 2 (NCT02481947) which compared Pizensy to previously approved drug (lubiprostone) for CIC, and Trial 3 (NCT02819310) in which patients used Pizensy for one year as well as data from published literature.[8]
The benefit and side effects of Pizensy were evaluated in a clinical trial (Trial 1) of 594 patients with CIC.[8] In this trial, patients received treatment with either Pizensy or placebo once daily for 6 months.[8] Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trials were completed.[8]
In the second trial (Trial 2) of three months duration, improvement in CSBMs was used to compare Pizensy to the drug lubiprostonewhich was previously approved for CIC.[8] The third trial (Trial 3) was used to collect the side effects in patients treated with Pizensy for one year.[8]
SYN
Lactitol (CAS NO.: 585-86-4), with its other name of 4-O-beta-D-Galactopyranosyl-D-glucitol, could be produced through many synthetic methods.
Following is one of the synthesis routes: Lactitol is obtained by catalytic hydrogenation of lactose (I) in the presence of either, nickel catalysts such as Raney nickel (1-9), or ruthenium catalysts (10). Alternatively, lactose (I) is reduced by employing NaBH4 (9).
Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.
CLIP
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/apj.2275
Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.
MORE SYNTHESIS COMING, WATCH THIS SPACE…………………..
Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.![]()
SYNTHESIS
References
- ^ “Lactitol (Inactive Ingredient)”. Drugs.com. 23 September 2018. Retrieved 24 February 2020.
- ^ “Lactitol Monohydrate (Inactive Ingredient)”. Drugs.com. 3 October 2018. Retrieved 24 February 2020.
- ^ Miller LE, Tennilä J, Ouwehand AC (2014). “Efficacy and tolerance of lactitol supplementation for adult constipation: a systematic review and meta-analysis”. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 7: 241–8. doi:10.2147/CEG.S58952. PMC 4103919. PMID 25050074.
- ^ “Importal”. Drugs.com. 3 February 2020. Retrieved 24 February 2020.
- ^ FASS.se (the Swedish Medicines Information Engine). Revised 2003-02-12.
- ^ “Pizensy: FDA-Approved Drugs”. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 24 February 2020.
- ^ “Pizensy- lactitol powder, for solution”. DailyMed. 21 February 2020. Retrieved 24 February 2020.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e f g h “Drug Trial Snapshot: Pizensy”. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 12 February 2020. Retrieved 4 March 2020. Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.![]() This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ^ Grimble GK, Patil DH, Silk DB (1988). “Assimilation of lactitol, an unabsorbed disaccharide in the normal human colon”. Gut. 29 (12): 1666–1671. doi:10.1136/gut.29.12.1666. PMC 1434111. PMID 3220306.
External links
- Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.![]() Media related to Lactitol at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Lactitol at Wikimedia Commons - “Lactitol”. Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
| Image may be NSFW. Clik here to view.  |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-O-α-D-Galactopyranosyl-D-glucitol
|
|
| Other names
Lactitol
Lacty |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.698 |
| E number | E966 (glazing agents, …) |
| KEGG |
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C12H24O11 | |
| Molar mass | 344.313 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 146 °C (295 °F; 419 K) |
| Pharmacology | |
| A06AD12 (WHO) | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Image may be NSFW. Clik here to view.  verify (what is Image may be NSFW. verify (what is Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.  Image may be NSFW. Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.  ?) ?) |
|
| Infobox references | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Importal, Pizensy |
| Other names | Lactitol Hydrate (JANJP) |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | E966 (glazing agents, …) Image may be NSFW. Clik here to view. |
| CompTox Dashboard(EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.698 Image may be NSFW. Clik here to view. |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H24O11 |
| Molar mass | 344.313 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
CLIP
https://www.drugfuture.com/Pharmacopoeia/USP32/pub/data/v32270/usp32nf27s0_m44100.html
C12H24O11. Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view. Image may be NSFW.
Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view. Image may be NSFW.
Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view. Image may be NSFW.
Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view. Image may be NSFW.
Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view. 344.31
344.31
Clik here to view.
 –D-Galactopyranosyl-D-glucitol Image may be NSFW.
–D-Galactopyranosyl-D-glucitol Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 Image may be NSFW.
Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 Image may be NSFW.
Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 [585-86-4].
[585-86-4].Clik here to view.
 Image may be NSFW.
Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 Image may be NSFW.
Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 [81025-04-9].
[81025-04-9].Clik here to view.
 Image may be NSFW.
Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 Image may be NSFW.
Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 [81025-03-8].
[81025-03-8].Clik here to view.
 11Image may be NSFW.
11Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 —
— USP Lactitol RS.
Clik here to view.
 197KImage may be NSFW.
197KImage may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 .
.Clik here to view.
 921Image may be NSFW.
921Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 — between 4.5% and 5.5% (monohydrate); between 9.5% and 10.5% (dihydrate); and not more than 0.5% for the anhydrous form.
— between 4.5% and 5.5% (monohydrate); between 9.5% and 10.5% (dihydrate); and not more than 0.5% for the anhydrous form.Clik here to view.
 281Image may be NSFW.
281Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 : not more than 0.5%.
: not more than 0.5%.Clik here to view.
 231Image may be NSFW.
231Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 — Dissolve 4 g of it in 25 mL of water: the limit is 5 µg per g.
— Dissolve 4 g of it in 25 mL of water: the limit is 5 µg per g.Related compounds—
Procedure— Separately inject equal volumes (about 25 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses. The relative retention times are about 0.53 for lactose, 0.58 for glucose, 0.67 for galactose, 0.72 for lactulitol, 1.0 for lactitol, 1.55 for galactitol, and 1.68 for sorbitol. Calculate the percentages of galactitol, sorbitol, lactulitol, lactose, glucose, and galactose in the portion of Lactitol taken by the formula:
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Lactitol RS in the Standard solution; V is the volume, in mL, of the Test solution; W is the weight, in mg, of Lactitol in the Test solution; rU is the peak response of the relevant related compound, if observed, obtained from the Test solution; and rS is the lactitol peak response obtained from the Standard solution. The total of the percentages of all related compounds is not more than 1.5%.
Assay—
Clik here to view.
 621Image may be NSFW.
621Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 )—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 7.8-mm × 30-cm column that contains packing L34. The column is maintained at 85Image may be NSFW.
)—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 7.8-mm × 30-cm column that contains packing L34. The column is maintained at 85Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.
 , and the flow rate is about 0.7 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 1.0% for lactitol.
, and the flow rate is about 0.7 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 1.0% for lactitol.Procedure— Separately inject equal volumes (about 25 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of C12H24O11 in the portion of Lactitol taken by the formula:
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Lactitol RS in the Standard preparation, and rU and rS are the lactitol peak responses obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information— Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Elena Gonikberg, Ph.D. Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8251 |
(MDGRE05) Monograph Development-Gastrointestinal Renal and Endocrine |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(4) Page 1143
Chromatographic Column—
//////////////////Lactitol, ラクチトール , APPROVALS 2020, FDA 2020, NS-4, Portolac, Importal
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2020/211281Orig1s000ltr.pdf