


Racecadotril
- Molecular FormulaC21H23NO4S
- Average mass385.477 Da
(±)-Acetorphan
(RS)-Benzyl N-[3-(acetylthio)-2-benzylpropanoyl]glycinate
2-{[2-[(acetylthio)methyl]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropyl]amino}acetic acid (phenylmethyl) ester7378
76K53XP4TO
81110-73-8[RN]
Benzyl N-[3-(acetylsulfanyl)-2-benzylpropanoyl]glycinate [ACD/IUPAC Name]
Cadotril
Dexecadotril[INN]
Glycine, N-[3-(acetylthio)-1-oxo-2-(phenylmethyl)propyl]-, phenylmethyl ester
Hidrasec [Trade name]
рацекадотрил[Russian][INN]
راسيكادوتريل[Arabic][INN]
消旋卡多曲[Chinese][INN]
RacecadotrilCAS Registry Number: 81110-73-8
CAS Name:N-[2-[(Acetylthio)methyl]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropyl]glycine phenylmethyl ester
Additional Names:N-[(R,S)-3-acetylthio-2-benzylpropanoyl]glycine benzyl ester; acetorphan
Trademarks: Hidrasec (GSK); Tiorfan (Bioprojet)
Molecular Formula: C21H23NO4S, Molecular Weight: 385.48
Percent Composition: C 65.43%, H 6.01%, N 3.63%, O 16.60%, S 8.32%
Literature References: Antisecretory enkephalinase inhibitor. Prepn: B. Roques et al.,EP38758 (1981); eidem,US4513009 (1985 to Bioprojet). Pharmacology: J.-M. Lecomte et al.,J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.237, 937 (1986). Effect on intestinal transit: J. F. Bergmann et al.,Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.6, 305 (1992). Clinical trial in acute diarrhea: P. Baumer et al.,Gut33, 753 (1992); in children: E. Salazar-Lindo et al.,N. Engl. J. Med.343, 463 (2000). Symposium on pharmacology and clinical experience: Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.13, Suppl. 6, 1-32 (1999). Review of clinical development: J.-C. Schwartz, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents14, 75-79 (2000); J. M. Lecomte, ibid. 81-87.
Properties: White crystals from ether mp 89°., Melting point: mp 89°
Derivative Type: (S)-Form
CAS Registry Number: 112573-73-6
Additional Names: Ecadotril; sinorphan
Manufacturers’ Codes: Bay-y-7432
Molecular Formula: C21H23NO4S, Molecular Weight: 385.48
Percent Composition: C 65.43%, H 6.01%, N 3.63%, O 16.60%, S 8.32%
Literature References: Prepn: P. Duhamel et al.,EP318377; eidem,US5208255 (1989, 1993 both to Bioprojet); and pharmacology: B. Giros et al.,J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.243, 666 (1987). Clinical effect on plasma ANP levels in CHF: J. C. Kahn et al.,Lancet335, 118 (1990); on renal function: F. Schmitt et al.,Am. J. Physiol.267, F20 (1994). Clinical trial in heart failure: C. M. O’Connor et al.,Am. Heart J.138, 1140 (1999); J. G. F. Cleland, K. Swedberg, Lancet351, 1657 (1998).
Properties: mp 71°. [a]D25 -24.1° (c = 1.3 in methanol). LD50 i.v. in mice: >100 mg/kg (Duhamel, 1993).
Melting point: mp 71°
Optical Rotation: [a]D25 -24.1° (c = 1.3 in methanol)
Toxicity data: LD50 i.v. in mice: >100 mg/kg (Duhamel, 1993)
Therap-Cat: Antidiarrheal.
Keywords: Antidiarrheal; Neutral Endopeptidase Inhibitor.

Racecadotril is an anti-secretory enkephalinase inhibitor useful in the treatment of diarrhea.Racecadotril has been investigated for the basic science and treatment of Diarrhea, Acute Diarrhea, and Acute Gastroenteritis.
