
| Originator |
Daiichi Sankyo
|
|---|---|
| Therapeutic Claim |
Treatment of fibromyalgia
|
Phase III clinical trials at Daiichi Sankyo for the treatment of pain associated with fibromyalgia

| Class |
Analgesic drugs (small molecules)
|
|---|---|
| Mechanism of action |
CACNA2D1 protein modulators
|
SYNTHESIS

Mirogabalin (DS-5565) is a drug developed by Daiichi Sankyo and related to drugs such as gabapentin and pregabalin. Similarly to these drugs, mirogabalin binds to the α2δ calcium channels (1 and 2), but with significantly higher potency than pregabalin. It has shown promising results in Phase II clinical trials for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain,[1][2] and is currently in Phase III trials.
Mirogabalin, a voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 ligand, is in phase III clinical trials at Daiichi Sankyo for the treatment of pain associated with fibromyalgia. The company is also conducting phase III clinical studies for the treatment of chronic pain and pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Mirogabalin besylate
cas 1138245-21-2
UNII: 01F4FRP8YL
C12-H19-N-O2.C6-H6-O3-S, 367.4635
Bicyclo(3.2.0)hept-3-ene-6-acetic acid, 6-(aminomethyl)-3-ethyl-, (1R,5S,6S)-, benzenesulfonate (1:1)
SEE
Tert-butyl [(1R,5S,6S)-6-aminomethyl-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetate D-mandelate…..http://www.google.com/patents/US20140094623?cl=zh
PATENT
WO 2009041453
https://www.google.co.in/patents/EP2192109A1
- (Example 21) [(1S,5S,6S)-6-aminomethyl-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetic acid (exemplary compound No: 8, optically active form of the compound of Example 8)
(21-a) Resolution of tert-butyl (±)-[(1R,5S,6S)-3-ethyl-6-(nitromethyl)bicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetate
-
Tert-butyl (±)-[(1R,5S,6S)-3-ethyl-6-(nitromethyl)bicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetate (230 g, 778 mmol) was resolved using Chiralpak IC (N-Hex:EtOH=98:2, 1.0 mL/min, 40°C) manufactured by Daicel Chemical Industries, Ltd. to respectively obtain 115 g of a peak 1 (retention time: 5.2 min) and 93.7 g of a peak 2 (retention time: 6.3 min).
(21-b) Tert-butyl ([(1R,5S,6S)-6-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)methyl-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetate
-
Tert-butyl [(1R,5S,6S)-3-ethyl-6-(nitromethyl)bicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetate (peak 1, 7.0 g, 23.7 mmol) was dissolved in ethanol (60 mL) and water (21 mL). To the solution, iron powder (13.27 g, 237 mmol) and ammonium chloride (628.1 mg, 11.9 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred for 5.5 hours under heating to reflux. The mixture was allowed to cool, then diluted with saturated saline, a saturated aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate, and ethyl acetate, and filtered through Celite to remove insoluble matter. The filtrate was separated into organic and aqueous layers. The organic layer was washed with saturated saline and then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Then, the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to obtain a pale yellow oil substance (7.02 g). This substance was dissolved in dichloromethane (200 mL). To the solution, (Boc)2O (5.25 g, 25 mmol) and triethylamine (5.01 g, 50 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature. The solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the residue was then purified by silica gel chromatography to obtain the title compound of interest as a pale yellow oil substance (8.82 g, <100%). (21-c) [(1R,5S,6S)-6-aminomethyl-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetic acid
-
A 4 N hydrochloric acid-ethyl acetate solution (100 mL) was added to tert-butyl (1R,5S,6S)-[6-(tert-butoxycarbonylaminomethyl)-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetate (9.82 g, 23.7 mmol), and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. Then, the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. The residue was dissolved in dichloromethane. To the solution, triethylamine was added dropwise, and the resulting powder was collected by filtration, then washed with dichloromethane, and then dried to obtain 4.02 g of a white powder. This powder was washed with ethanol and ethyl acetate to obtain the title compound of interest as a white powder (2.14 g, 43%).
- (Example 31) [(1R,5S,6S)-6-(aminomethyl)-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetic acid benzenesulfonate (exemplary compound No: 8, optically active benzenesulfonate)
-
(1R,5S,6S)-6-(aminomethyl)-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetic acid (4.50 g, 20.6 mmol) was dissolved by heating in a 1 M aqueous solution (22.7 mL) of benzenesulfonic acid monohydrate, and the solution was then allowed to cool to room temperature. The resulting solid was collected by filtration. The solid was washed with water (15 mL) and then dried using a vacuum pump to obtain the compound of interest as a colorless solid (6.45 g, 77%).
PATENT
JP 2010241796
PATENT
WO 2012169475
-
- Reference Example 1[6-Aminomethyl-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetic acid
(1-a) Ethyl 4-ethyl-3-hydroxyhept-6-enoate
-
Sodium hydride (>63% oil, 2.09 g, 55 mmol) was added to a solution of ethyl 3-oxohexanoate (7.91 g, 50 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (50 mL) under ice cooling, and the mixture was stirred in this state for 10 minutes. To the reaction solution, n-butyllithium (1.58 M solution in hexane, 34.8 mL, 55 mmol) was added dropwise, and the mixture was further stirred for 10 minutes under ice cooling. Then, allyl bromide (4.7 mL, 55 mmol) was added thereto, and the mixture was stirred in this state for 1 hour and then further stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. To the reaction solution, 1 N hydrochloric acid and a saturated aqueous solution of ammonium chloride were added, followed by extraction with n-pentane. The organic layer was washed with saturated saline and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was dissolved in ethanol (80 mL). To the solution, sodium borohydride (1.51 g, 40 mmol) was added under ice cooling, and the mixture was stirred in this state for 2 hours. 1 N hydrochloric acid (50 mL) was added thereto, and the mixture was stirred for 30 minutes. Then, saturated saline was added thereto, followed by extraction with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with saturated saline and then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to obtain the compound of interest as a pale yellow oil substance (3.64 g, 37%, mixture of diastereomers).
-
1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ ppm: 0.91 (3H, t, J=7.5 Hz), 1.28 (3H, t, J=7.2 Hz), 1.43-1.55 (2H, m), 1.98-2.28 (2H, m), 2.45-2.48 (2H, m), 2.88-2.93 (1H, m), 4.07-4.10 (1H, m), 4.10-4.20 (2H, m), 5.01-5.09 (2H, m), 5.75-5.86 (1H, m).
(1-b) 4-Ethyl-3-hydroxyhept-6-enoic acid
-
