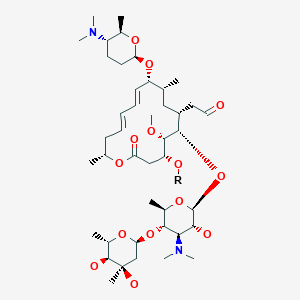
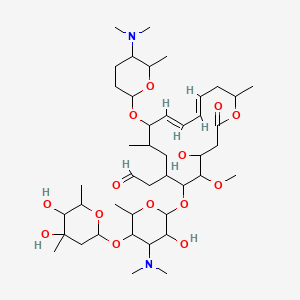
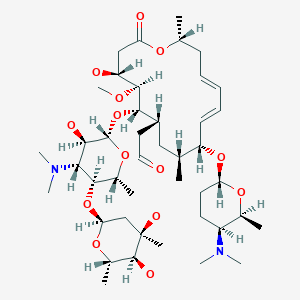
Spiramycin
スピラマイシン
CAS: 8025-81-8
Sanofi INNOVATOR
| Molecular Formula: | C43H74N2O14 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 843.065 g/mol |
[(11E,13E)-6-({5-[(4,5-Dihydroxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy]-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl}oxy)-10-{[5-(dimethylamino)-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy }-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-9,16-dimethyl-2-oxooxacyclohexadeca-11,13-dien-7-yl]acetaldehyde
2-[(11E,13E)-6-[5-(4,5-dihydroxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl)oxy-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-10-[5-(dimethylamino)-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-9,16-dimethyl-2-oxo-1-oxacyclohexadeca-11,13-dien-7-yl]acetaldehyde
Leucomycin V, 9-O-[(2R,5S,6R)-5-(dimethylamino)tetrahydro-6-methyl-2H-pyran-2-yl]-
-
Provamycin
-
Rovamycin
-
RP 5337
-
Sequamycin
-
IL 5902
-
NSC-64393
- ATC:J01FA02
- Use:macrolide antibiotic
- EINECS:232-429-6
- LD50:130 mg/kg (M, i.v.); 2900 mg/kg (M, p.o.);
170 mg/kg (R, i.v.); 3550 mg/kg (R, p.o.);
5200 mg/kg (dog, p.o.)
2018/7/2 japan approved, UNII: 71ODY0V87H
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water
Soluble in most organic solvents
Spectral Properties
UV max (ethanol): 231nm
Specific optical rotation: -80 deg at 20 deg C/D
| スピラマイシン Spiramycin 
[検索ページへ戻る]
|
|
|
| スピラマイシン酢酸エステル JP17 Spiramycin Acetate  |
A macrolide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces ambofaciens. The drug is effective against gram-positive aerobic pathogens, N. gonorrhoeae, and staphylococci. It is used to treat infections caused by bacteria and Toxoplasma gondii.
Spiramycin is a macrolide antimicrobial agent with activity against gram-positive organisms, including Streptococcus pyogenes (group A beta-hemolytic streptococci), S. viridans, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus. Spiramycin is a 16-membered ring macrolide. It was discovered in 1952 as a product of Streptomyces ambofaciens. As a preparation for oral administration it has been used since 1955, in 1987 also the parenteral form was introduced into practice. The antibacterial spectrum comprises Gram-positive cocci and rods, Gram-negative cocci and also Legionellae, mycoplasmas, chlamydiae, some types of spirochetes, Toxoplasma gondii and Cryptosporidium species. Enterobacteria, pseudomonads and pathogenic moulds are resistant. Its action is mainly bacteriostatic, on highly sensitive strains it exerts a bactericide action.
Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic and antiparasitic It is used to treat toxoplasmosis and various other infections of soft tissues. Although used in Europe, Canada and Mexico,[1] spiramycin is still considered an experimental drug in the United States, but can sometimes be obtained by special permission from the FDA for toxoplasmosis in the first trimester of pregnancy.[2]
Spiramycin has been used in Europe since the year 2000 under the trade name “Rovamycine”, produced by Rhone-Poulenc Rorer and Famar Lyon, France and Eczacıbaşı İlaç, Turkey. It also goes under the name Rovamycine in Canada (distributed by OdanLaboratories), where it is mostly marketed to dentists for mouth infections.