Racecadotril, also known as acetorphan, is an antidiarrheal medication which acts as a peripheral enkephalinase inhibitor.[3] Unlike other opioid medications used to treat diarrhea, which reduce intestinal motility, racecadotril has an antisecretory effect — it reduces the secretion of water and electrolytes into the intestine.[3] It is available in France (where it was first introduced in ~1990) and other European countries (including Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, Spain, Portugal, Poland, Finland, Russia and the Czech Republic) as well as most of South America and some South East Asian countries (including China, India and Thailand), but not in the United States. It is sold under the tradename Hidrasec, among others.[4] Thiorphan is the active metabolite of racecadotril, which exerts the bulk of its inhibitory actions on enkephalinases.[5]
Medical uses
Racecadotril is used for the treatment of acute diarrhea in children and adults and has better tolerability than loperamide, as it causes less constipation and flatulence.[6][7] Several guidelines have recommended racecadotril use in addition to oral rehydration treatment in children with acute diarrhea.[8]
Contraindications
Racecadotril has no contraindications apart from known hypersensitivity to the substance.[9][10]
There is insufficient data for the therapy of chronic diarrhea, for patients with renal or hepatic failure, and for children under three months. Additional contraindications for the children’s formulation are hereditary fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption and saccharase deficiency, as it contains sugar.[7][9]
Racecadotril (CAS NO.: 81110-73-8), with its systematic name of Glycine, N-(2-((acetylthio)methyl)-1-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)-, phenylmethyl ester, (+-)-, could be produced through many synthetic methods.
Following is one of the synthesis routes: 2-Benzylacrylic acid (I) reacts with SOCl2 in hot toluene to afford the acyl chloride (II), which is condensed with N-tosylglycine benzyl ester (III) in the presence of TEA in toluene to yield the corresponding amide (IV). Finally, this compound is condensed with thioacetic acid by heating at 80 °C to afford the target acylthio compound.
Racecadotril is a neutral endopeptidase inhibitor used as antidiarrheal in the treatment of chronic cardiac insufficiency and is available under the brand names Hidrasec and Tiorfan. Racecadotril is chemically known as N-[2-[(acetylthio) methyl]- l-oxo-3-phenylpropyl] glycine phenyl methyl ester, (herein after referred by its generic name racecadotril) and represented by the formula (I).

U.S. Patent No. US 4,513,009 describes amino acid derivatives including racecadotril, a pharmaceutical composition and a method of treatment.
The US’009 patent also discloses a process for the preparation of racecadotril which is illustrated by below scheme:

U.S. Patent No. US 6,835,851 B2 discloses a process for the preparation of racecadotril which is illustrated by scheme below:

European Patent No. EP 0501870B 1 discloses a process for the preparation of racec

Racecadotril
The use of coupling agents like hydroxyl benzotriazole (HOBT) and dicyclohexyl amine carbodiimide (DCC) generally induces the formation of side products such as dicyclohexylurea. These side products do lead to major problems, wherein purification by chromatography may be contemplated, but the side products are extremely difficult to remove on an industrial scale.
Consequently, efforts have been made to replace the peptidic coupling step
so as to avoid the formation of side products associated with the use of the coupling agents. Thus, it appears that, even if the preparation of N-(mercaptoacyl)amino acid derivatives from .alpha.-substituted acrylic acids by Michael addition of a thio acid and conversion of acid to acid chloride by using thionyl chloride and then coupling of an amino ester may be advantageous on a laboratory scale, such reactions are difficult to adapt on an industrial use.
The aforementioned processes described above involves expensive reagents such as hydroxyl benzotriazole (HOBT) and dicyclohexyl amine carbodiimide (DCC) and hazardous reagent like thionyl chloride thus rendering the processes expensive and not feasible on industrial scale.
