
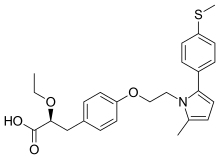
(2S)-2-Ethoxy-3-[4-(2-{2-methyl-5-[4-(methylsulfanyl)phenyl]-1H-pyrrol-1-yl}ethoxy)phenyl]propanoic acid
(αS)-α-Ethoxy-4-[2-[2-methyl-5-[4-(methylthio)phenyl]-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]ethoxy]benzenepropanoic Acid
alpha-ethoxy-4-(2-(2-methyl-5-(4-methylthio)phenyl))-1H-pyrrol-1-yl)ethoxy))benzenepropanoic acid
alpha-ethoxy-4-(2-(2-methyl-5-(4-methylthio)phenyl))-1H-pyrrol-1-yl)ethoxy))benzenepropanoic acid magnesium salt
(2S)-2-ethoxy-3-[4-[2-[2-methyl-5-(4-methylsulfanylphenyl)pyrrol-1-yl]ethoxy]phenyl]propanoic acid
Benzenepropanoic acid, α-ethoxy-4-[2-[2-methyl-5-[4-(methylthio)phenyl]-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]ethoxy]-, (αS)-
ZYH1 compound
Cas no 495399-09-2
Saroglitazar, Lipaglyn
| Molecular Weight | 439.56706 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H29NO4S |
Cadila Healthcare Ltd innovator
Zydus-Cadila has developed and launched saroglitazar for treating diabetic dyslipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia.
In September 2013, saroglitazar was launched in India for treating dyslipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia.
As of March 2015, Zydus-Cadila is developing saroglitazar for treating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and type II diabetes (both in phase III clinical trials).


Saroglitazar (INN, trade name Lipaglyn) is a drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. It is approved for use in India by the Drug Controller General of India.[1] Saroglitazar is indicated for the treatment of diabetic dyslipidemia andhypertriglyceridemia with type 2 diabetes mellitus not controlled by statin therapy. In clinical studies, saroglitazar has demonstrated reduction of triglycerides (TG), LDL cholesterol, VLDL cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol and an increase in HDL cholesterol a characteristic hallmark of atherogenic diabetic dyslipidemia (ADD). It has also shown favorable Anti-diabetic medication property by reducing the fasting plasma glucose and HBA1c in diabetes patients. The recommended dose of saroglitazar is one tablet of 4 mg once a day.
In February 2013, Saroglitazar became the first glitazar that has been approved by any FDA for clinical use. Saroglitazar is marketed under the trade name Lipaglyn and developed by Zydus Cadila. Saroglitazar (2 and 4 mg q.d.) is currently approved in India by Drug Controller General of India (DCGI ) for the management of diabetic dyslipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia in T2DM not controlled by statin therapy. Lipaglyn provides the option of a once-daily oral therapy for the patients suffering from diabetic dyslipidemia.
Saroglitazar has another first attached to it. It is the first indigenously developed NCE by any Indian company; in this case Zydus Cadila.
Lipaglyn is indicated 4 mg (or 2 mg where such a need arise) oral dose once daily.
Saroglitazar Synthesis
http://ayurajan.blogspot.in/2016/01/saroglitazar.html
WO2003009841A1:

Identification:

| 1H NMR (Estimated) for Saroglitazar |
Experimental: 1H NMR: 1.14 (3H, t, J = 6.9Hz); 2.37 (3H, s); 2.48 (3H, s); 2.92-3.06 (2H, m); 3.32-3.42 (1H, m); 3.57-3.64 (1H, m); 3.9 (2H, t, J=6.36 Hz); 4.0 (1H, dd); 4.28(2H, t, J = 6.2 Hz); 5.9 (1H, d, J = 3.3 Hz); 6.08 (1H, d, J = 3.38 Hz); 6.6 (2H, d, J = 8.5Hz); 7.1(2H, d, J = 8.5Hz); 7.26 (2H, d, J = 8.4Hz); 7.3 (2H, d, J = 8.34Hz)
Details see below
Mechanism of action
Saroglitazar is novel first in class drug which acts as a dual PPAR agonist at the subtypes α (alpha) and γ (gamma) of theperoxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR). Agonist action at PPARα lowers high blood triglycerides, and agonist action onPPARγ improves insulin resistance and consequently lowers blood sugar.[2]
Efficacy
Being a dual PPAR agonist, Saroglitazar (Lipaglyn) helps in controlling blood glucose and Lipid parameters especially high triglycerides and high non HDL-Cholesterol.[3] Lipaglyn effectively reduces triglycerides and non HDL-C and controlles high blood sugar, a typical situation in Insulin Resistance condition.[4][5]
Safety
Saroglitazar has not demonstrated any of the adverse effects like weight gain and edema that are usually identified with similar molecules like the glitazone class of drugs.[6] Because it is an insulin sensitizer, Saroglitazar (Lipaglyn) has less potential for hypoglycemia. No major serious adverse events have been reported; however, long-term cardiovascular safety has not been established.[7]
| Saroglitazar, is a drug for the treatment of diabetic dyslipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia with Type 2 diabetes mellitus not controlled by statin therapy. Its trade name is Lipaglyn. It is also a 1,2-Diarylpyrroles derivative, which can be used in the preparation of Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). |
| References: Khanna, I. K., et al.: J. Med. Chem., 40, 1619 (1997) |
PAPER
A new enantioselective synthesis of (S)-2-ethoxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid esters (EEHP and IEHP), useful pharmaceutical intermediates of PPAR agonists
Tetrahedron Lett 2014, 55(21): 3223
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040403914006200

