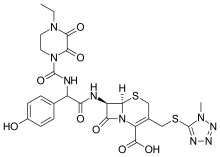

Cefoperazone
- Molecular FormulaC25H27N9O8S2
- Average mass645.667 Da
Product Ingredients
| INGREDIENT | UNII | CAS | INCHI KEY |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cefoperazone sodium | 5FQG9774WD | 62893-20-3 | NCFTXMQPRQZFMZ-WERGMSTESA-M |
(6R,7R)-7-{[(2R)-2-{[(4-ethyl-2,3-dioxopiperazin-1-yl)carbonyl]amino}-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino}-3-{[(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl}-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
(6R,7R)-7-[(2R)-2-[(4-ethyl-2,3-dioxopiperazine-1-carbonyl)amino]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3-{[(1-methyl-1H-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
263-749-4[EINECS], 4742
5-Thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-[[(2R)-2-[[(4-ethyl-2,3-dioxo-1-piperazinyl)carbonyl]amino]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino]-3-[[(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl]-8-oxo- , (6R,7R)- [ACD/Index Name]
5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-[[(2R)-2-[[(4-ethyl-2,3-dioxo-1-piperazinyl)carbonyl]amino]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino]-3-[[(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl]-8-oxo-, (6R,7R)-
62893-19-0[RN]
7-[D-(-)-a-(4-Ethyl-2,3-dioxo-1-piperazinecarboxamido)-a-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3-[[(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl]-3-cephem-4-carboxylic Acid
7U75I1278D
Experimental Properties
| PROPERTY | VALUE | SOURCE |
|---|---|---|
| melting point (°C) | 188-190 | Saikawa, I., Takano, S., Yoshida, C., Takashima, 0..Momonoi, K., Kuroda, S., Komatsu, M., Yasuda, T.and Kodama, Y.; British Patent 1,508,071; April 19,1978; assigned to Toyama Chemical Co., Ltd. and U.S. Patent 4,110,327; August 29,1978; also assigned to Toyama Chemical Co., Ltd. |
| logP | -0.74 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
Cefoperazone
CAS Registry Number: 62893-19-0
CAS Name: (6R,7R)-7-[[(2R)-[[(4-Ethyl-2,3-dioxo-1-piperazinyl)carbonyl]amino](4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino]-3-[[(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acidAdditional Names: 7-[D-(-)-a-(4-ethyl-2,3-dioxo-1-piperazinecarboxamido)-a-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3-[[(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl]-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid
Molecular Formula: C25H27N9O8S2
Molecular Weight: 645.67
Percent Composition: C 46.50%, H 4.21%, N 19.52%, O 19.82%, S 9.93%
Literature References: Broad spectrum third generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Prepn: I. Saikawa et al.,BE837682; eidem,US4410522 (1976, 1983 both to Toyama); eidem,Yakugaku Zasshi99, 929 (1979). Stability in aq soln: eidem,ibid. 1207. In vitro activity: M. V. Borobio et al.,Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.17, 129 (1980). Kinetics in rats: J. Fabre et al.,Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr.110, 264 (1980); in humans: A. F. Allaz, ibid.109, 1999 (1979). Review of pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy: R. N. Brogden et al.,Drugs22, 423-460 (1981). Symposium on clinical studies: ibid. Suppl. 1, 1-124.
Properties: Crystals from acetonitrile/water, mp 169-171° (hydrated). Stable at pH 4.0-7.0; slightly unstable in acid; highly unstable in alkaline soln.
Melting point: mp 169-171° (hydrated)
Derivative Type: Sodium salt
CAS Registry Number: 62893-20-3
Manufacturers’ Codes: CP-52640-2; T-1551
Trademarks: Bioperazone (Biopharma); Cefazone (Firma); Cefobid (Pfizer); Cefobine (Pfizer); Cefobis (Pfizer); Cefogram (Metapharma); Cefoneg (Tosi); Cefosint (Proter); Dardum (Lisapharma); Farecef (Lafare); Kefazon (Esseti); Novobiocyl (Francia); Pathozone (Pfizer); Peracef (Pfizer); Perocef (Pulitzer); Tomabef (Aandersen)
Molecular Formula: C25H26N9NaO8S2
Molecular Weight: 667.65
Percent Composition: C 44.97%, H 3.93%, N 18.88%, Na 3.44%, O 19.17%, S 9.61%
Therap-Cat: Antibacterial., Therap-Cat-Vet: Antibacterial.
Keywords: Antibacterial (Antibiotics); ?Lactams; Cephalosporins.
Cefoperazone is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, marketed by Pfizer under the name Cefobid. It is one of few cephalosporin antibiotics effective in treating Pseudomonas bacterial infections which are otherwise resistant to these antibiotics.
It was patented in 1974 and approved for medical use in 1981.[1] Cefoperazone/sulbactam (Sulperazon) is a co-formulation with sulbactam.
Cefoperazone is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of bacterial infections in various locations, including the respiratory tract, abdomen, skin, and female genital tracts.
Cefoperazone is a semisynthetic broad-spectrum cephalosporin proposed to be effective against Pseudomonas infections. It is a third-generation antiobiotic agent and it is used in the treatment of various bacterial infections caused by susceptible organisms in the body, including respiratory tract infections, peritonitis, skin infections, endometritis, and bacterial septicemia. While its clinical use has been discontinued in the U.S., cefoperazone is available in several European countries most commonly under the product name, Sulperazon.