SYNTHESIS BY WORLDDRUGTRACKER

Patent
https://www.google.com/patents/WO2013098826A1?cl=en
EXAMPLES
Example-1: Preparation of Racecadotril (I):
Step A) Preparation of 2-acetyIsulfanyI methyI-3-phenyI propionic acid (IV)
16.2 g of 2-benzylacrylic acid and 12.3 ml of thioacetic acid were were charged into a clean and dry R.B.flask and stirred at about 30°C for about 1 hour. The reaction mixture was heated to about 60°C and stirred for about 4 hours.The excess of thioacetic acid was distilled off completely to afford the title compound as residue. Yield: 23.8 g. Step B) Preparation of Racecadotril crude (la)
23.8 g. of 2-acetyl sulfanylmethyl-3-phenyl-propionic acid (IV), 200ml of methylene chloride and 16.7 ml of triethylamine were charged into a clean and dry R.B.flask. 10. 5 ml of ethylchloroformate was added at about -5°C. The resultant reaction mixture was stirred at about 0°C for about 30 min. 33.7 g of glycine benzyl ester p-tosyalte (II), 14 ml of triethylamine and 100ml of methylene chloride was added as a mixture to the reaction mass at about 0°C. Then the resultant reaction mixture was stirred at about 0°C for about 1 hr. followed by at about 30°C for about 30 min. After completion of the reaction as determined by TLC, the reaction mass was washed with 65 ml of distilled water, 65 ml 4% sodium bicarbonate solution and followed by 65 ml distilled water. The organic and aqueous phases were separated and the solvent was distilled completely, 2 x 50 ml Isopropyl alcohol was charged and again distilled off the solvent completely to give residue. The residue
obtained was triturated with a mixture of isopropyl alcohol 4 ml) and n-hexane (94 ml) at about 5°C to the title compound as crude. Yield: 34 g.
ExampIe-2: Purification of Racecadotril (Crude):
34 g. of crude Racecadotril and 35 ml of 20 % v/v aqueous .methanol were charged in a clean and dry R.B.flask and heated to about 65°C. 3g. of SP.carbon was charged and stirred at about 65°C for about 10 min. The reaction suspension was stirred at about 65°C for about 10 min. The reaction suspension was filtered on hyflow bed (diatomous earth) and washed the hyflow bed with 30 ml of aqueous methanol. The filtrate obtained was cooled to about 0°C for about 30 min. The solid separated was filtered and the solid obtained washed with 60 ml of precooled aqueous methanol to afford the pure racecadotril (I).
Yield: 29 g.; Purity by HPLC: 99.5 area %; The overall yield is 75.3%.
PATENT
https://www.google.com/patents/CN104356036A?cl=en
Example 1
The 40. 0g Racecadotril dissolved in 200ml of absolute ethanol and water bath heated to 40 ° C, and stir until the whole solution, stirring was stopped, the solution was placed in 15 ° C water bath was allowed to stand, when starting When there is precipitation of crystals, and then placed under the 0 ° C crystallization, after filtration, to 45 ° C under hot air drying cycle 6 hours to obtain 29. 2g, purity 99.6% of Racecadotril a polymorph crystals.
reflection angle X-ray powder diffraction pattern 20 at 4.3 °, 8.7 °, 13.2 °, 16.8 °, 17.8 ° and 20.0 ° at the show X-ray powder diffraction peaks. In 1135. 19CHT1,1551. 46CHT1,1644. 73CHT1,1687. 57CHT1, 1731. 35CHT1 and 3289. 20CHT1 displayed at an infrared absorption peak.
Clips
US 20020055645
PATENT
Racecadotril, chemical name N_ [(R, S) -3- acetyl-mercapto-2-benzyl-propionyl)] glycine benzyl ester, is a neprilysin inhibitor, selectively, reversible inhibition of neprilysin, so that the inner protection from degradation of endogenous enkephalins, prolong the physiological activity of endogenous enkephalins in the digestive tract, mainly used in clinical treatment of children and adults with acute diarrhea. Its structural formula is as follows:

Racecadotril as enkephalinase inhibitors, developed in France in 1993 Bioprojet listed acute diarrhea treatment, trade name Tiorfan.