PATENT
WO 2003009841
http://www.google.co.in/patents/WO2003009841A1?cl=en
PATENT
US 20030236254
http://www.google.com/patents/US20030236254
PATENT
US 20140099333
http://www.google.com/patents/US20140099333
PATENT
http://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/WO2014174524
 (I)
(I)
The compound as claimed in claim 1 wherein R is -SMe and M+ is Mg+2.
The compound of claim 1 is Saroglitazar.
wherein ‘R’ is selected from hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, acyl, alkoxy, alkylthio, thioalkyl, aryloxy, arylthio and M+ represents suitable metal cations such as Na+, K+, Ca+2, Mg+2 and the like. r .
PATENT
3-Aryl-2-hydroxy propanoic acid derivatives serve as a key intermediate for the synthesis of many pharmaceutically important compounds especially, peroxime proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) agonist.
Optically active 3-aryl-2-alkoxy propanoic acid and its esters, particularly, ethyl (2S)-2-ethoxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate (EEHP) and isopropyl (2S)-2-ethoxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate (IEHP) are versatile chiral pharmacophores present in many pharmaceutically important compounds, especially in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) agonists that have beneficial effects in treating Type 2 diabetes.
Several PPAR agonists, in particular PPAR α/γ dual agonists, commonly termed as glitazars (Ragaglitazar, Tesaglitazar, Navaglitazar etc.), as shown in the figure below were developed by many pharmaceutical companies that have a potential application in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia.
However, many of these drugs were discontinued due to their undesirable side effects, but some of them still have great potential [For example, Saraglitazar (LipaglynTM) developed by Zydus Cadila got approval in India for the treatment of diabetic dyslipidemia or hypertriglyceridemia]. Several PPAR α/γ agonists possessing chiral (S)-l moieties are shown below.

Tesaglitazar Naveglitazar
In addition, these derivatives find an application in photosensitive materials, sweetening agents, treatment of certain eating disorders etc. Therefore, these compounds have attracted a great deal of attention of synthetic chemists and different methods of preparation of the compound of formula (S)-l have been extensively studied.
Generally, the reported protocols for the synthesis involve chiral pool approaches starting from L-tyrosine and its derivatives (Refer WO 02/24625, US 6559335B2, WO 2003/027084), asymmetric synthesis (Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 1947, US 2007/0149804) and resolution processes using chiral amines or enzymes (WO 2000/026200, WO 2001/11073, Org. Process Res. Dev. 2003, 7, 82, Org. Process Res. Dev. 2004, 8, 838, Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2009, 20, 2594).
Some of these methods have disadvantages such as expensive chiral starting materials and catalysts, low enantioselectivity and overall yields, problems associated with the O-alkylation step which often leads to the loss of optical purity, and many others.
The processes described in WO20026200 (Rao et. al.) uses benzyl bromide for benzylation, which is highly lachrymatory. Again, in the processes described, the debenzylation of the final intermediate was done by using Pd/C under pressure, which escalates the process economics.
WO2003024915 describes a process for the preparation 3-aryl-2-hydroxy propanoic acid derivatives from 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-oxopropanoic acid.
WO 2003008362 describes 3-Aryl-2-hydroxy propanoic acid derivatives of formula I and the preparation thereof.

wherein Rland R2 may be same or different and represent hydrogen or (CI- C6) alkyl.
The process is depicted in Scheme 1 below.
Scheme 1

In another process variant as in Scheme 2, WO’362 discloses a process for the preparation of novel 3-aryl-2 -hydroxy propanol and their derivatives of the formula (I)

wherein OR and OR together form a substituted or unsubstituted 5 membered cyclic structure containing carbon and oxygen atoms, which comprises: i) reducing the compound of formula (III) where R represents hydrogen or alkyl group, R3 represents benzyl to a compound of formula (IV) where R3 represents benzyl, ii) cyclizing the compound of formula (IV) to a compound of formula (V) where ORl and OR2 together form a substituted or unsubstituted 5 membered cyclic structure containing carbon and oxygen atoms and R3 represents benzyl and iii) debenzylating the compound of formula (V) in the presence of metal catalysts to yield pure compound of formula (I).
Scheme 2

Both the processes described in WO’362 result in poor overall yield and further fail to describe the preparation of compound of formula V using different alkylating agents. This document exemplifies the compound of formula V with similar ether groups as it fails to teach selective alkylation of formula IV.
WO2005019152 discloses an improved process for the preparation of compound of the general formula (la) and (lb).