Ethyl 4-ethyl-3-hydroxyhept-6-enoate (3.64 g, 18.2 mmol) was dissolved in a 2 N solution of potassium hydroxide in methanol (120 mL), and the solution was stirred overnight at room temperature. From the reaction solution, the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. To the residue, a 1 N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (200 mL) was then added, followed by extraction with diethyl ether. The aqueous layer was made acidic by the addition of concentrated hydrochloric acid under ice cooling, followed by extraction with diethyl ether again. The organic layer was washed with saturated saline and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Then, the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to obtain the compound of interest as a pale yellow oil substance (3.14 g, <100%, mixture of diastereomers).
-
1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ ppm: 0.91-0.96 (3H, m), 1.39-1.52 (3H, m), 2.01-2.28 (2H, m), 2.52-2.55 (2H, m), 4.05-4.15 (2H, m), 5.03-5.10 (2H, m), 5.74-5.86 (1H, m).
(1-c) Tert-butyl 3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-ylideneacetate
-
4-Ethyl-3-hydroxyhept-6-enoic acid (3.13 g, 18.2 mmol) was dissolved in acetic anhydride (15 mL). To the solution, potassium acetate (4.27 g, 43.6 mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 100 minutes. The reaction solution was heated to reflux and stirred for 3.5 hours to form “3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-6-en-6-one” in the reaction solution. To the reaction solution, ice water and toluene were then added, and this mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature. The mixture was separated into aqueous and organic layers by the addition of saturated saline (50 mL) and toluene (20 mL). Then, the organic layer was washed with a 1 N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and saturated saline in this order, then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and filtered. The filtrate was added to a reaction solution prepared by adding sodium hydride (>65% oil, 761.9 mg, 20 mmol) to a solution of tert-butyl dimethoxyphosphorylacetate (4.48 g, 20 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (50 mL) under ice cooling, and the mixture was further stirred for 1 hour. The reaction solution was separated into aqueous and organic layers by the addition of a saturated aqueous solution of ammonium chloride and saturated saline. The aqueous layer was subjected to extraction with ethyl acetate. The organic layers were combined, then washed with saturated saline, and then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to obtain the compound of interest as a pale yellow oil substance (1.32 g, 31%, E/Z mixture).
-
1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ ppm:
-
Major isomer: 1.06 (3H, t, J=7.4 Hz), 1.45 (9H, s), 2.07-2.22 (3H, m), 2.59-2.70 (2H, m), 2.87-2.96 (1H, m), 3.30 (1H, ddt, J=8.6, 18.4, 2.7 Hz), 3.86-3.88 (1H, m), 5.22-5.23 (1H, m), 5.45-5.47 (1H, m).
-
Minor isomer: 1.08 (3H, t, J=7.3 Hz), 1.49 (9H, s), 2.07-2.21 (3H, m), 2.43-2.47 (1H, m), 2.59-2.70 (1H, m), 2.75-2.85 (1H, m), 2.87-2.96 (1H, m), 4.28-4.31 (1H, m), 5.35-5.38 (1H, m), 5.45-5.47 (1H, m).
(1-d) Tert-butyl [3-ethyl-6-(nitromethyl)bicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetate
-
Tert-butyl [3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-ylideneacetate (1.32 g, 5.63 mmol) was dissolved in nitromethane (7 mL). To the solution, 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (1.2 mL, 7.3 mmol) was added, and the mixture was heated with stirring at 50 to 60° C. for 7 hours. The mixture was allowed to cool, and a saturated aqueous solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate was then added thereto, followed by extraction with ethyl acetate. Then, the organic layer was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to obtain the compound of interest as a colorless oil substance (1.39 g, 84%).
-
1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ ppm: 1.09 (3H, t, J=7.4 Hz), 1.46 (9H, s), 1.52 (1H, dd, J=7.6, 13.2 Hz), 2.06 (1H,d, 16.6 Hz), 2.14 (2H, q, J=7.4 Hz), 2.30 (1H, ddd, J=2.4, 7.6, 13.2 Hz), 2.47 (2H, s), 2.49 (1H, dd, J=7.6,16.6 Hz), 2.86 (1H, quint, J=7.6 Hz), 3.21-3.22 (1H, m), 4.75 (1H, d, J=11.7 Hz), 4.84 (1H, d, J=11.7 Hz), 5.27 (1H, s).
(1-e) [6-Aminomethyl-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetic acid
-
Tert-butyl [3-ethyl-6-(nitromethyl)bicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetate (1.09 g, 4.71 mmol) was dissolved in ethanol (10 mL) and water (5 mL). To the solution, iron powder (1.32 g, 23.5 mmol) and ammonium chloride (249.6 mg, 4.71 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred for 2 hours under heating to reflux. The mixture was allowed to cool, then diluted with saturated saline, a saturated aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate, and ethyl acetate, and filtered through Celite to remove insoluble matter. The filtrate was separated into organic and aqueous layers. The organic layer was washed with saturated saline and then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was then distilled off under reduced pressure. To the residue, a 4 N solution of hydrochloric acid in ethyl acetate (20 mL) was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. Then, the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. The residue was suspended in dichloromethane. To the suspension, triethylamine was added dropwise, and the resulting powder was collected by filtration, then washed with dichloromethane, and then dried to obtain the compound of interest as a white powder (425.1 mg, 43%).
-
1H-NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD): δ ppm: 1.10 (3H, t, J=7.4 Hz), 1.48 (1H, dd, J=7.5, 12.5 Hz), 2.03-2.08 (2H, m), 2.14 (2H, q, J=7.4 Hz), 2.46 (1H, d, J=16.2 Hz), 2.46-2.53 (1H, m), 2.51 (1H, d, J=16.2 Hz), 2.85 (1H, quint, J=7.5 Hz), 3.09-3.10 (1H, m), 3.14 (1H, d, J=13.0 Hz), 3.18 (1H, d, J=13.0 Hz), 5.38 (1H, dd, J=1.7, 3.7 Hz).
-
(Step of Performing Optical Resolution from Diastereomeric Mixture)
- Reference Example 2Tert-butyl [(1R,5S,6S)-6-aminomethyl-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetate D-mandelate
-
Acetonitrile (4.7 L, 8.6 v/w) was added to tert-butyl [6-aminomethyl-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetate (627.0 g, net: 543.6 g, 2.05 mol, 85:15 diastereomeric mixture), and the mixture was stirred at 40° C. To the reaction solution, D-mandelic acid (116.3 g, 0.76 mmol, 0.37 eq.) was added, and the mixture was stirred at 40° C. for 1 hour and then allowed to cool slowly to 3° C. After stirring at 3° C. for 1 hour, the resulting crystal was collected by filtration. Then, the crystal was dried under reduced pressure under the condition of 40° C. to obtain tert-butyl [(1R,5S,6S)-6-aminomethyl-3-ethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-yl]acetate D-mandelate as a white powder (251.2 g, yield: 29.4%, 97.6% ee, 99.6% de).
-
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm: 1.04 (3H, t, J=7.6 Hz), 1.28-1.35 (1H, m), 1.39 (9H, s), 1.96-2.11 (4H, m), 2.28 (1H, d, J=15.6 Hz), 2.33 (1H, d, J=15.6 Hz), 2.36-2.40 (1H, m), 2.72 (1H, quint, J=7.6 Hz), 3.00 (1H, d, J=13.2 Hz), 3.03 (1H, d, J=13.2 Hz), 3.31 (1H, br s), 4.54 (1H, s), 5.21-5.23 (1H, m), 7.13-7.25 (3H, m), 7.35-7.37 (2H, m).
-
[α]20 D −104.4° (C=0.108, MeOH).
-
Anal. calcd for C24H35NO5: C, 69.04; H, 8.45; N, 3.35; Found C, 69.15; H, 8.46; N, 3.46.
PATENT
WO 2012169474
PATENT