In W02011116490A1, US5945548 and CN101768095A and other documents, documented racecadotril the synthesis process, but did not report the crystal form; therefore the present inventors have not reported Racecadotril crystalline polymorph conduct further
Example 1
[0032] The 40. 0g Racecadotril dissolved in 200ml of absolute ethanol and water bath heated to 40 ° C, and stir until the whole solution, stirring was stopped, the solution was placed in 15 ° C water bath was allowed to stand, when starting When there is precipitation of crystals, and then placed under the 0 ° C crystallization, after filtration, to 45 ° C under hot air drying cycle 6 hours to obtain 29. 2g, purity 99.6% of Racecadotril a polymorph crystals.
[0033] reflection angle X-ray powder diffraction pattern 20 at 4.3 °, 8.7 °, 13.2 °, 16.8 °, 17.8 ° and 20.0 ° at the show X-ray powder diffraction peaks. In 1135. 19CHT1,1551. 46CHT1,1644. 73CHT1,1687. 57CHT1, 1731. 35CHT1 and 3289. 20CHT1 displayed at an infrared absorption peak.
SYN
EP 0038758
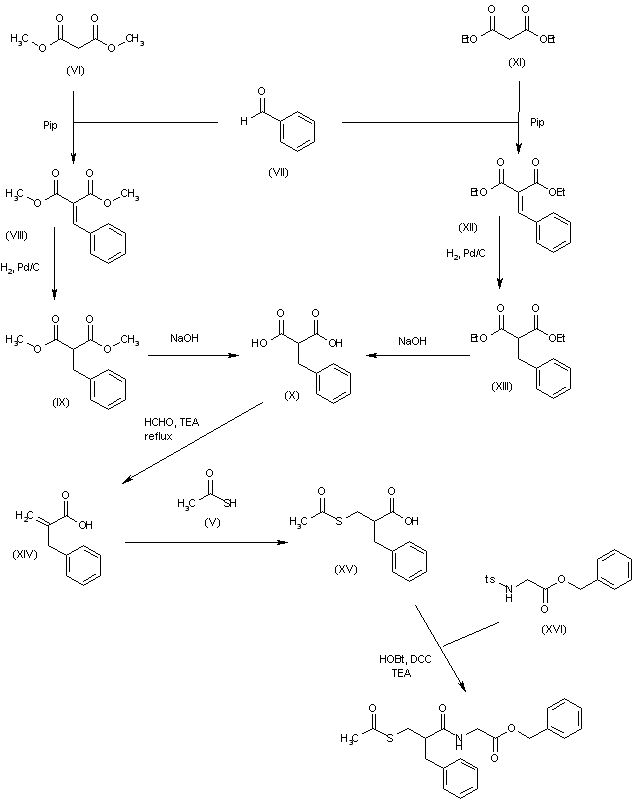
Alternatively, the condensation of dimethyl malonate (VI) with benzaldehyde (VII) by means of piperidine in refluxing toluene gives dimethyl benzylidenemalonate (VIII), which is reduced with H2 over Pd/C in toluene to yield the corresponding benzyl derivative (IX). The hydrolysis of (IX) with NaOH in water affords the benzylmalonic acid (X). Alternatively, intermediate (X) can also be obtained starting from diethyl malonate (XI), which is condensed with with benzaldehyde (VII) by means of piperidine in refluxing toluene to give diethyl benzylidenemalonate (XII). Reduction of (XII) with H2 over Pd/C in toluene yields the corresponding benzyl derivative (XIII), which is then hydrolized with NaOH in water. The monodecarboxylation of (X) and its condensation with paraformaldehyde and diethylamine in refluxing ethyl acetate provides 2-benzylacrylic acid (XIV), which is condensed with thioacetic acid (V) by heating at 70 C to afford 2-(acetylsulfanylmethyl)-3-phenylpropionic acid (XV). Finally, this compound is condensed with N-tosylglycine benzyl ester (XVI) by means of HOBt, DCC and TEA in THF.