Wherein, Rl represent H or (C1-C6) alkyl group such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, isobutyl, t-butyl and the like. R2 represents (Ci-Ce) alkyl group such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, isobutyl, t- butyl and the like. R3 represents H, protecting groups such as benzyl, substituted benzyl, (C1-C3) alkyl and like.
The compound of general formula (la) is prepared according to the following schemes 3 and 4.
Scheme 3

Both the processes start with selective O-alkylation or O-aralkylation of L-Tyrosine of formula (2a) using a base, a chelating agent, an alkyl or aralkyl halide in the presence of solvents to obtain the compound of formula (3a), which is diazotized to obtain formula (4a) which upon dialkylation using an excess of alkylating agent and excess base, in presence of suitable solvent to obtain optically pure compound of formula (la). Alternatively, compound of formula (4a) may be selectively esterified to obtain compound of formula (5a), which is subsequently O-alkylated to obtain compound of formula (la) (Scheme 2).
However, the above processes have many disadvantages such as multistep synthesis including protection & deprotection and low overall yield. Further, low temperature diazotization on industrial scale is not viable. Moreover, the starting material is very expensive and hence escalates the process.
In the light of the foregoing, development of a new, alternate enantio-selective synthetic route to these important chiral intermediates, which are simple and can preserve the optical purity at the C-2 carbon of 3-Aryl-2-hydroxy propanoic acid derivatives, is highly desirable. There is a need for an efficient process for synthesis of 3-Aryl-2-hydroxy propanoic acid derivatives of formula (S)-l in high enantiopurity and good overall yield from commercially available starting material.

OR
Synthesis of saroglitazar
1. 2-Bromo-1-[4-(methylthio)phenyl]ethanone is condensed with methyl acetoacetate in the presence of NaOMe and Na2SO4 in toluene, to give alpha-keto methyl ester ,
2. This alpha-keto methyl ester ,is hydrolyzed and decarboxylated by means of NaOH in MeOH/toluene at 50 °C giving diketone .
3. Diketone is subjected to Paal-Knorr reaction with ethanolamine in the presence of pivallic acid in toluene at 110 °C to yield pyrrole primary alcohol derivative .
4. Sulfonylation of this pyrrole primary alcohol with MsCl in the presence of Et3N,
5. O-alkylation of mesylate with ethyl 2(S)-ethoxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate in the presence of K2CO3, optionally in the presence of 18-crown-6 in toluene/THF at 80 °C provides ether.
6. Finally, hydrolysis of ethyl ester using NaOH in H2O affords the target saroglitazar.
PATENT
saroglitazar magnesium alongwith its intermediates may be prepared by the reaction scheme- 1, scheme-2 and scheme-3 as shown below, which is also the scope of the present invention.

Scheme-1

EXAMPLES
Example-l:
Preparation of methanesulfonic acid 2-r2-methyl-5-(4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-pyrrol-l-yl]-ethyl ester (Al)

In a 5 Liter three necked round bottom flask equipped with nitrogen atmosphere facility, mechanical stirrer, thermometer and an addition funnel, sodium methoxide (165 g) and toluene (1000.0 ml) were added under nitrogen environment and cooled to 8°C to 12°C. Methyl acetoacetate (331.55 g) was added dropwise and stirred for 1 hour. 2-bromo-l-(4-methyl sulfonyl phenyl) ethanone (500.0 g) compound (El) in toluene (1500.0 ml) and sodium sulfate
(75.0 g) mixture was stirred for 10 min and filtered at 25° to 35°C. The filtrate as obtained was added dropwise into the previous reaction mixture and stirred at 30°C to 35°C for 30 min. The organic layer was collected and washed with 10% sodium bicarbonate solution. The separated organic layer was collected and washed with water. 2-[2-(4-Methyl sulfanyl-phenyl)-2-oxo-ethyl]-3-oxo-butynic acid methyl ester as obtained in toluene layer is diluted with methanol (2500 ml) and sodium hydroxide solution (89.75 g) in water (2500 ml) was added and heated to 50° to 55°C for 1 hour. The layers were separated and the toluene layer was collected and heated to 45° to 55°C and charcoalized. The reaction mixture was filtered and pivalic acid (57.3 g) and ethanol amine (143.9 g) were added and heated to 105° to 1 15°C for removing water azeotropically. The toluene layer was separated and triethyl amine (271.85 g) was added at 25° to 35°C and the reaction mixture was cooled to 10° to 20°C. Methane sulphonyl chloride (282.5 g) was added dropwise, and stirred for 2 hours and heated to 35° to 45°C. The reaction mixture was filtered and washed with toluene. Toluene was distilled out completely under the vacuum to obtain the residue. The residue was dissolved in toluene (1500 mL) and used for further process.
ExampIe-2:
Preparation of methanesulfonic acid 2-f2-methyl-5-(4-methylsulfanyl-pheny0-pyrrol- 1-viyethyl ester (Al)