a compound having the formula (Va) (and its enantiomers), and to carry out optical resolution by chloride with optically active organic amine, and is a process for preparing a compound having the general formula (VIa) .
[Formula 19] The solvent used in this step, MTBE, CPME, ethers such as THF; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene; esters such as ethyl acetate; EtOH, alcohols such as diisopropyl alcohol CH; s three nitriles such as CN; ketones such as acetone; or is a mixed solvent of these solvents and water, preferably toluene, ethyl acetate, CH 3 CN, are MTBE, More preferably, toluene, MTBE. Optically active organic amine used in this step, preferably, (1R, 2R) -trans-1- amino-2-indanol, (S) -2- phenylglycinol, (R) -1- ( p- tolyl) ethylamine, (1R, 2S) -2- amino-1,2-diphenyl ethanol, (S) -1- (2- naphthyl) ethylamine, (R) -1- (4- bromophenyl) ethylamine, (1S, 2R) – (+) – 1- amino-2-indanol is a L- phenylalaninol, etc., more preferably, (1R, 2R) -trans-1- amino-2-indanol, (S ) -2-phenylglycinol. Equivalent of the optically active organic amine to be used have the general formula (Va) compound having a relative (and its enantiomers) are 0.5-1.1 equivalents. The reaction temperature of this step is such as about 0-50 ℃, preferably, after aging the crystals at about 10-30 ℃, is obtained by filtering the compound of formula (VIa). The time required to chloride present step is not particularly limited, but is usually 4 to about 48 hours. In this step, (1) with respect to (Va) compound with (and its enantiomers), directly to a compound of formula (VIa) with the desired configuration by the action of the above-mentioned optically active amine How to get, or, with respect to (2) compounds having formula (Va) (or its enantiomer), first, quinine, (1S, 2S) -trans-1- amino-2-indanol, (R) -2- by the action of an optically active amine such as phenylglycinol, it allowed to temporarily deposit the enantiomer having the unnecessary configuration, after removing the precipitate by filtration, against followed by compound obtained from the filtrate, (1R, 2R ) -trans-1- amino-2-indanol, by the action of optically active amines such as (S) -2- phenylglycinol, to precipitate the salt of the compound of formula (VIa) with the desired configuration How to get Te, one of the methods is used.
 Known compounds having the general formula (Va) which are used in the above Step D-1 or step D-2, which can be prepared according to step A-C, as otherwise, it is disclosed in Patent Document 5 It can be prepared by method (the following scheme).
Known compounds having the general formula (Va) which are used in the above Step D-1 or step D-2, which can be prepared according to step A-C, as otherwise, it is disclosed in Patent Document 5 It can be prepared by method (the following scheme).[Formula 20] specific production method according to the present method will be described later as a reference example.