join me on Linkedin
Anthony Melvin Crasto Ph.D – India | LinkedIn
join me on Researchgate
RESEARCHGATE

join me on Facebook
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | Facebook
join me on twitter
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | twitter
+919321316780 call whatsaapp
EMAIL. amcrasto@amcrasto
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
SYN

English: I. Saikawa, S. Takano, Y. Shuntaro, C. Yoshida, 0.
Takashima, K. Momonoi, S. Kuroda, M. Komatsu, T. Yasuda, and Y. Kodama, German Offen., DE 2,600,880 (1977); Chem.
Abstr., 87_, 184533b (1977).
SYN
Following is one of the synthesis routes:
alpha-(4-Ethyl-2,3-dioxo-1-piperazinocarbonylamino)-p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (I) is condensed with 7-amino-3-[(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)thiomethyl]-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid (II) in the presence of ethyl chlorocarbonate and N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide in acetonitrile to produce Cefoperazone sodium.

SYN
Antibiotics
R.S. Vardanyan, V.J. Hruby, in Synthesis of Essential Drugs, 2006
Cefoperazone
Cefoperazone, (6R,7R)-7-[(R)-2-(4-ethyl-2,3-dioxo-1-piperazincarboxamido)-2-(p-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3-[[(1-methyl-1 H-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-en-2-carboxylic acid (32.1.2.84), is synthesized by acylating 7-amino-3-(1-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)-thiomethyl-3-cefem-4-carboxylic acid (32.1.2.24) with a mixed anhydride synthesized from ethyl chloroformate and α-(4-ethylpiperazin-2, 3-dion-1-carbonylamino)-4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (32.1.2.83), which in turn is synthesized from 4-ethylpiperazin-2,3-dion-1-carboxylic acid (32.1.1.29) and the sodium salt of 4-hydroxyphenylglycine [163–168].


Cefoperazone also has a broad spectrum of antimicrobial action, including most clinically significant microorganisms: Gram-positive, Gram-negative, aerobic, and anaerobic. It is stable with respect to most beta-lactamases of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Cefoperazone is used for bacterial infections of the lower respiratory tract, urinary and sexual tracts, bones, joints, skin, soft tissues, abdominal, and gynecological infections. Synonyms of this drug are cefazon, cefobid, cefobis, and many others.
Spectrum of bacterial susceptibility
Cefoperazone has a broad spectrum of activity and has been used to target bacteria responsible for causing infections of the respiratory and urinary tract, skin, and the female genital tract. The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant microorganisms.
- Haemophilus influenzae: 0.12 – 0.25 µg/ml
- Staphylococcus aureus: 0.125 – 32 µg/ml
- Streptococcus pneumoniae: ≤0.007 – 1 µg/ml[2]
Adverse effects
Cefoperazone contains an N-methylthiotetrazole (NMTT or 1-MTT) side chain. As the antibiotic is broken down in the body, it releases free NMTT, which can cause hypoprothrombinemia (likely due to inhibition of the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase) and a reaction with ethanol similar to that produced by disulfiram (Antabuse), due to inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase.[3]
Mechanism of action
Cefoperazone exerts its bactericidal effect by inhibiting the bacterial cell wall synthesis, and sulbactam acts as a beta-lactamase inhibitor, to increase the antibacterial activity of cefoperazone against beta-lactamase-producing organisms.
References
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 494. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ “Cefoperazone (Cefobid) – The Antimicrobial Index Knowledgebase – TOKU-E”. antibiotics.toku-e.com.
- ^ Stork CM (2006). “Antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals”. In Nelson LH, Flomenbaum N, Goldfrank LR, Hoffman RL, Howland MD, Lewin NA (eds.). Goldfrank’s toxicologic emergencies. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 847. ISBN 0-07-143763-0. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a601206 |
| ATC code | J01DD12 (WHO) QJ51DD12 (WHO) |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Excretion | Hepatic |
| Identifiers | |
| showIUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 62893-19-0 |
| PubChem CID | 44185 |
| DrugBank | DB01329 |
| ChemSpider | 40206 |
| UNII | 7U75I1278D |
| KEGG | D07645 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL507674 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID2022759 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.057.936 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H27N9O8S2 |
| Molar mass | 645.67 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| showSMILES | |
| showInChI | |
| (verify) |
//////////cefoperazone, Antibacterial, Antibiotics, Lactams, Cephalosporins, CP-52640-2, T-1551, CP 52640-2, T 1551
[H][C@]12SCC(CSC3=NN=NN3C)=C(N1C(=O)[C@@]2([H])NC(=O)[C@H](NC(=O)N1CCN(CC)C(=O)C1=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1)C(O)=O