In a 250 mL three necked round bottom flask equipped with nitrogen atmosphere facility, mechanical stirrer, thermometer and an addition funnel, 4-(methylthio)benzaldehyde (10 g), methyl vinyl ketone (3.63 g), triethylamine (9.95 g) and 3-methyl-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyI thiazolium iodide (stetter
catalyst) (2.8 g) were heated to 70°C to 80°C and maintained overnight. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and ethanol (100 mL) was added. The reaction mixture was stirred for 30 min and filtered. The product was washed with ethanol and dried to obtain 1 ,4-diketo compound (CI).
1 ,4-diketo compound (CI) obtained above and toluene (50 mL) were heated to 45° to 55°C and charcoalized. The reaction mixture was filtered and pivalic acid (5.7 g) and ethanol amine (14.4 g) were added and heated to 105° to 1 15°C and cooled to 25°C. Triethyl amine (27.2 g) was added at 25° to 35°C and the reaction mixture was cooled to 10° to 20°C. Methane sulphonyl chloride (28.3 g) was added dropwise, and stirred for 2 hours and heated to 35° to 45°C. The reaction mixture was filtered and washed with toluene. Toluene was distilled out completely under the vacuum, methanol (2500 ml) was added and heated to 55° to 65 °C and charcoalized for 30 min. The reaction mixture was filtered and washed with methanol. The reaction mixture was cooled to 25° to 35°C and stirred for 30 min. Reaction mass was further cooled to -5° to 5°C and filtered. The wet-cake was washed with methanol and dried to obtain compound (Al). The compound (Al) was characterized as crystalline solid by x-ray powder diffraction (FIG.2).
Example-3:
Purification of methanesulfonic acid 2-r2-methyl-5-(4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-pyrrol-l-yl]-ethyl ester (Al)
In a 250 mL three necked round bottom flask equipped with nitrogen atmosphere facility, mechanical stirrer, thermometer and an addition funnel, 70 g methanesulfonic acid 2-[2-methyl-5-(4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-pyrrol-l -yl]-ethyl ester (Al) and 420 mL ethyl acetate were added at 25°C. The reaction mixture was stirred for 30 min to obtain clear solution. 3.5 g charcoal was added and stirred for 30 min. The reaction mixture was filtered and washed with ethyl acetate. The filtrate was concentrated and 315 mL methanol was added. The reaction mixture was stirred for 2 hours at 25°C and cooled to 0°C. The product precipitated was filtered and washed with methanol to obtain crystalline
compound (Al). The compound (Al) was characterized as crystalline solid by x-ray powder diffraction (FIG.3).
Example-4:
Preparation of saroglitazar magnesium (T)

In a 5 Liter three necked round bottom flask equipped with nitrogen atmosphere facility, mechanical stirrer, thermometer and an addition funnel, 2-ethoxy-3-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-propionic acid ethyl ester (A) (100.0 g) and toluene (1300.0 ml) were charged and reaction mixture was heated to 45° to 55°C. Potassium carbonate (58.0 g) was added and stirred for 30 min. Toluene solution of methanesulfonic acid 2-[2-methyl-5-(4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-pyrrol- 1 -yl]-ethyl ester (Al) (150.24 g) obtained in example- 1, 18-Crown-6 (5.0 g) and THF (200.0 ml) were added and heated to 75°C to 85°C for 36 hour, The reaction mixture was cooled to 25° to 35°C and water (1000.0 ml) was added and stirred for 15 min. The separated aqueous layer was treated with toluene (200.0 ml) and stirred for 15 min. The organic, layers were combined and washed with caustic solution (600.0 ml). The separated organic layer was washed with water (600.0 ml) and characoalized with HP-120 (5.0 g) charcoal and stirred for 30 min and filtered. The filtrate was added sodium hydroxide 20.14 g solution in water (200.0 ml) and the reaction mixture was stirred for 3 hours. The reaction mixture was diluted with water (1800.0 ml) and stirred for 15 min. The separated aqueous layer was washed with n-butyl acetate. The separated aqueous layer was added magnesium acetate tetrahydrate solution (90.0 g) in water (100.0 ml) and stirred for 1 hour. The aqueous layer was extracted with methylene dichloride (2000 ml). The separated organic layer was washed with sodium chloride solution and charcoalized. The charcoalized solution was filtered and filtrate was distilled to remove toluene completely. The residue was diluted with toluene (1000 ml) and stirred for 30 min. The organic solution was added into n-heptane (1500 mL) and stirred for 3 hours. The product was filtered and washed with n-heptane and dried in vacuum tray dryer at 25°C to 30°C for 3 hours. The product was sieved through 0.5 mm sieve and milled through jet-milled. The product was further dried in vacuum tray drier at 40°C to 50°C for 6 hours followed by drying at 55°C to 65°C for 40 hours to obtain amorphous saroglitazar magnesium (I). The compound is characterized by x-ray power diffraction (FIG.l).
The reaction of methanesulfonic acid 2-[2-methyl-5-(4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-pyrrol-l-yl]-ethyl ester (Al) and 2-ethoxy-3-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-propionic acid ethyl ester (A) may also be performed in similar manner as above in absence of phase transfer catalyst 18-Crown-6.
ExampIe-5:
Preparation of saroglitazar (S)-(-)-phenyl ethylamine salt:

In a 250 mL three necked round bottom flask equipped with nitrogen atmosphere facility, mechanical stirrer, thermometer and an addition funnel, residue-A obtained in example- 1 and ethanol (400 mL) were stirred for 15 min. Sodium hydroxide 20.14 g solution in water (200.0 ml) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred for 3 hours. The reaction mixture was diluted with water (1800.0 ml) and stirred for 15 min. The separated aqueous layer was washed with isopropyl acetate (400 mL). The separated aqueous layer was diluted with isopropyl acetate (500 mL) and acidified with cone. HCI at adjust the pH 2-3. The separated aqueous layer was washed with isopropyl acetate. The combined organic layer was treated with (S)-(-)-phenyl ethylamine (55.94 g) and stirred for 2 hours at 25°C and 30 min at 45°C. The reaction mixture was cooled to 0°C and stirred for 2 hours, filtered and washed with isopropyl acetate. The wet-cake was dried to obtain saroglitazar phenyl ethylamine salt.
ExampIe-6:
Preparation of saroglitazar magnesium from saroglitazar (SH-)-phenyl ethylamine salt:
In a 250 mL three necked round bottom flask equipped with nitrogen atmosphere facility, mechanical stirrer, thermometer and an addition funnel, saroglitazar phenyl ethylamine wet-cake obtained in example-7 and isopropyl acetate (800 mL) were added at 25°C. The reaction mixture was diluted with water (400.0 ml) and acidified with cone. HCI at adjust the pH 2-3. The separated aqueous layer was washed with isopropyl acetate. The combined organic layer was treated with sodium hydroxide solution (20.14 g) in water (200 mL) and stirred for 30 min. The separated aqueous layer was treated with magnesium acetate tetrahydrate (2.29 g) in water (5 mL) solution and stirred for 60 min. The reaction mixture was extracted with methylene dichloride (800 mL). The methylene dichloride was complete removed by distillation under vacuum below 40°C to obtain the residue. The residue was diluted with methylene dichloride (50 ml) and stirred for 30 min. The organic solution was added into n-heptane (1500 mL) and stirred for 3 hours. The product was filtered and washed with n-heptane and dried in vacuum tray dryer at 25°C to 30°C for 3 hours. The product was sieved through 0.5 mm sieve and milled through jet-milled. The product was further dried in vacuum tray drier at 40°C to 50°C for 6 hours followed by drying at 55°C to 65°C for 40 hours to obtain substantially amorphous saroglitazar magnesium (I). The compound is characterized by x-ray power diffraction (FIG.l).

PATENT
WO 2015029066
Dwivedi, Shri Prakash Dhar; Singh, Ramesh Chandra; Patel, Vikas; Desai, Amar Rajendra
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Polymorphic form of pyrrole derivative and intermediate thereof
Pyrrole derivative of present invention is chemically 2-ethoxy-3-(4-(2-(2-methyl-5-(4-(methylthio)phenyl)-lH-pyrrol-l-yl)ethoxy)pKenyl)propanoate, which may be optically active or racemic and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates, polymorphs or intermediates thereof. The INN name for pyrrole derivative is Saroglitazar® which is magnesium salt of pyrrole compound of Formula (I), having below chemical structure.

The present invention relates to Saroglitazar free acid of Formula (IA) or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts, pharmaceutically acceptable solvates, pharmaceutically acceptable esters, stereoisomers, tautomers, analogs and derivs. thereof. The present invention also provides an amorphous form of saroglitazar free acid and processes of prepn. thereof. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compn. comprising an amorphous form saroglitazar magnesium.
Amorphous forms of saroglitazar free acid and its salt form are claimed. Also claims the process for the synthesis the same compound. Useful for treating obesity, hyperlipidemia and hypercholesteremia. Picks up from WO2015011730, claiming the stable composition comprising saroglitazar magnesium or its derivatives. Zydus-Cadila has developed and launched saroglitazar for treating diabetic dyslipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia.
In September 2013, saroglitazar was launched for treating dyslipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia.
As of March 2015, Zydus-Cadila is developing saroglitazar for treating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and type II diabetes (both in phase III clainical trials).
Pyrrole derivative of present invention is chemically 2-ethoxy-3-(4-(2-(2-methyl- 5-(4-(methylthio)phenyl)-lH-pyrrol-l-yl)ethoxy)ph’enyl)propanoate, which may be optically active or racemic and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates, polymorphs or intermediates thereof. The INN name for pyrrole derivative is Saroglitazar® which is magnesium salt of pyrrole compound o f saroglitazar,
the process comprising: 5WO 2015/029066 PCT/IN2014/000551 (a) dissolving saroglitazar magnesium of Formula (I) in one or more organic solvents to obtain a solution, (b) adding the solution in one or more o f anti-solvent at temperature from about -80°C to about 150°C to obtain saroglitazar magnesium o f Formula (I); and (c) obtaining the amorphous saroglitazar magnesium by removal of anti-solvent.
Example-1: Preparation of saroglitazar magnesium (Ί) In a 5 Liter three necked round bottom flask equipped with nitrogen atmosphere facility, mechanical stirrer, thermometer and an addition funnel, 2-ethoxy-3-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)- propionic acid ethyl ester (A) (100.0 g) and cyclohexane (1300.0 ml) were charged and reaction mixture was heated to 45° to 55°C. Potassium carbonate (58.0 g) was added and stirred for 30 min. methanesulfonic acid 2-[2-methyl-5-(4-methyIsulfanyl-phenyl)-pyrroll-yl]-ethyl ester (A l) (150.24 g) and THF (200.0 ml) were added and heated to 75°C to 85°C for 36 hour. The reaction mixture was cooled to 25° to 35°C and water (1000.0 ml) was added and stirred for 15 min. The separated aqueous layer was treated with cyclohexane (200.0 ml) and stirred for 15 min. The organic layers were combined and washed with caustic solution (600.0 ml). The separated organic layer was washed with water (600.0 ml) and characoalized with (5.0 g) charcoal and stirred for 30 min and filtered. The filtrate was distilled to remove cyclohexane and the residue was collected (residue-A). The residue-A as obtained was treated with ethanol (400.0 ml) and stirred for 15 min. Sodium hydroxide 20.14 g solution in water (200.0 ml) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred for 3 hours. The reaction mixture was diluted with water (1800.0 ml) and stirred for 15 min. The separated aqueous layer was washed with n-butyl acetate. The separated aqueous layer was added magnesium acetate tetrahydrate solution (90.0 g) in water (100.0 ml) and stirred for I hour. The aqueous layer was extracted with methylene dichloride (200 ml). The separated organic layer was washed with sodium chloride solution and charcoalized. The charcoalized solution was filtered and filtrate was distilled to remove methylene dichloride completely. The residue was diluted with methylene dichloride (1000 ml) and stirred for 30 min. The organic solution was added into n-heptane (1500 mL) and stirred for 3 hours. The product was filtered and washed with n-heptane and dried in vacuum tray dryer at 25°C to 30°C for 3 hours. The product was sieved through 0.5 mm sieve and milled through jet-milled. The product was further dried in vacuum tray drier at 40°C to 50°C for 6 hours followed by drying at 55°C to 65°C for 40 hours to obtain substantially amorphous saroglitazar magnesium (I). The compound is characterized by x-ray power diffraction (FIG.I).
PATENT
| WO/2015/011730 |
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2015011730
The present invention relates to the stable pharmaceutical composition of a suitable hypolipidemic agent. Preferably, the present invention discloses novel formulations of the compound of formula (I), or pharmaceutically acceptable salts of compounds of formula (I). More particularly the present invention relates to the stable pharmaceutical composition of compounds of formula (I) comprising compounds of formula (I) or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts, wherein the pH of the formulation is maintained above 7. formula (I)
The compounds of formula (I) are new synthetic compounds having hypolipidemic activity. The compounds of formula (I) are used primarily for triglyceride lowering, with concomitant beneficial effect on glucose lowering and cholesterol lowering.
The structural formula of compounds of formula (I) is shown below.