Formula (V) or a compound having the general formula (VI) from (and / or its enantiomer) is a process for preparing a compound of formula (VII) (and / or its enantiomer), the general formula (V) is a compound having (and / or its enantiomer), under a hydrogen atmosphere in the presence of a metal catalyst, reduction with a solvent, or a compound having the general formula (VI) (and / or its enantiomer) solution compounds having the general formula (V) obtained by salt (and / or its enantiomer) solution, under a hydrogen atmosphere to carry out a reduction reaction in the presence of a metal catalyst, by a compound of formula (VII) This is a method of manufacturing a.
Formula 21] (1) Kaishio step formula compound with a (VI) (and / or its enantiomer) is suspended in an organic solvent, washed with an aqueous solution obtained by adding an acid, by liquid separation and the organic layer , compounds having general formula (V) (and / or its enantiomer) solution containing it can get. The solvent used in this step include aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene, ethers such as MTBE, an ester such as ethyl acetate, and the like, preferably toluene, or is MTBE. Acid used in this step is not particularly limited, hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, citric acid, malonic acid can be used.

compounds having the general formula (V) (and / or its enantiomer), under a hydrogen atmosphere in the presence of a metal catalyst was reduced in a solvent, a cyano group (or a nitro group) and an amino group It is converted into, and is a step for preparing a compound of formula (VII). This reaction is usually carried out in a neutral or basic conditions.
The solvent used in this step include aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene, MTBE, ethers such as THF, alcohols of C1-C4, or is water, preferably toluene, MTBE, or water , and the Particularly preferred is water.
Metal catalyst used in this step, vinegar Sanskrit nickel, sponge cobalt, or palladium – is carbon, preferably, sponge nickel (eg, Kawaken Fine Chemicals Co., Ltd. of PL-9T, NDT-65, NDT- 90, NDHT-90M, NDHT-M3, and the like, or, Nikko Rika Co., Ltd. R-100, R-200, such as R-205, R-211, R-2311), or, sponge cobalt (for example, the river Research ODHT-60 manufactured by Fine Chemical Co., Ltd., OFT-55, or the like, or is a Nikko Rika Co., Ltd. R-400, R-400K, such as R-401, R-455, such as A-8B46 manufactured by Johnson Matthey) .
In this step, when carrying water as a solvent is usually added to the base. As the base used, preferably an inorganic base, particularly preferred are lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, alkali metal hydroxides such as potassium hydroxide.
In this step, by the addition of aqueous ammonia, it is possible to improve the yield, it is not necessarily added aqueous ammonia.
In this step, by the addition of dimethyl polysiloxane, it is possible to suppress the generation of bubbles from the reaction liquid, it is not necessarily added dimethylpolysiloxane.
The reaction temperature in this step is about 20-60 ℃, preferably, is about 30-50 ℃.
The reaction time of this step, the raw material is not particularly limited as long as it is a time that is substantially consumed, it is usually 2 to about 12 hours.
In this step, after the completion of the reaction, the catalyst was removed by filtration, by adding an acid to the filtrate, by then crystallizing the compound of formula (VII), and filtering and washing the precipitate, pure products a you can get.
Chemical Formula 22] The solvent used in this step include water, anisole, aqueous acetone, water CH 3 CN, MTBE water – acetone, anisole – acetate, anisole – acetone, anisole – acetate – acetone, acetone – water -CH 3 CN single like, or it is a mixed solvent, preferably, water, anisole. The organic acid used in this step is an organic acid that is pharmacologically today preferably a benzenesulfonic acid. Equivalent of the organic acid used in this step is preferably a compound having the formula (VII) with respect to (and / or its enantiomer) is about 1.00-1.10 equivalents. This step is carried out in the range of usually about -15-50 ℃, preferably, after aging the crystals at a temperature of about -10-30 ℃, filtration, by washing, the general formula (VIII) a compound having a (and / or its enantiomers) get. The time required for chloride in this step is not particularly limited, but is usually 1 to about 24 hours.
 In the present invention, compounds having formula (IX) prepared via the process F from Step A (and / or its enantiomer) may be very produced as pure compounds. Compounds of formula (IX) which can be obtained by the present invention typically have a quality below.
In the present invention, compounds having formula (IX) prepared via the process F from Step A (and / or its enantiomer) may be very produced as pure compounds. Compounds of formula (IX) which can be obtained by the present invention typically have a quality below.content of the enantiomers represented by the formula (XI): 1.0% less than
the formula (XII) and the double bond represented by the formula (XIII) The total content of regioisomers: less than 0.5%
(Note that each content is calculated from the area percentage of the free form of formula (IX) (VII) in the by test High Performance Liquid Chromatography)
[formula 23] [of 24]


The internal standard substance in a magnetic resonance spectra (NMR), and using tetramethylsilane and abbreviations indicate the multiplicity, s = singlet, d = doublet, t = triplet, q = quartet, m = multiplet, and brs = It shows a broad singlet.
In the name of the compound, “R” and “S” indicate the absolute configuration at the asymmetric carbon. Furthermore, “RS” and “SR” indicates that the asymmetric carbon atom is racemic. In addition, “(1RS, and 5SR) -” if such a can shows the relative arrangement of the 1-position and the 5-position, as well shows only one of the diastereomers, its diastereomers are racemic We show that.
In the name of the compound, “E” and “Z” indicates the arrangement of positional isomers in the structure of the compound having a position isomerism.


(Example 7) [(1R, 5S)-3-Echirubishikuro [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-ylidene] propane two acid diethyl Diethyl [(1R, 5S) -3-ethylbicyclo [3.2.0 ] hept-3-en-6-Ylidene] Propanedioate [of 31] to CPME (159 mL), 0 ° C with Ti (Oi-Pr) 4 (16.0 mL, 54.6 mmol) After addition of, TiCl 4 and stirred for 1 hour at (18.0 mL, 164 mmol) and over 8 minutes was added dropwise 0 ° C. Then diethyl malonate (25.72 g, 161 mmol), was added (1R, 5S) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-one (19.87 g, 146 mmol), 30-40 ° it was stirred for 4 hours at C. The reaction was quenched with water (100 mL), and extracted with toluene (40 mL). After the organic layer is concentrated under reduced pressure, to obtain a crude product of the title compound as a yellow oil (43.61 g).

