

Gadobenate Dimeglumine
| Molecular Formula: | C36H62GdN5O21 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 1058.156 g/mol |
cas 113662-23-0 FREEFORM
| INGREDIENT | UNII | CAS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gadobenate dimeglumine | 3Q6PPC19PO | 127000-20-8 |
Used in MR imaging of liver.
UNII-15G12L5X8K
- 3,6,9-triaza-12-oxa-3,6,9-tricarboxymethylene-10-carboxy-13-phenyltridecanoic acid, gadolinium
- B 19036
- B-19036
- gadobenate dimeglumine
- gadobenic acid
- gadobenic acid, dimeglumine salt
- gadolinium-benzyloxypropionyl tetraacetate
- gadolinium-BOPTA-Dimeg
- Gd(BOPTA)2
- Gd-BOPTA
- Multihance (TN)
- E-7155
2-[2-[carboxylatomethyl-[2-[carboxylatomethyl(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl]amino]ethyl-(carboxymethyl)amino]-3-phenylmethoxypropanoate;gadolinium(3+);(2R,3R,4R,5S)-6-(methylamino)hexane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol
gadolinium(3+) ion bis((2R,3R,4R,5S)-6-(methylamino)hexane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol) 8-(carboxylatomethyl)-5,11-bis(carboxymethyl)-1-phenyl-2-oxa-5,8,11-triazatridecane-4,13-dioate
Gadolinium hydrogen 4-carboxylato-5,8,11-tris(carboxylatomethyl)-1-phenyl-2-oxa-5,8,11-triazatridecan-13-oate – 1-deoxy-1-(methylamino)-D-glucitol (1:2:1:2)
4-Carboxylato-5,8,11-tris(carboxylatométhyl)-1-phényl-2-oxa-5,8,11-triazatridécan-13-oate de gadolinium et de hydrogène – 1-désoxy-1-(méthylamino)-D-glucitol (1:1:2:2)
- D-Glucitol, 1-deoxy-1-(methylamino)-, [4-carboxy-5,8,11-tris(carboxymethyl)-1-phenyl-2-oxa-5,8,11-triazatridecan-13-oato(5-)-N5,N8,N11,O4,O5,O8,O11,O13]gadolinate(2-) (2:1)
- 2-Oxa-5,8,11-triazatridecan-13-oic acid, 4-carboxy-5,8,11-tris(carboxymethyl)-1-phenyl-, gadolinium complex
- Gadolinate(2-), [4-(carboxy-κO)-5,8,11-tris[(carboxy-κO)methyl]-1-phenyl-2-oxa-5,8,11-triazatridecan-13-oato(5-)-κN5,κN8,κN11,κO13]-, dihydrogen, compd. with 1-deoxy-1-(methylamino)-D-glucitol (1:2) (9CI)
- Gadolinate(2-), [4-carboxy-5,8,11-tris(carboxymethyl)-1-phenyl-2-oxa-5,8,11-triazatridecan-13-oato(5-)-N5,N8,N11,O4,O5,O8,O11,O13]-, dihydrogen, compd. with 1-deoxy-1-(methylamino)-D-glucitol (1:2)
- B 19036/7
Hygroscopic powder
Melting Point
124 deg C
Spectral Properties
Specific optical rotation: -26.9 deg at 20 deg C/365 deg C (c = 1.45 in water)
Absorption maximum: 257.8 nm (epsilon 203)
Launched – 1998 Bracco,
| Imaging, magnetic resonance |
MultiHance injection is supplied as a sterile, nonpyrogenic, clear, colorless to slightly yellow aqueous solution intended for intravenous use only. Each mL of MultiHance contains 529 mg gadobenate dimeglumine and water for injection. MultiHance contains no preservatives.