Spiramycin is a 16-membered ring macrolide. It was discovered in 1952 as a product of Streptomyces ambofaciens. As a preparation for oral administration it has been used since 1955, in 1987 also the parenteral form was introduced into practice. The antibiotic action involves inhibition of protein synthesis in the bacterial cell during translocation. Resistance to spiramycin can develop by several mechanisms and its prevalence is to a considerable extent proportional to the frequency of prescription in a given area. The antibacterial spectrum comprises Gram-positive cocci and rods, Gram-negative cocci and also Legionellae, mycoplasmas, chlamydiae, some types of spirochetes, Toxoplasma gondii and Cryptosporidium species. Enterobacteria, pseudomonads and pathogenic moulds are resistant. Its action is mainly bacteriostatic, on highly sensitive strains it exerts a bactericide action. As compared with erythromycin, it is in vitro weight for weight 5 to 20 less effective, an equipotential therapeutic dose is, however, only double. This difference between the effectiveness in vitro and in vivo is explained above all by the great affinity of spiramycin to tissues where it achieves concentrations many times higher than serum levels. An important part is played also by the slow release of the antibiotic from the tissue compartment, the marked action on microbes in sub-inhibition concentrations and the relatively long persisting post-antibiotic effect. Its great advantage is the exceptionally favourable tolerance-gastrointestinal and general. It is available for parenteral and oral administration
Synthesis Path
- From culture of Streptomyces ambofaciens.
Trade Names
| Country | Trade Name | Vendor | Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| D | Rovamycine | Teofarma | |
| Selectomycin | Grünenthal | ||
| F | Bi Missilor | Pierre Fabre | |
| Birodogyl | Sanofi-Aventis | ||
| Missilor | Pierre Fabre | comb. | |
| Rodogyl | Pierre Fabre | ||
| Rovamycine | Grünenthal | ||
| I | Rovamicina | Sanofi-Aventis | |
| Rovamycina | Teofarma | ||
| Spiromix | Pulitzer |

 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 2-[(4R,5S,6S,7R,9R,10R,11E,13E,16R)-6-{[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-5-{[(2S,5S,6S)-4,5-dihydroxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-10-{[(2R,5S,6R)-5-(dimethylamino)-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-9,16-dimethyl-2-oxo-1-oxacyclohexadeca-11,13-dien-7-yl]acetaldehyde |
| Routes of administration |
oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| E number | E710 (antibiotics)  |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.476  |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C43H74N2O14 |
| Molar mass | 843.053 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble in water; Very soluble in acetonitrile and methanol; Almost completely(>99.5) in ethanol. mg/mL (20 °C) |
References
- Jump up^ Spiramycin advanced consumer information | Drugs.com
- Jump up^ Toxoplasmosis at MayoClinic.com
References
-
- Pinnert-Sindico, S. et al.: Antibiot. Annu. (ABANAE) 1954-1955, 724.
- US 2 943 023 (Rhône-Poulenc; 28.6.1960; F-prior. 30.5.1956).
- US 2 978 380 (Rhône-Poulenc; 4.4.1961; F-prior. 30.11.1955).
- US 3 000 785 (Rhône-Poulenc; 19.9.1961; F-prior. 31.7.1953).
- US 3 011 947 (Rhône-Poulenc; 5.12.1961; F-prior. 30.11.1955).
- CN 107266512
CN 107840864
///////////Spiramycin, スピラマイシン , japan 2018, Provamycin, Rovamycin, RP 5337, Sequamycin, IL 5902, NSC-64393, ATC:J01FA02, Use:macrolide antibiotic, EINECS:232-429-6
O=CCC4C(OC2OC(C(OC1OC(C)C(O)C(O)(C)C1)C(N(C)C)C2O)C)C(OC)C(O)CC(=O)OC(C)C\C=C\C=C\C(OC3OC(C)C(N(C)C)CC3)C(C)C4