(Example 8) [(RS, 5SR)-3-Echirubishikuro [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-ylidene] propane diacid di -tert- butyl (racemic) Di-tert-butyl [( RS, 5SR) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-Ylidene] Propanedioate (Racemate) [of 32] with respect to THF (30 mL), and TiCl at 0 ° C 4 and (1.6 mL, and the mixture was stirred for 30 minutes was added 14.7 mmol). Subsequently (1RS, 5SR) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-one (1.00 g, 7.34 mmol), malonic acid di -tert- butyl (1.91 g, 8.81 mmol) was added After stirring for 1.5 hours, it was added pyridine (2.2 mL, 29.4 mmol). 0 ° 3.5 hours after stirring at C, and subjected to stirring overnight with warming to room temperature, quenched with water (10 mL), and extracted two times with toluene (10 mL). After washed with saturated brine (10 mL), the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure, silica gel column chromatography (hexane: ethyl acetate = 20: 1) and subjected to purification to give the title compound (2.26 g, 92% ). 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ) (500 MHz): delta = 1.07 (3H, t, J = 7.5 Hz), 1.47 (9H, s), 1.52 (9H, s), 2.06-2.14 (2H, M), 2.16 -2.24 (1H, m), 2.60-2.69 (2H, m), 2.90 (1H, quint, J = 7.0 Hz), 3.25 (1H, ddd, J = 18.6, 8.5, 3.5 Hz), 4.12-4.23 (1H , m), 5.36 (1H, s).

(Example 9) 5 – [(RS, 5SR)-3-Echirubishikuro [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-ylidene] -2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane -4-6- dione (racemic) 5 – [(RS, 5SR) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-Ylidene] 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-6-dione (Racemate) [of 33] THF for (80 mL), TiCl at 0 ° C 4 was stirred for 10 minutes was added (4.5 mL, 41 mmol). Subsequently (1RS, 5SR) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-one (2.81 g, 20.6 mmol), Meldrum’s acid (3.57 g, 24.8 mmol) was added and after stirring for 50 minutes , pyridine (6.53 g, 82.6 mmol) it was added. After 1.5 h stirring at 0 ° C, and subjected to stirring overnight with warming to room temperature, quenched with water (80 mL), and extracted three times with toluene (50 mL). The organic layers with saturated brine (50 mL), washed with 1 M HCl (10 mL), after distilling off the solvent, silica gel column chromatography (hexane: ethyl acetate = 9: 1-6: 1) to perform purification, as a white solid to give the title compound (4.51 g, 83.2%). 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ) (400 MHz): delta = 1.05 (3H, t, J = 7.6 Hz), 1.69 (3H, s), 1.71 (3H, s), 2.11 (2H, Q, J = 7.6 Hz ), 2.20-2.35 (1H, m), 2.65-2.85 (1H, m), 2.92-3.13 (2H, m), 3.47-3.63 (1H, m), 4.45-4.59 (1H, m), 5.43 (1H , s). 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ) (100 MHz): delta = 12.1, 24.3, 27.59, 27.64, 34.1, 42.3, 42.8, 60.7, 104.4, 108.5, 119.4, 150.3, 160.1, 160.7.

(Example 10) [(1R, 5S, 6R)-6-cyano-3-Echirubishikuro [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-yl] propane two acid dimethyl Dimethyl [(1R, 5S, 6R) -6-cyano-3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-YL] Propanedioate [of 34] Dimethyl [(1R, 5S) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en- 6-ylidene] propanedioate (517 mg, 1.66 mmol) was dissolved in MeOH (5.2 mL), was added sodium cyanide (90 mg, 1.84 mmol) at room temperature and stirred for 2 hours at room temperature. After quenching with 10% aqueous acetic acid (5 mL), and extracted three times with ethyl acetate (5 mL), the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to give the title compound as an oil (667 mg). 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ) (400 MHz): delta = 1.08 (3H, t, J = 7.6 Hz), 1.80 (1H, dd, J = 12.4, 8.0 Hz), 2.01-2.22 (3H, M), 2.54 (1H, dd, J = 16.8, 7.6 Hz), 2.73 (1H, ddd, J = 12.8, 8.8, 2.8 Hz), 3.18 (1H, quint, J = 7.6 Hz), 3.67 (1H, s), 3.78 ( . 3H, s), 3.82 (3H, s), 5.16-5.28 (1H, M) 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ) (100 MHz): delta = 12.2, 24.4, 32.1, 37.5, 39.2, 42.5, 52.9, 53.0 , 54.6, 55.0, 118.8, 123.2, 153.9, 166.62, 166.63.