Gadobenate dimeglumine is a gadolinium-based, paramagnetic contrast agent that was launched by Bracco in 1998 for use in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The drug is administered as an injection, and is approved in the U.S. for use in imaging of the central nervous system in adults and for visualization of lesions, abnormalities in the blood brain barrier, or abnormal vascularity of the brain, spine and associated tissues. Commercialization took place in 2010. In 2012, the product was approved and launched in the U.S. as a contrast agent for magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) to evaluate adults with known or suspected renal or aorto-ilio-femoral occlusive vascular disease
Gadobenate dimeglumine is chemically designated as (4RS)-[4-carboxy-5,8,11-tris(carboxymethyl)-1phenyl-2-oxa-5,8,11-triazatridecan-13-oato(5-)] gadolinate(2-) dihydrogen compound with 1-deoxy-1(methylamino)-D-glucitol (1:2) with a molecular weight of 1058.2 and an empirical formula of C22H28GdN3O11 • 2C7H17NO5. The structural formula is as follows:

Prescription Drug Products
| Prescription Drug Products: 1 of 2 (RX Drug Ingredient) | |
|---|---|
| Drug Ingredient | GADOBENATE DIMEGLUMINE |
| Proprietary Name | MULTIHANCE MULTIPACK |
| Applicant | BRACCO (Application Number: N021358) |
| Prescription Drug Products: 2 of 2 (RX Drug Ingredient) | |
|---|---|
| Drug Ingredient | GADOBENATE DIMEGLUMINE |
| Proprietary Name | MULTIHANCE |
| Applicant | BRACCO (Application Number: N021357) |
PATENT
| US4916246 | Paramagnetic chelates useful for NMR imaging |
1990-04-10
|
Gadolinium-Based, paramagnetic contrast agent launched by Bracco in 1998 for use in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Gadobenate Dimeglumine is a gadolinium-based paramagnetic contrast agent. When placed in a magnetic field, gadobenate dimeglumine produces a large magnetic moment and so a large local magnetic field, which can enhance the relaxation rate of nearby protons; as a result, the signal intensity of tissue images observed with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be enhanced. Because this agent is preferentially taken up by normal functioning hepatocytes, normal hepatic tissue is enhanced with MRI while tumor tissue is unenhanced. In addition, because gadobenate dimeglumine is excreted in the bile, it may be used to visualize the biliary system using MRI.
FDA
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2004/021357s000_Multihance_Chemr.pdf

Gadobenate Dimeglumine is an MRI contrast agent used primarily for MR imaging of the liver. It can also be used for MRI of the heart, as well as and central nervous system in adults to visualize lesions with abnormal brain vascularity or abnormalities in the blood brain barrier, the brain, spine, or other associated tissues.
The drug is administered as an injection, and is approved in the U.S. for use in imaging of the central nervous system in adults and for visualization of lesions, abnormalities in the blood brain barrier, or abnormal vascularity of the brain, spine and associated tissues
Gadobenic acid (INN, trade name MultiHance) is a complex of gadolinium with the ligand BOPTA. In the form of the methylglucaminesalt meglumine gadobenate (INNm) or gadobenate dimeglumine (USAN), it is used as a gadolinium-based MRI contrast medium.[1]
BOPTA is a derivative of DTPA in which one terminal carboxyl group, –C(O)OH is replaced by -C–O–CH2C6H5. Thus gadobenic acid is closely related to gadopentetic acid. BOPTA itself was first synthesized in 1995. [2] In the “gadobenate” ion gadolinium ion is 9-coordinate with BOPTA acting as an 8-coordinating ligand. The ninth position is occupied by a water molecule, which exchanges rapidly with water molecules in the immediate vicinity of the strongly paramagnetic complex, providing a mechanism for MRI contrast enhancement. 139La NMR studies on the diamagnetic La-BOPTA2− complex suggest that the Gd complex maintains in solution the same kind of coordination as found, by X-ray crystallography, in the solid state for Gd-BOPTA disodium salt.[2]
MW: 670.7469
PATENT
https://encrypted.google.com/patents/US20090155181
-
Gadolinium-based contrast agents are commonly used to improve visibility of internal structures when a patient undergoes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These agents are typically administered intravenously immediately prior to imaging. Many contrast agents used in MRI cause toxicity in various areas of the body if they are not excreted rapidly by the kidney. These include for example, chelated organic gadolinium compounds which are not nephrotoxic in themselves, but which if retained in the body for extended periods of time release gadolinium ions which are toxic to various organs and cells of the body including skin, nerves, etc. The problems particularly occur in patients who are at risk for reduced kidney function. Serious diseases including nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) are among the consequences of this problem. (see, for example, Briguori et al., Catheter Cardiovasc. Intery (2006) 67(2): 175-80; Grobner et al., Kidney Int. (2007) 72(3): 260-4; Nortier et al., Nephrol. Dial. Transplant (2007) 22(11): 3097-101).
