
SCYX-7158
SCYX-7158 [4-fluoro-N-(1-hydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1,3-dihydro-benzo[c]oxaborol-6-yl-2-trifluoromethyl benzamide]
- C17H14BF4NO3
- Average mass 367.103 Da
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) is an important public health problem in sub-Saharan Africa, affecting hundreds of thousands of individuals. An urgent need exists for the discovery and development of new, safe, and effective drugs to treat HAT, as existing therapies suffer from poor safety profiles, difficult treatment regimens, limited effectiveness, and a high cost of goods. We have discovered and optimized a novel class of small-molecule boron-containing compounds, benzoxaboroles, to identify SCYX-7158 as an effective, safe and orally active treatment for HAT.
The presence of a boron atom in the heterocyclic core structure has been found essential for trypanocidal activity of orally active series of benzoxaborole-6-carboxamides in murine models of human African trypanosomiasis. SCYX-7158 (Fig. 13) has been identified as an effective, safe and orally active treatment for human African trypanoso-miasis to enter preclinical studies, with expected progression to phase 1 clinical trials in 2011 (21,22)………http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3764666/
A drug discovery project employing integrated biological screening, medicinal chemistry and pharmacokinetic characterization identified SCYX-7158 as an optimized analog, as it is active in vitro against relevant strains of Trypanosoma brucei, including T. b. rhodesiense and T. b. gambiense, is efficacious in both stage 1 and stage 2 murine HAT models and has physicochemical and in vitro absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination and toxicology (ADMET) properties consistent with the compound being orally available, metabolically stable and CNS permeable. In a murine stage 2 study, SCYX-7158 is effective orally at doses as low as 12.5 mg/kg (QD×7 days). In vivo pharmacokinetic characterization of SCYX-7158 demonstrates that the compound is highly bioavailable in rodents and non-human primates, has low intravenous plasma clearance and has a 24-h elimination half-life and a volume of distribution that indicate good tissue distribution. Most importantly, in rodents brain exposure of SCYX-7158 is high, with Cmax >10 µg/mL and AUC0–24 hr >100 µg*h/mL following a 25 mg/kg oral dose. Furthermore, SCYX-7158 readily distributes into cerebrospinal fluid to achieve therapeutically relevant concentrations in this compartment.

Medicinal Chemistry Synthesis of SCYX-7158 SCHEME1
While the original route was eff ective for producing multi-gram quantities of the API, it was not amenable to scale-up. The route started with 2, a relatively expensive aryl boronic acid. This was protected as borocan 3 and halogen-lithium exchange followed by reaction with acetone and subsequent deprotection provided the oxaborole 4. This protection/alkylation/deprotection sequence added two steps to the overall synthesis and the metalation was not reliable. However, the biggest concern in the sequence was nitration of 4 to give 5. This was accomplished by adding a concentrated solution of 4 to cold fuming nitric acid. Besides the signifi cant safety considerations, the reaction did not scale well. Reduction of the nitro group to give aniline 6 was followed by amide formation to provide 1. While this end game was effi cient, the material produced was dark in color. The colored impurities were not removed by crystallization of 1 and furthermore a mixture of two polymorphs was formed under the original conditions.

The process chemistry route to SCYX-7158 is shown in Scheme 2. When considering alternative routes to 1, the readily available and inexpensive methyl 2-bromobenzoate (8) was identifi ed as an attractive starting point. Gratifyingly, treatment of 8 with methylmagnesium bromide aff orded 2-bromocumyl alcohol (9) in high yield using simple operating conditions. Lithiumhalogen exchange followed by reaction with triisopropyl borate and acidic work-up provided benzoxaborole 4, along with cumyl alcohol (10). While this conversion was not completely atom-effi cient, it was easily scalable and several strategies are available to suppress the by-product in the future.
With benzoxaborole 4 in hand, attention turned to the introduction of a nitrogen-linked amide at the C(6) position. This was accomplished using the same nitration/reduction/acylation strategy used in Scheme 1. Yet signifi cant changes to the chemistry were required for safety and reliability reasons. The fi rst task was introduction of the nitrogen. Nitration was demonstrated using acetic anhydride/nitric acid. However, due to slow rates of nitration and potential for accumulation of a reactive intermediate, alternative conditions had to be identifi ed. These limitations were overcome by use of trifl uoroacetic anhydride/nitric acid, which provided a more reactive nitrating intermediate, thus improving the rate of nitration and aff ording a process in which nitric acid was slowly added until 4 was consumed. Full safety assessment of the nitration reaction, including extensive calorimetry studies, demonstrated the safety of this reaction. This process was used to prepare kilogram quantities of 5.
Following reduction of nitrobenzoxaborole 5 to aniline 6 under standard catalytic hydrogenation conditions, acylation with 7 provided the fi nal drug candidate in high chemical yield. Two challenges remained which needed to be addressed through further optimization of the process. The fi rst challenge was color and purity of the API, which derived from a highly colored impurity generated in the nitration reaction which carried through to fi nal product and was not removed by crystallization. The second challenge was to consistently obtain a single polymorph of the API. Both challenges were addressed by isolation of crystalline isopropyl boronate 11 which rejected colored impurities, followed by regeneration of 1 through addition of water and azeotropic removal of isopropanol. This crystallization provided the API as a single polymorph. The API was isolated in good yield, very high purity and was white in color.