wherein ‘R’ is selected from hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, acyl, alkoxy, alkylthio, thioalkyl, aryloxy, arylthio and M+ represents suitable metal cations such as Na+, K+, Ca+2, Mg+2 and the like. Preferably, R is selected from alkylthio or thioalkyl groups; most preferably R represents -SCH3.The Mg+2 salt is preferred. The compounds of formula (I) are generally insoluble in water, but freely soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, dichloromethane & slightly soluble in methanol and IPA.
REFERENCES
- “Zydus Group launches new diabetic drug”. The Times of India. Jun 6, 2013.
- “Lipaglyn (Saroglitazar) for Treating Hypertriglycerdemia in Type II Diabetes, India”. Drug Development and Technology.
- “The nuances of atherogenic dyslipidemia in diabetes: focus on triglycerides and current management strategies.”. Indian Heart Journal.
- “Observational Study of Effects of Saroglitazar on Glycaemic and Lipid Parameters on Indian Patients with Type 2 Diabetes”. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS.
- “From ‘Make in India’ to ‘Made in India’: the saroglitazar story.”. Indian Heart Journal.
- “Observational study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of saroglitazar in Indian diabetic dyslipidemia patients.”. Indian Heart Journal.
- Munigoti, SrinivasaP; Harinarayan, CV (2014). “Role of Glitazars in atherogenic dyslipidemia and diabetes: Two birds with one stone?”. Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism 18 (3): 283. doi:10.4103/2230-8210.131134. PMC 4056123.PMID 24944919.
Indian Pat. Appl. (2015), IN 2013MU02905
WO 2015033357
WO 2015150565
WO 2015001573
IN 2013MU02828
WO 2015029066
IN 2013MU01910
| Cited Patent | Filing date | Publication date | Applicant | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2003009841A1 * | Jul 25, 2002 | Feb 6, 2003 | Cadila Healthcare Ltd | Novel pyrroles having hypolipidemic hypocholesteremic activities, process for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in medicine |
| WO2012104869A1 | Jan 30, 2012 | Aug 9, 2012 | Cadila Healthcare Limited | Treatment for lipodystrophy |
| INMU19102013A | Title not available | |||
| US6987123 | Aug 10, 2001 | Jan 17, 2006 | Cadila Healthcare Limited | Heterocyclic compounds, their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in medicine |
| US7041837 | Jul 19, 2002 | May 9, 2006 | Cadilla Healthcare Limited | Heterocyclic compounds having hypolipidemic, hypocholesteremic activities process for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in medicine |
| US7323491 | Mar 1, 2004 | Jan 29, 2008 | Cadila Healthcare Limited | Heterocyclic compounds, their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in medicine |
| US8110598 | Feb 7, 2012 | Cadila Healthcare Limited | Heterocyclic compounds, their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in medicine | |
| US8212057 | Jul 25, 2002 | Jul 3, 2012 | Cadila Healthcare Limited | Pyrroles having hypolipidemic hypocholesteremic activities, process for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in medicine |
| US20110275669 | Nov 10, 2011 | Cadilla Healthcare Limited | Novel pyrroles having hypolipidemic hypocholesteremic activities, process for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in medicine |
 |
| Zydus Cadila chairman and MD Pankaj R. Patel (centre) and deputy managing director Sharvil P. Patel (left) in Mumbai on Wednesday. (PTI)JUNE 5, 2013 |
Cadila banks on diabetes drug
Calcutta Telegraph
It generally takes around 10-15 years for a drug to be developed from the time of its discovery In the case of Lipaglyn, the molecule was identified in 2001, and Phase III clinical trials was completed around four years ago. While Zydus has not yet …http://www.telegraphindia.com/1130606/jsp/business/story_16976915.jsp