SYN
| EP 0729936 |
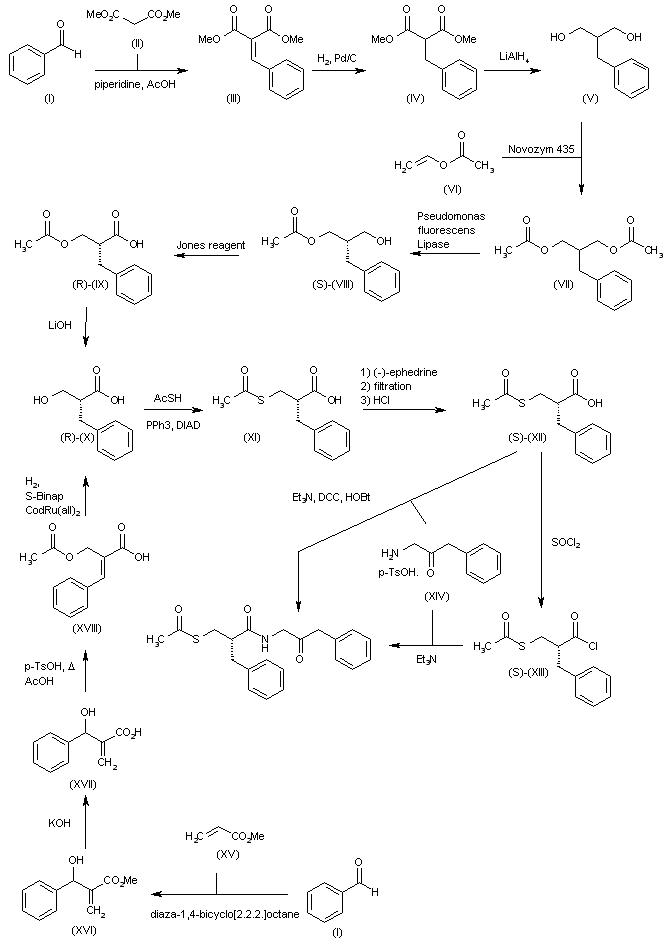
Reaction of benzaldehyde (I) with dimethyl malonate (II) in refluxing toluene in the presence of piperidine and HOAc provides dimethyl benzylidene malonate (III), which is then hydrogenated over Pd/C to afford dimethyl benzyl malonate (IV). Reduction of (IV) with LiAlH4 in refluxing THF furnishes 2-benzyl-1,3-propanediol (V), which is then subjected to reaction with vinyl acetate (VI) by means of Novozym 435 enzyme to yield diacetate (VII). Enantioselective removal of one acetyl group from (VII) by treatment with Pseudomonas fluorescens Lipase in acetone/phosphate buffer (pH = 7) at 30 C gives 3-acetoxy-2(S)-benzyl-propanol (S)-(VIII), which is then oxidized by means of Jones reagent in acetone/isopropanol to provide carboxylic acid (R)-(IX). The hydrolysis of (IX) with LiOH in THF/H2O gives 2(R)-benzyl-3-hydroxypropanoic acid (R)-(X). Alternatively, intermediate (X) can also be synthesized as follows: Condensation of benzaldehyde (I) with methyl acrylate (XV) by means of diaza-1,4-bicyclo[2.2.2.]octane affords methyl beta-hydroxy-alpha-methylene-benzenepropanoate (XVI), which is then subjected to hydrolysis with KOH in MeOH/H2O to yield carboxylic acid (XVII). Treatment of (XVII) with p-toluenesulfonic acid in refluxing HOAc gives (E)-2-(acetoxymethyl)-3-phenylpropionic acid (XVIII), which is finally converted into (X) by enantioselective hydrogenation in the presence of S-Binap and ruthenium catalyst [CodRu(all)2]. Derivative (R)-(X) is then converted into 3-(acetylsulfanyl)-2(S)-benzylpropionic acid (XI) by means of a Mitsunobu reaction with thioacetic acid, diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (DIAD) and triphenylphosphine (PPh3). Compound (XI) is then subjected to optical purification by formation and isolation of the corresponding salt with (-)-ephedrine and subsequent hydrolysis with HCl to furnish enantiomerically pure (S)-(XII). Finally, carboxylic acid (S)-(XII) is converted into ecadotril by its coupling with benzyl glycinate (XIV), either by means of Et3N, DCC and HOBt in CHCl3, or by first reaction with thionyl chloride to give acid chloride (S)-(XIII) and subsequent coupling with glycinate (XIV) by means of Et3N in CH2Cl2.