(Example 11) [(1R, 5S, 6R)-6-cyano-3-Echirubishikuro [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-yl] propane two acid diethyl Diethyl [(1R, 5S, 6R) -6-cyano-3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-YL] Propanedioate [of 35] Diethyl obtained by the method shown in Example 7 [(1R, 5S) -3-ethylbicyclo [3.2 .0] hept-3-en-6-Ylidene] Propanedioate crude product (43.61 g, 146 mmol) was dissolved in EtOH (262 mL) and was added sodium cyanide (7.15 g, 146 mmol) at room temperature , it was stirred for 4 hours at room temperature. Acetate (8.76 g), after the reaction quenched with water (180 mL), the solvent it was concentrated to approximately 340 mL under reduced pressure. Water was added (80 mL), then extracted three times with ethyl acetate (150 mL), the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to give the title compound as an oil (HPLC quantitative value: 44.29 g, 96.3% (( 1R, 5S) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] total yield from hept-3-en-6-one)). 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ) (400 MHz): delta = 1.07 (3H, t, J = 7.6 Hz), 1.28 (3H, t, J = 7.2 Hz), 1.31 (3H, t, J = 7.2 Hz), 1.80 (1H, dd, J = 12.6, 7.6 Hz), 2.01-2.19 (3H, m), 2.53 (1H, dd, J = 16.8, 7.6 Hz), 2.72 (1H, ddd, J = 12.6, 9.2, 2.8 Hz), 3.16 (1H, quint, J = 7.6 Hz), 3.61 (1H, s), 3.67-3.82 (1H, M), 4.15-4.33 (4H, M), 5.21-5.26 (1H, M). 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ) (100 MHz):. delta = 12.2, 14.0, 24.4, 32.2, 37.7, 39.3, 42.5, 55.0, 55.2, 62.00, 62.02, 119.0, 123.3, 153.7, 166.21, 166.23 (HPLC analysis conditions) Diethyl [(1R, 5S, 6R) -6-cyano-3-ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-yl] propanedioate quantification method column: Cadenza CW-C18 (Imtakt, 3 μm, 4.6 mm × 150 mm), 40 ° Cdetection wavelength: UV 205 nm mobile phase: MeCN: 0.1% AcOH aqueous solution = 10: 90-80: 20 (gradient) (0-2 min: MeCN 10%, 2-17 min: MeCN 10 → 80%, 17-25 min: MeCN 80%, 25-30 min: MeCN 80 → 10%, 40 min: STOP) measurement time: 40 min flow rate: 1.0 mL / min retention time: Diethyl [(1R, 5S, 6R) -6-cyano-3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-YL] Propanedioate: 18.6 min, Diethyl [(1R, 5S) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3 en-6-ylidene] propanedioate: 19.7 min








Column: CHIRALPAK AD-RH 4.6 × 250 mm
mobile phase: 10 mM pH 2.0 phosphate buffer / MeCN = 25/75 (isocratic)
flow rate: 1.0 mL / min
Column temperature: 40 ° C
Detection wavelength: UV 210 nm
analysis time: 80 minutes
retention time: (1S, 5R, 6R) – Body: 35.2 min, (1R, 5S, 6S) – Body: 42.1 min

(Example 28) [(1R, 5S, 6S)-6-cyano-3-Echirubishikuro [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-yl] acetic acid benzyl amine salt Benzylammonium [(1R, 5S, 6S) -6-cyano-3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-YL] acetate [of 52] Diethyl obtained by the method of Example 12 [(1RS, 5SR, 6RS) -6-cyano -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] Hept- 3-en-6-YL] After the addition of EtOH (390 mL) to CPME solution of propanedioate, heating under reflux, 8 N aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide (6.9 mL, 55.07 mmol ) after adding a total of 5 times every 1 hour, refluxed for 5 hours and returned to room temperature. The addition of water (60 mL) and 8N aqueous potassium hydroxide (24 mL) to the above EtOH solution, and after stirring for 2 h at 26-27 ° C, under reduced pressure at an external temperature of 40-45 ° C until 150 mL It was concentrated. To remove the organic layer by water (180 mL) and toluene (90 mL) was added for liquid separation. The resulting aqueous solution Toluene (150 mL) added, cooled to, was added concentrated hydrochloric acid 42.5 mL at 2-9 ° C, the pH was adjusted to 1.4. By separation to remove the aqueous layer was added toluene (300 mL) benzylamine (23.6 g, 220.28 mmol) and. After stirring for 30 minutes at 44-46 ° C make the inoculation, and concentrated under reduced pressure until 300 mL at 44-46 ° C. After stirring overnight at 22-23 ° C, and crystals were filtered off. And vacuum dried at 40 ° C, was obtained as a white crystalline title compound 54.4 g (79.2% from (1R, 5S) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-one) a.

(Example 33) [(1R, 5S, 6S)-6-(aminomethyl) -3-Echirubishikuro [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-yl] acetic acid [(1R, 5S, 6S) – 6 (aminomethyl) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-YL] acetic acid [of 57] Benzylammonium [(1R, 5S, 6S) -6-cyano-3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2. 0] hept-3-en-6-yl] acetate (40.0 g) in toluene (200 mL), was added 2 mol / L hydrochloric acid (100 mL) at room temperature and dissolved. And allowed to stand the solution to drain the aqueous layer to obtain an organic layer. To the stirred addition of 10% aqueous sodium chloride solution (about 100 mL), and the aqueous layer was removed after standing. The solution of water (100 mL) was added to, was adjusted to 10.0 to pH added 8 mol / L aqueous potassium hydroxide solution (about 15.7 mL), the organic layer was removed to standing. The solution to the sponge cobalt (10 g), 28% aqueous ammonia (13 mL), 2% dimethylpolysiloxane / toluene solution (2 mL) was added and warmed to 40 ° C in a hydrogen gas pressure (0.45 MPa) It was stirred for 8 hours.After cooling to room temperature, filtering the reaction mixture to remove the sponge cobalt. The sponge cobalt on the filter it was washed with water (80 mL). The resulting solution was stirred for 0.5 hours added the activated carbon (4 g), to remove the charcoal by filtration. The activated carbon on the filter it was washed with water (60 mL). The solution I was adjusted to about pH 6.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid (about 32.7g) a. Then, after stirring for 0.5 hours was added potassium chloride (55.0 g), and cooled to 0 ° C. The resulting was filtered and crystals were washed with 20% brine cooled to about 0 ° C (80 mL), and dried overnight in vacuum at 50 ° C to give the title compound as white crystals (26.9 g, content 88.3 %, 88.7% content in terms of yield).