Mumbai, June 5: Cadila Healthcare will launch a homegrown drug against diabetes by the third quarter of this year.
The Drug Controller General of India has approved its drug — Lipaglyn — to treat “diabetic dyslipidemia”.
Diabetic dyslipidemia is a condition where a person is diabetic and has elevated levels of total cholesterol. Over 80 per cent of diabetic patients are dyslipidemic.
http://www.telegraphindia.com/1130606/jsp/business/story_16976915.jsp
Zydus Cadila said it is looking for partnership to market its new chemical entity (NCE) Lipaglyn, to be used for treating a type of diabetes in developed and developing markets. “Lipaglyn is the first glitazar to be approved in the world and the first NCE discovered and developed indigenously by an Indian pharma company.
The new drug is expected to be launched in Q3 of this fiscal in the country,” Zydus Cadila Chairman and Manging Director Pankaj Patel told reporters.
The company has spent USD 250 million in developing Lipaglyn and aims to spend another USD 150-200 million to launch the drug in overseas markets in next 3-5 years period, Patel said, adding that the company is looking for marketing partnerships.
“We expect this to be a blockbuster drug, which means over USD 1 billion sales a year, when the drug is sold globally, he said. The market for this drug is estimated at Rs 100 crore in the local market over the next three years and having market potential size of over USD 30 billion in the world market, he said.
Zydus Cadila took about eight years to develop the molecule and conducted clinical trials on more than 1,000 patients in India, Patel said, adding that the company is yet to finalise the price, but believes that it will be reasonably priced in the local market.
The company said that the Indian drug regulator Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) has approved Lipaglyn to be used for treating ‘diabetic dyslipidemia’.
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
(2S)-2-Ethoxy-3-[4-(2-{2-methyl-5-[4-(methylsulfanyl)phenyl]-1H-pyrrol-1-yl}ethoxy)phenyl]propanoic acid
|
|
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Lipaglyn |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 495399-09-2 |
| ATC code | None |
| PubChem | CID 60151560 |
| ChemSpider | 32079086 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C25H29NO4S |
| Molar mass | 439.56 g/mol |
by WORLD DRUG TRACKER
DR ANTHONY
do not miss out on updates
see my update at https://newdrugapprovals.org/2015/03/09/saroglitazar-magnesium-new-patent-wo-2015029066-cadila-healthcare-ltd/ 9 may 2015
Lipaglyn (Saroglitazar) won a lot of support at the 75th Anniversary Conference of the American Diabetes Association. Lipaglyn is currently under Phase III clinical development for treatment of Non Alcoholic SteatoHepatitis (NASH), a serious liver disease and an unmet healthcare need, globally. There is currently no drug approved for treating NASH. Lipaglyn is already approved in India for the treatment of diabetic dyslipidemia


Speaking on the development, Mr. Pankaj R. Patel, Chairman and Managing Director, Zydus Cadila said, “These new robust scientific data on the safety and efficacy of Lipaglyn
(Saroglitazar) being presented at the 75th Annual Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) reflect our continued commitment to millions of patients living with Diabetes, Dyslipidemia, Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).”
Zydus Cadila, a leading global healthcare provider, today announced that new scientific and clinical data on Saroglitazar will be presented at the 75th Annual Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) in Boston, Massachusetts, USA from 5thto 9th June, 2015. Several analyses of real-world patient data of Saroglitazar will also be presented. The abstracts are available on theADA website.
Lipaglyn – The world’s first drug for treating Diabetic Dyslipidemia combines lipid and glucose lowering effects in one single molecule.

Pankaj Patel, chairman and MD, Cadila Healthcare Ltd

Zydus is an innovation-led global healthcare provider that discovers, manufactures and markets a broad range of healthcare therapies. The group employs over 19,000 people worldwide including over 1200 scientists engaged in research and is dedicated to creating healthier communities globally.
With a strong research pipeline of NCEs, biologics and vaccines, the group became India’s first pharmaceutical company to launch its own indigenously researched therapy Lipaglyn which is also the world’s first approved therapy for diabetic dyslipidaemia. Exemptia, the world’s first biosimilar of Adalimumab is also a product of Zydus innovation. Zydus also collaborates with partners to support and make therapies affordable and accessible to communities across the world.
As a leading healthcare provider, it aims to become a global research-based pharmaceutical company by 2020.