-
[0003]The FDA requested a boxed warning for contrast agents used to improve MRI images on May 23, 2007 stating that patients with severe kidney insufficiency who receive gadolinium-based agents are at risk for developing NSF, a debilitating and potentially fatal disease. In addition, patients just before or just after liver transplantation, or those with chronic liver disease, are also at risk for developing NSF if they are experiencing kidney insufficiency of any severity. The boxed warning is now included in each of the five gadolinium-based contrast agents currently approved for use in the United States. Thus, a need exists to reduce the toxicity that is caused by contrast agents in patients with risk factors for compromised renal function.
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/CN104606686A/en
gadobenate dimeglumine according to the present invention is a pharmaceutical composition, a chemical reaction equation I and the preparation was prepared as follows:
Example 1 were added to the vessel IOOmL 7. 7gBOPTA and 4. 2g thirty-two gadolinia weighed, followed by addition of 47mL water for injection, stirring and heated to 60 ° C. After incubation the reaction at this temperature for 1.5h, added the same amount in ten batches 5.77g meglumine. After each addition was complete meglumine, taking a small sample using a pH meter to monitor the reaction solution pH. If the sample pH <6. 9, the reaction was continued until the reaction solution was added next batch PH interposed between Meglumine 6.9 ~ 7.3. After the addition of meglumine, the reaction was continued heating and stirring 1.5 hours. Followed by addition of decolorizing charcoal 〇.16g pharmaceutically acceptable, holding the temperature, stirred for 1.5 hours. Finally hot filtration, the filtrate was collected, concentrated in vacuo to give a white solid 14. 2g.
[0022] Example 2 were added to the vessel IOOmL 7. 7gBOPTA weighed and 5. Ig trioxide followed by addition of 68mL of water for injection, stirring and heated to 65 ° C. After incubation the reaction I. 5h at that temperature, was added an equal amount of sub-batches twelve 6. 24g meglumine. After each addition was complete meglumine, taking a small sample using a pH meter to monitor the reaction solution pH. If the sample pH <6. 9, the reaction was continued until the reaction solution was added at a pH between batch Meglumine between 6.9 ~ 7.3.After the addition of meglumine, the reaction solution and heating was continued for 2 hours. Followed by addition of decolorizing charcoal 〇.23g pharmaceutically acceptable, holding the temperature, stirring for 2 hours. Finally hot filtration, the filtrate was collected, concentrated in vacuo to give a white solid 14. 8g.
[0023] Example 3 were added to the vessel IOOOmL 77gBOPTA weighed 42g and gadolinium oxide, followed by addition of 470mL injection water and heated with stirring to 60 ° C. After incubation the reaction at this temperature for 2h, the same amount was added in ten 58g batches meglumine. After each addition was complete meglumine, small sample, monitoring the reaction solution with a PH meter pH. If the sample pH <6. 9, the reaction was continued until the reaction solution was added next batch PH interposed between Meglumine 6.9 ~ 7.3. After the addition of meglumine, the reaction solution and heating was continued for 2 hours. Followed by addition of 2. 5g medicinal charcoal decolorization, holding the temperature, stirring for 2 hours. Finally hot filtration, the filtrate was collected, and concentrated to give a white solid 131g.