REFERENCES
http://journals.plos.org/plosntds/article?id=10.1371/journal.pntd.0001151
- touguia J, Costa J (1999) Therapy of human African trypanosomiasis: current situation. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 94: 221–224
- Barrett MP, Boykin DW, Brun R, Tidwell RR (2007) Human African trypanosomiasis: pharmacological re-engagement with a neglected disease. Br J Pharmacol 152: 1155–1171.
- 1986. Epidemiology and control of African trypanosomiasis. Report of a WHO expert committee. World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland. Technical Report Series, No. 739. 126 pp.
- Benzoxaboroles: a new class of potential drugs for human African trypanosomiasis. Robert T Jacobs, Jacob J Plattner, Bakela Nare, Stephen A Wring, Daitao Chen, Yvonne Freund, Eric G Gaukel, Matthew D Orr, Joe B Perales, Matthew Jenks, Robert A Noe, Jessica M Sligar, Yong-Kang Zhang, Cyrus J Bacchi, Nigel Yarlett, and Robert Don. Future Medicinal Chemistry. August 2011. Vol. 3, No. 10. Pages 1259-1278.
http://www.swisstph.ch/fileadmin/user_upload/Pdfs/Events/2010_09_Jacobs.pdf ……….POWERPOINT
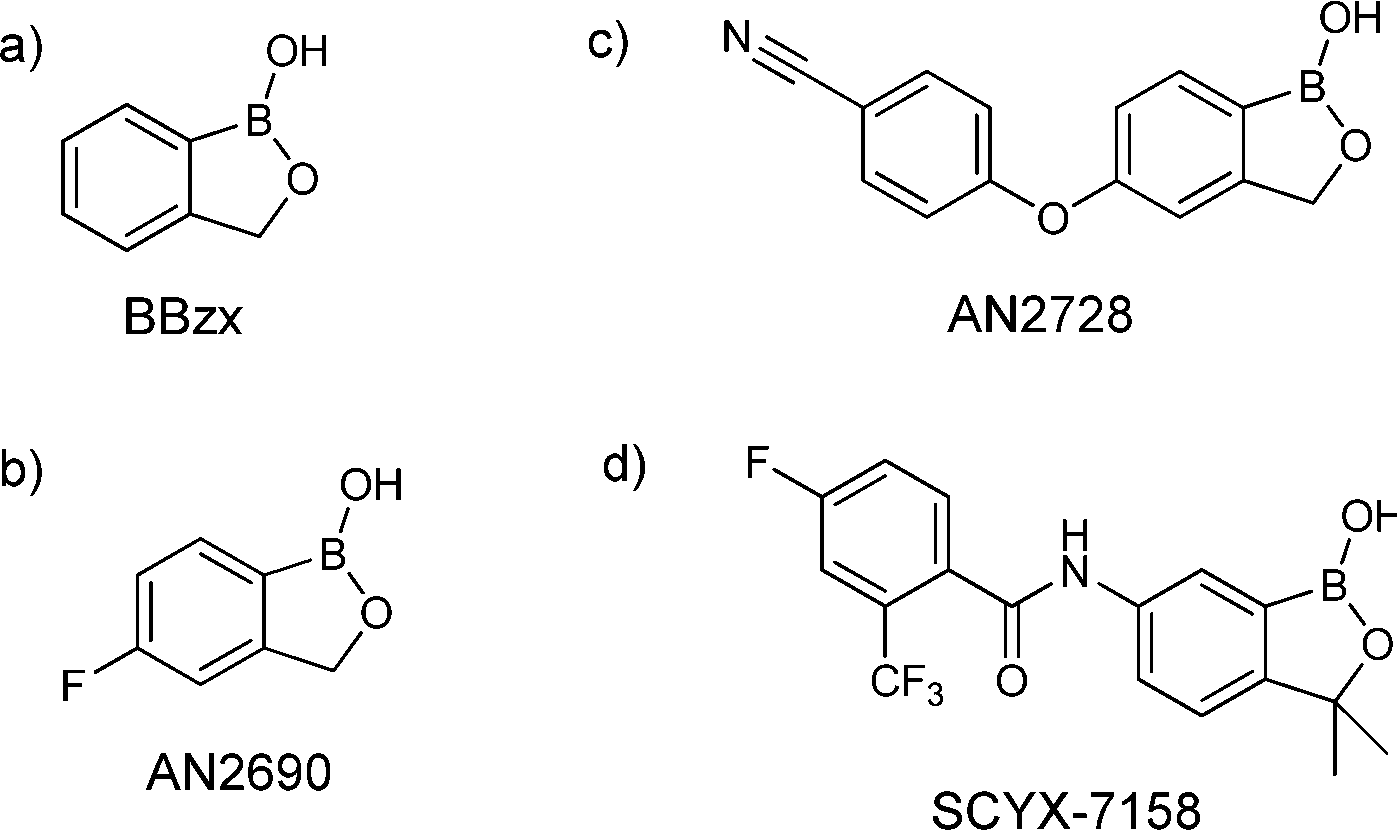
///////////SCYX-7158
Filed under: Uncategorized Tagged: AN 5568, human African trypanosomiasis, SCYNEXIS, SCYX-7158