Pankaj R. Patel (left), Chairman & Managing Director, Zybus Cadila,

Ganesh Nayak, Chief Operating Officer and Executive Director, Zydus Cadila


Zydus Cadila has announced a breakthrough in the anti-diabetic drug Lipaglyn. Lipaglyn – The world’s first drug for treating Diabetic Dyslipidemia combines lipid and glucose lowering effects in one single molecule.
The Zydus Group announced a breakthrough in its research efforts with Lipaglyn (Saroglilazar), a novel drug targeted at bridging an unmet healthcare need for treating Diabetic Dyslipidemia or Hypertriglyeeridemia in Type II diabetes, not controlled by statins alone. The drug has been approved for launch in India by the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI). With a novel action that offers lipid and glucose lowering effects in one molecule, Lipaglyn is the first Glitazar to be approved anywhere in the world.
“Lipaglyn provides patients suffering from diabetic dyslipidemia the option of a once-daily oral therapy that has a beneficial effect on both lipid parameters as well as glycemic control,” said Pankaj R. Fatel, Chairman and Managing Director, Zydus Cadila. “It has always been our dream to take a molecule right from the concept stage up to its launch. Today, we have realized this dream. It is an important breakthrough and I would like to dedicate this to all the Indian research scientists in the Held of drug discovery,” Patel added,
Diabetic Dyslipidemia is a condition where a person is diabetic and has elevated levels of the total cholesterol, the “bad” low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and the triglycerides and a decrease in the “good” high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol concentration in the blood. Optimal LDL cholesterol levels ibr adults with diabetes are less than 100 mg/dh, optimal HDL cholesterol levels are equal to or greater than 40 mg/dL, and desirable triglycerides levels are less than 150 mg/dLT LipaglynrM, a non-thiazoKdinedione, is the first therapy to be approved for this condition,
World over, it is estimated that 30% of all deaths occur due lo cardiovascular diseases (CVD). In India, one out of every five persons is at serious risk of developing CVD, Research has shown that diabetes is one of the major risk factors of CVD. India has a population of nearly 65 million diabetics and 77 million prc-diabctics, 85 – 97% of the diabetes patients suffer from dyslipidemia or lipid abnormalities. Hence, addressing the problem of diabetes and dyslipidemia is crucial in tackling the health risk posed by CVD.
Discovered by the Zydus Research Centre, the dedicated NCE research arm of the Zydus group, LipaglynrM is a best-in-class innovation, designed to have a unique cellular mechanism of action following an extensive structure-activity relationship study initiated in the year 2000, Lipaglyn1M has a predominant affinity to PPAR alpha isoform and moderate affinity to PPAR gamma isoform of PPAR nuclear receptor subfamily. The molecule has shown beneficial effects on lipids and glyeemic control without side effects. This molecule underwent extensive pre-clinical characterisation and the I.ND was submitted in the year 2004,
As a part of the clinical development programme, extensive Phase-I, Phase-II and Phase-Ill clinical trials were conducted to evaluate the phamacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, efficacy and safety of Lipaglyn. The new drug application for Lipaglyn1 was based on a comprehensive clinical development programme spanning eight years.
Results from the first Phase III programme with Pioglitazone as a comparator drug in diabetes patients showed that the 4 mg dose of Lipaglyn led to a reduction of triglycerides and LDL (bad) cholesterol, and an increase in HDL (good) cholesterol and also showed a reduction in Fasting Plasma Glucose and glycosylated haemoglobin (HbAlc) thereby confirming its beneficial effects of both lipid and glyeemic control in diabetic patients,
In the second Phase III study, Lipaglyn was studied in diabetic dyslipidemic patients insufficiently controlled with statin therapy. The results from this study confirmed that Lipaglyn had a pronounced beneficial effect on both the lipid and glyeemic parameters in these subjects.
In both the studies, Lipaglyn was well tolerated and had a better safety profile than the comparators. Importantly Lipaglyn1 M has a non-renal route of elimination, and did not show adverse events like edema, weight gain, myopathies or derangement of liver and/or kidney functions, thus making it sale and efficacious. LipaglynIM is recommended for once daily administration as 4 mg tablets.
Zydus will offer a dedicated LipaglynIM support programme to patients and earegivers, The programme shall provide important support and information regarding access, adherence, education and thereby help patients to start and appropriately manage their disease and therapy over time.

About Lipaglyn
Lipaglyn[TM] (Saroglitazar) was launched in September 2013 in India, for treating Hypertriglyceridemia and Diabetic Dyslipidemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes not controlled by statins. Since then, more than 80,000 patients are availing this drug with a prescriber base over 3500 diabetologists, cardiologists and physicians. Lipaglyn[TM] helps in a reduction of triglycerides and LDL (bad) cholesterol, and an increase in HDL (good) cholesterol and has also shown a reduction in Fasting Plasma Glucose and glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c), thereby confirming its beneficial effects on both lipid and glycemic control in diabetic patients. Lipaglyn[TM] is a prescription medicine, and can be taken only under the advice and guidance of a registered medical practitioner.
About Zydus
Zydus Cadila is an innovative, global pharmaceutical company that discovers, manufactures and markets a broad range of healthcare therapies, including small molecule drugs, biologic therapeutics and vaccines. The group employs over 16,500 people worldwide including over 1200 scientists engaged in R & D and is dedicated to creating healthier communities globally. As a leading healthcare provider, it aims to become a global research based pharmaceutical company by 2020.
References
Zydus to present new scientific data on Lipaglyn in the US
New Delhi, Jun 8 (UNI) Healthcare services provider, Zydus Cadila today said the new scientific and clinical data on Lipaglyn (Saroglitazar) will be presented at the 75th annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) in Boston, Massachusetts, US from 5th to 9th June,2015.
Read more at http://www.uniindia.com/news/business-economy/zydus-to-present-new-scientific-data-on-lipaglyn-in-the-us/84440.html
READ …..https://newdrugapprovals.org/2013/06/07/cadila-banks-on-diabetes-druglipaglynsaroglitazar/
http://lipaglyn.com/downloads/Lipaglyn_Product_Monograph.pdf
http://www.ijpcs.net/sites/default/files/IJPCS_3_1_02_0.pdf
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/prp2.136/pdf
////////////
CCO[C@@H](Cc1ccc(cc1)OCCn2c(ccc2c3ccc(cc3)SC)C)C(=O)O
CCOC(CC1=CC=C(C=C1)OCCN2C(=CC=C2C3=CC=C(C=C3)SC)C)C(=O)O
Filed under: Uncategorized Tagged: CADILA, lipaglyn, Saroglitazar, zydus