SYN
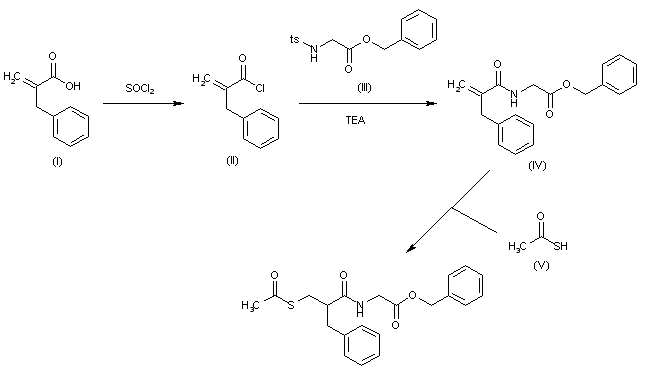
The reaction of 2-benzylacrylic acid (I) with SOCl2 in hot toluene gives the acyl chloride (II), which is condensed with N-tosylglycine benzyl ester (III) by means of TEA in toluene to yield the corresponding amide (IV). Finally, this compound is condensed with thioacetic acid by heating at 80 C to afford the target acylthio compound.
| FR 2816309; US 2002055645 |

AS ON DEC2021 3,491,869 VIEWS ON BLOG WORLDREACH AVAILABLEFOR YOUR ADVERTISEMENT

join me on Linkedin
Anthony Melvin Crasto Ph.D – India | LinkedIn
join me on Researchgate
RESEARCHGATE

join me on Facebook
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | Facebook
join me on twitter
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | twitter
+919321316780 call whatsaapp
EMAIL. amcrasto@amcrasto
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Side effects
The most common adverse effect is headache, which occurs in 1–2% of patients.[7] Rashes occur in fewer than 1% of patients. Other described skin reactions include itching, urticaria, angioedema, erythema multiforme, and erythema nodosum.[9][10]
Overdose
No cases of overdose are known. Adults have tolerated 20-fold therapeutic doses without ill effects.[10]
Interactions
No interactions in humans have been described. Combining racecadotril with an ACE inhibitor can theoretically increase the risk for angioedema.[9][10]
Racecadotril and its main metabolites neither inhibit nor induce the liver enzymes CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4. They also do not induce UGT enzymes.[10] This means that racecadotril has a low potential for pharmacokinetic interactions.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Enkephalins are peptides produced by the body that act on opioid receptors with preference for the δ subtype.[11] Activation of δ receptors inhibits the enzyme adenylyl cyclase, decreasing intracellular levels of the messenger molecule cAMP.[7]
The active metabolite of racecadotril, thiorphan, inhibits enkephalinase enzymes in the intestinal epithelium with an IC50 of 6.1 nM, protecting enkephalins from being broken down by these enzymes. (Racecadotril itself is much less potent at 4500 nM.)[7][8] This reduces diarrhea related hypersecretion in the small intestine without influencing basal secretion. Racecadotril also has no influence on the time substances, bacteria or virus particles stay in the intestine.[10]
Pharmacokinetics

Some metabolites of racecadotril.