(Example 34) [(1R, 5S, 6S)-6-(aminomethyl) -3-Echirubishikuro [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-yl] acetic acid [(1R, 5S, 6S) – 6 (aminomethyl) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-YL] acetic acid [of 58] (R) -Phenylethanaminium [(1R, 5S, 6S) -6-cyano-3 ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-yl] acetate (35.9g, 99.2 mmol, 95.7% de, ee 99.2%) in toluene (120 mL) and 1 mol / L hydrochloric acid (150 mL) was added , it was stirred. After removing the aqueous layer, the organic layer was washed twice with water (120 mL), and concentrated. The obtained residue in MTBE to (150 mL) and sponge nickel (10.1 g) was added, under hydrogen pressure (approximately 4 atm) and stirred for 3 hours at room temperature. The reaction of 2 mol / L aqueous potassium hydroxide solution (72 mL) was added, After stirring for 30 minutes, a sponge nickel was filtered off. It was washed with a filtration sponge nickel 2 mol / L potassium hydroxide solution (12 mL). After combining the filtrate and washings, the organic layer was removed to obtain an aqueous layer. The organic layer was re-extracted with 2M aqueous potassium hydroxide solution. The matched aqueous layer was cooled, after adjusting the pH adding concentrated hydrochloric acid (about 12 mL) to 7.5, and the mixture was stirred at 0 ° C for about 3 hours. Filtered the precipitated crystals were washed with ice-cold water (24 mL), and dried under reduced pressure at 50 ° C, to give the title compound (18.3g, 88%, 99.8% de) and.

(Example 35) [(1R, 5S, 6S)-6-(aminomethyl) -3-Echirubishikuro [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-yl] acetic acid one benzenesulfonate [(1R, 5S, 6S)-6-(aminomethyl) -3-Ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-YL] acetic acid Monobenzenesulfonate [of 59] MTBE (83 mL), acetone (4.0 mL), water ( with respect to a mixture of 0.98 mL), at 0 ° C [(1R, 5S, 6S) -6- (Aminomethyl) -3-ethylbicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-en-6-yl] acetic acid ( 4.07 g, 19.5 mmol) was added and stirred to form a slurry solution. This BsOH (3.08 g, 19.5 mmol) it was added acetone (10.1 mL) solution of. 0 ° After stirring for 1 hour at C, and stirred for 2 hours and allowed to warm to room temperature. Over 1 hour and gradually cooled to -10 ° C, and stirred for 2.5 hours. The resulting was filtered crystals, after washing with acetone and cooled to 0 ° C (12 mL), and by vacuum-dried at 40 ° C, as white crystals of the title compound was obtained (6.44 g, 90.1% ). Various spectrum data of the obtained title compound was almost (extent the structure can be identified) coincides with (described in Patent Documents 5 and 6) the known information. (Purity measurement method -1) column: Cadenza CW-C18 (Imtakt, 3 μm, 4.6 mm × 150 mm), 40 ° C detection wavelength: UV 205 nm mobile phase: MeCN: 5 mM ammonium hydrogen carbonate aqueous solution = ten ninety -80: 20 (gradient) (0-12 min: MeCN 10%, 12-27 min: MeCN 10 → 80%, 27-45 min: MeCN 80%, 45-50 min: MeCN 80 → 10%, 50- 60 min: MeCN 10%, 60 min: STOP) measurement time: 60 min flow rate: 1.0 mL / min infusion sample concentration: 5mg / mL sample injection volume: 2μL retention time: the title compound (as free form): 12.5 min diastereoisomers Marr (Compound X): 13.5 min double bond position isomer (compound XII or XIII): 9.4 min, 9.6 min, 11.4 min

| Patent | Submitted | Granted |
|---|---|---|
| Bicyclic [gamma]-amino acid derivative [US7947738] | 2010-09-30 | 2011-05-24 |
| Optical Resolution Methods for Bicyclic Compounds Using Enzymes [US2015038738] | 2014-10-10 | 2015-02-05 |
| WO2015005298A1 * | Jul 8, 2014 | Jan 15, 2015 | Daiichi Sankyo Company,Limited | METHOD FOR PRODUCING OPTICALLY ACTIVE BICYCLIC γ-AMINO ACID DERIVATIVE |
CONSTRUCTION