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/CN104606686A/en
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a tomographic image, which is obtained using a magnetic resonance phenomenon of electromagnetic signals from the body, the body information and reconstructed. Currently in clinical use development speed is very fast, widely used in nerve, spinal cord, heart and great vessels, joint bone, soft tissue and pelvic enhanced prosecution, has a three-dimensional object to be measured non-destructive and can perform high-resolution imaging and so on.
[0003] paramagnetic contrast agent is a contrast agent suitable for diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and into the body tissue can shorten the imaging time of protons, thereby enhancing the image sharpness and contrast. The paramagnetic contrast agents include Gd-DTPA and gadobenate dimeglumine.
[0004] Patent No. US5733528 discloses a metal chelate Gd-DTPA is applied to a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) imaging study based on human organs; CN100325733C Patent discloses a gadolinia and diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) complex , to give after separation of gadolinium diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA), Gd-DTPA method of re-chelated meglumine obtained.
[0005] gadobenate dimeglumine gadolinium DTPA derivatives, widely used as paramagnetic contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Clinical research shows that traitor, compared to Gd-DTPA, Gd Tony dimeglumine showed obvious advantages in terms of allergy, side effects and efficacy and so on. Moreover, Gd-DTPA was prepared using the purified and then after intermediate isolation, reacted not only with the stepwise synthesis of certain other compounds prepared by reacting the starting material many steps, long reaction period, and intermediate separation and purification operation complicated and likely to cause loss of product increased production costs. Therefore, the development of a simple method of synthesis Gadobenate dimeglumine is of great significance.
Patent
WO 2007031390
WO 2011073236
WO 2000002847
CN 102603550
PATENT
IN 201203216
IN 2012MU03216


The last step is Coordination of a Metal 12064-62-9, Gadolinium(III) oxide, to Carbon and Heteroatom


FIRST REPORT
- By Vittadini, Giorgio; Felder, Ernst; Musu, Carlo; Tirone, Piero
- From Investigative Radiology (1990), 25(Suppl. 1), S59-S60.
PRODUCT PATENT
- By Cavagna, Friedrich; Dapra, Massimo; De Haen, Christoph; Maggioni, Fabio; Vicinanza, Eleonora
- From Ital. Appl. (1992), IT 91MI1422 A1
AND WO 2011073236
References
- Jump up^ Sweetman, Sean C., ed. (2009). “Contrast Media”. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference (36th ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. p. 1478. ISBN 978-0-85369-840-1.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Uggeri, F.; Aime, S., Anelli, P.L., Botta, M., Brocchetta, M., De Haën, C., Ermondi, G., Grandi, M., Paoli, P. (1995). “Novel contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Synthesis and characterization of the ligand BOPTA and its Ln(III) complexes (Ln = Gd, La, Lu). X-ray structure of disodium (TPS-9-145337286-C-S)-[4-carboxy-5,8,11-tris(carboxymethyl)-1-phenyl-2-oxa-5,8, 11-triazatridecan-13-oato(5-)]gadolinate(2-) in a mixture with its enantiomer”. Inorg. Chem. 34 (3): 633–642. doi:10.1021/ic00107a017.
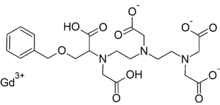 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H28GdN3O11 |
| Molar mass | 667.72 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
////////////////Gadobenate Dimeglumine, 113662-23-0, x ray contrast agent, b 1906, Gd(BOPTA)2, Gd-BOPTA, Multihance, E-7155
CNCC(C(C(C(CO)O)O)O)O.CNCC(C(C(C(CO)O)O)O)O.C1=CC=C(C=C1)COCC(C(=O)[O-])N(CCN(CCN(CC(=O)O)CC(=O)[O-])CC(=O)[O-])CC(=O)O.[Gd+3]