top left: precursor to the active metabolite
top right: active metabolite
bottom row: inactive metabolites
Racecadotril is rapidly absorbed after oral administration and reaches Cmax within 60 minutes. Food delays Cmax by 60 to 90 minutes but does not affect the overall bioavailability. Racecadotril is rapidly and effectively metabolized to the moderately active S-acetylthiorphan the main active metabolite thiorphan, of which 90% are bound to blood plasma proteins. In therapeutic doses, racecadotril does not pass the blood–brain barrier. Inhibition of enkephalinases starts 30 minutes after administration, reaches its maximum (75–90% inhibition with a therapeutic dose) two hours after administration, and lasts for eight hours. The elimination half-life, measured from enkephalinase inhibition, is three hours.[7][8][9]
Thiorphan is further metabolized to inactive metabolites such as the methyl thioether and the methyl sulfoxide. Both active and inactive metabolites are excreted, mostly via the kidney (81.4%), and to a lesser extent via the feces (8%).[10]
Society and culture
Brand names
In both France and Portugal it is sold as Tiorfan and in Italy as Tiorfix. In India it is available as Redotril and Enuff.[4]
See also
- Ecadotril, the (S)-enantiomer of racecadotril
- D/DL-Phenylalanine
- RB-101
References
- ^ https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/psusa/racecadotril-list-nationally-authorised-medicinal-products-psusa/00002602/202003_en.pdf
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d “SPC-DOC_PL 39418-0003.PDF” (PDF). Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. Bioprojet Europe Ltd. 26 December 2012. Retrieved 7 May 2014.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Matheson AJ, Noble S (April 2000). “Racecadotril”. Drugs. 59 (4): 829–35, discussion 836–7. doi:10.2165/00003495-200059040-00010. PMID 10804038.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Brayfield, A, ed. (13 December 2013). “Racecadotril”. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press. Retrieved 6 May 2014.
- ^ Spillantini MG, Geppetti P, Fanciullacci M, Michelacci S, Lecomte JM, Sicuteri F (June 1986). “In vivo ‘enkephalinase’ inhibition by acetorphan in human plasma and CSF”. European Journal of Pharmacology. 125 (1): 147–50. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(86)90094-4. PMID 3015640.
- ^ Fischbach, Wolfgang; Andresen, Viola; Eberlin, Marion; Mueck, Tobias; Layer, Peter (2016). “A Comprehensive Comparison of the Efficacy and Tolerability of Racecadotril with Other Treatments of Acute Diarrhea in Adults”. Frontiers in Medicine. 3: 44. doi:10.3389/fmed.2016.00044. ISSN 2296-858X. PMC 5064048. PMID 27790616.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e f Dinnendahl, V; Fricke, U, eds. (1982). Arzneistoff-Profile (in German). Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c Eberlin, Marion; Mück, Thomas; Michel, Martin C. (2012). “A Comprehensive Review of the Pharmacodynamics, Pharmacokinetics, and Clinical Effects of the Neutral Endopeptidase Inhibitor Racecadotril”. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 3: 93. doi:10.3389/fphar.2012.00093. ISSN 1663-9812. PMC 3362754. PMID 22661949.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e Mediq.ch: racecadotril. Accessed 2019-12-30.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e f g Haberfeld, H, ed. (2019). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. Hidrasec 100 mg-Hartkapseln.
- ^ Cumming, P (2019). “A Survey of Molecular Imaging of Opioid Receptors”. Molecules. 24 (22): 4190. doi:10.3390/molecules24224190. PMC 6891617. PMID 31752279.