References
- Vinik A, Rosenstock J, Sharma U, Feins K, Hsu C, Merante D, et al. Efficacy and safety of mirogabalin (DS-5565) for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active comparator-controlled, adaptive proof-of-concept phase 2 study. Diabetes Care. 2014 Dec;37(12):3253-61. doi: 10.2337/dc14-1044. PMID 25231896
- Vinik A, Sharma U, Feins K, Hsu C, Merante D. DS-5565 for the Treatment Of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo- And Active Comparator-Controlled Phase II Study (S20.004) Neurology April 8, 2014; 82(10): Supplement S20.004
Tokyo, Japan – (February 4, 2015) – Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited (hereafter, Daiichi Sankyo) today announced enrollment of the first patients in large-scale, multi-national clinical programs evaluating the safety and efficacy of investigational mirogabalin (DS-5565), the first preferentially selective alpha-2 delta ligand. The phase 3 clinical program across Asia includes the REDUCER (An Asian, phase 3, multicenter, RandomizEd, Double-blind, placebo-controlled 14-week stUdy of DS-5565 in patients with diabetiC pEripheral neuRopathic pain followed by a 52-week open-label extension) study and the NEUCOURSE (An AsiaN, phasE 3, mUltiCenter, randomized, dOUble-blind, placebo-contRolled 14-week study of DS-5565 in patientS with postherpetic neuralgia followed by a 52-week open-label Extension) study which will evaluate investigational mirogabalin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (DPNP) and postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), respectively. The phase 3 global ALDAY (A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo- and Active-Controlled Study of DS-5565 in Patients with Pain Associated with Fibromyalgia) clinical program is ongoing and will evaluate mirogabalin for the treatment of pain associated with fibromyalgia in three identical studies.
“Pain associated with the neurologic conditions of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain, postherpetic neuralgia and fibromyalgia can be debilitating,” said Lesley Arnold, MD, Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neuroscience and Director of the Women’s Health Research Program, University of Cincinnati and lead investigator of the ALDAY program. “New treatment options are needed to help people living with these neurologic conditions relieve and manage their chronic pain and hopefully, improve their function and quality of life.”
“We are pleased that our global clinical development program evaluating the efficacy and safety of mirogabalin continues to move forward and has progressed into phase 3,” said Mahmoud Ghazzi, MD, PhD, Executive Vice President and Global Head of Development for Daiichi Sankyo. “Daiichi Sankyo is committed to identifying and studying new medicines that could help improve the management of chronic pain for people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia and pain associated with fibromyalgia.”
About the REDUCER and NEUCOURSE Phase 3 Clinical Studies
The REDUCER study will last 14 weeks and is being conducted at approximately 200 centers in Japan, Taiwan and Korea. The NEUCOURSE study will also last 14 weeks and is being conducted at approximately 200 centers in Japan, Taiwan, Korea, Singapore, Malaysia and Thailand. The studies will include about 750 patients each with either diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain or postherpetic neuralgia, respectively. The objectives of the double-blind studies are to evaluate safety and efficacy of mirogabalin by comparing change in the average daily pain score (ADPS) from baseline to Week 14 in patients receiving a total daily dose of either 15 mg, 20 mg or 30 mg of mirogabalin versus placebo. Both studies will be followed by one-year open-label extension studies to assess long-term safety and efficacy of mirogabalin. For more information on the REDUCER study in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain, please visit
https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02318706?term=Mirogabalin&rank=3.
For more information on the NEUCOURSE study in patients with postherpetic neuralgia, please visithttps://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02318719?term=Mirogabalin&rank=1.
About the ALDAY Phase 3 Clinical Program
The ALDAY program is a large clinical phase 3 program evaluating mirogabalin for the treatment of pain associated with fibromyalgia, and includes three, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled studies, and an open label safety study that will be carried out over the next three years. Approximately 4,000 patients with pain associated with fibromyalgia will be enrolled at approximately 800 clinical centers at more than 40 countries worldwide. The primary objective of the studies in the ALDAY program is to compare change in weekly ADPS from baseline to Week 13 in patients receiving a total daily dose of either 15 mg or 30 mg of mirogabalin versus placebo. Weekly ADPS is based on daily pain scores reported by the patient that best describes his or her worst pain over the previous 24 hours. The primary objective of the phase 3 open-label extension study is to assess the long-term safety of a total daily dose of mirogabalin 15 mg or mirogabalin 30 mg in patients with pain associated with fibromyalgia. For more information on the studies in the ALDAY program, please visit
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02187471?term=DS5565&rank=1
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02187471?term=ds-5565&rank=2
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02146430?term=ds-5565&rank=3
For more information on the open-label extension study, please visithttps://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02234583?term=ds-5565&rank=4
For patient recruitment or additional clinical study information, please visit http://www.aldaystudy.com/.
About Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is a disorder that causes nerve damage to the extremities and is one of the most common long-term complications of diabetes.1 Symptoms include sharp pains or increased sensitivity, numbness, loss of balance and coordination, tingling, burning, or prickling sensations, which typically worsen at night.1 Up to 50 percent of people with diabetes have peripheral neuropathy2 and it is estimated that between 11 and 26 percent of people with diabetes experience diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (DPNP).3-6 However, DPNP is often undertreated and underreported.2
About Postherpetic Neuralgia
Postherpetic neuralgia is pain that occurs after recovering from shingles, an infection that is caused by the herpes zoster (chickenpox) virus. Pain from postherpetic neuralgia can range in severity, and is typically described as burning, sharp, or stabbing.7 Other symptoms include sensitivity to touch, itching, numbness, and in rare cases, muscle weakness or paralysis can occur.7 The risk of developing postherpetic neuralgia increases with age and it mainly affects people older than 60.7 Studies have shown that only half of all patients affected with the condition will be relieved from pain within a year.8 Most people will require more than one treatment to help ease the pain.7
About Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder that causes widespread muscle pain, generalized tender points and fatigue.9 Other common symptoms include sleep disturbances, morning stiffness, memory and thinking problems (sometimes called fibro fog), tingling in the hands and feet and headaches.9 Fibromyalgia is often misdiagnosed and suboptimally treated.10-17 The overall estimated prevalence of fibromyalgia is approximately two to three percent in the general population, with a higher prevalence in women.18-22 Pain that occurs with fibromyalgia has a substantial impact on the patient, and can be associated with societal and economic burdens.23-29
About Mirogabalin
Mirogabalin is an investigational drug that is currently being studied for the treatment of DPNP, PHN and pain associated with fibromyalgia. Mirogabalin is preferentially selective in regards to how it binds to α2δ-1 subunit, a protein that may help to regulate how the brain processes pain signals. It has a unique binding profile and long duration of action.30*,31
About Daiichi Sankyo
Daiichi Sankyo Group is dedicated to the creation and supply of innovative pharmaceutical products to address the diversified, unmet medical needs of patients in both mature and emerging markets. While maintaining its portfolio of marketed pharmaceuticals for hypertension, dyslipidemia and bacterial infections used by patients around the world, the Group has also launched treatments for thrombotic disorders and is building new product franchises. Furthermore, Daiichi Sankyo research and development is focused on bringing forth novel therapies in oncology and cardiovascular-metabolic diseases, including biologics. The Daiichi Sankyo Group has created a “Hybrid Business Model,” to respond to market and customer diversity and optimize growth opportunities across the value chain. For more information, please visit: www.daiichisankyo.com.
| trial(s) |
|
|---|
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
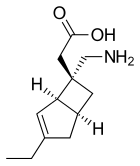
(1R,5S,6S)-6-(aminomethyl)-3-ethyl-bicyclo(3.2.0)hept-3-ene-6-acetic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Registry Number | 1138245-21-2  |
| PubChem | CID: 49802951 |
| ChemSpider | 32701007 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C12H19NO2 |
| Molecular mass | 209.285 g/mol |
Filed under: Phase3 drugs Tagged: A-2000700, DS-5565, Mirogabalin, PHASE 3