External links
- “Racecadotril”. Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Hidrasec, Tiorfan, Zedott, others |
| Other names | Benzyl 2-[3-(acetylthio)-2-benzylpropanamido]acetate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | A07XA04 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | UK: POM (Prescription only)EU: Rx-only [1] |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 90% (active metabolite thiorphan)[2] |
| Metabolism | Liver-mediated[2] |
| Onset of action | 30 min |
| Elimination half-life | 3 hours[2] |
| Excretion | Urine (81.4%), feces (8%)[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| showIUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 81110-73-8 |
| PubChem CID | 107751 |
| DrugBank | DB11696 |
| ChemSpider | 96913 |
| UNII | 76K53XP4TO |
| KEGG | D08464 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL2103772 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID8045513 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.214.352 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H23NO4S |
| Molar mass | 385.48 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| Melting point | 89 °C (192 °F) |
| showSMILES | |
| showInChI | |
| (what is this?) (verify) |

| CN101103960A * | Jul 14, 2006 | Jan 16, 2008 | 海南盛科生命科学研究院 | Dry mixed suspension containing racecadotril and preparation method thereof |
| CN101768095A * | Dec 26, 2008 | Jul 7, 2010 | 山东齐都药业有限公司 | Preparation method of racecadotril |
| WO2001097803A1 * | Jun 20, 2001 | Dec 27, 2001 | Laboratoire Glaxosmithkline | Pharmaceutical preparations comprising racecadotril (acetorphan) |
| WO2013098826A1 * | Dec 26, 2011 | Jul 4, 2013 | Symed Labs Limited | “a process for the preparation of n-[2-[(acetylthio) methyl]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropyl] glycine phenyl methyl ester and intermediates thereof” |
| Reference |
|---|
| Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101103960A * | Jul 14, 2006 | Jan 16, 2008 | 海南盛科生命科学研究院 | Dry mixed suspension containing racecadotril and preparation method thereof |
| CN101768095A * | Dec 26, 2008 | Jul 7, 2010 | 山东齐都药业有限公司 | Preparation method of racecadotril |
| WO2001097803A1 * | Jun 20, 2001 | Dec 27, 2001 | Laboratoire Glaxosmithkline | Pharmaceutical preparations comprising racecadotril (acetorphan) |
| WO2013098826A1 * | Dec 26, 2011 | Jul 4, 2013 | Symed Labs Limited | “a process for the preparation of n-[2-[(acetylthio) methyl]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropyl] glycine phenyl methyl ester and intermediates thereof” |
| 1 | * | 金庆平 等: “神经内肽酶抑制剂消旋卡多曲(Racecadotril)的合成工艺研究“, 《中国现代应用药学杂志》, vol. 20, no. 7, 31 August 2003 (2003-08-31) |
| Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citing Patent | Filing date | Publication date | Applicant | Title |
| US6013829 * | Feb 4, 1997 | Jan 11, 2000 | Societe Civile Bioprojet | Process for the asymmetric synthesis of S-acyl derivatives of 2-mercaptomethyl -3- phenyl propanoic acid, application to the synthesis of N-(mercaptoacyl) amino acid derivatives |
| US20040009956 * | Apr 29, 2003 | Jan 15, 2004 | Dehua Pei | Inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatases and SH2 domains by a neutral phosphotyrosine mimetic |
| 1 | * | MOHAMED A.O. ET AL.: ‘Stability-indicating methods for the determination of racecadotril in the presence of its degradation products‘ BIOSCIENCE TRENDS vol. 3, no. 6, 2009, pages 247 – 252, XP055074337 | ||
| CN104356036A * | Nov 7, 2014 | Feb 18, 2015 | 山东齐都药业有限公司 | Alpha crystal form of racecadotril and preparation method of alpha crystal form |
///////////Racecadotril, рацекадотрил , راسيكادوتريل , 消旋卡多曲 , Antidiarrheal, Neutral Endopeptidase Inhibitor, Cadotril, Dexecadotril ,
CC(=O)SCC(CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)NCC(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1

