
KEEPING WATCHING THIS POSTS FOR SYNTHESIS UPDATES
December 22, 2015
On December 21, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Uptravi (selexipag) tablets to treat adults with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a chronic, progressive, and debilitating rare lung disease that can lead to death or the need for transplantation.
“Uptravi offers an additional treatment option for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension,” said Ellis Unger, M.D., director of the Office of Drug Evaluation I in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “The FDA supports continued efforts to provide new treatment options for rare diseases.”
PAH is high blood pressure that occurs in the arteries that connect the heart to the lungs. It causes the right side of the heart to work harder than normal, which can lead to limitations on exercise ability and shortness of breath, among other more serious complications.
Uptravi belongs to a class of drugs called oral IP prostacyclin receptor agonists. The drug acts by relaxing muscles in the walls of blood vessels to dilate (open) blood vessels and decrease the elevated pressure in the vessels supplying blood to the lungs.
Uptravi’s safety and efficacy were established in a long-term clinical trial of 1,156 participants with PAH. Uptravi was shown to be effective in reducing hospitalization for PAH and reducing the risks of disease progression compared to placebo. Participants were exposed to Uptravi in this trial for a median duration of 1.4 years.
Common side effects observed in those treated with Uptravi in the trial include headache, diarrhea, jaw pain, nausea, muscle pain (myalgia), vomiting, pain in an extremity, and flushing.
Uptravi was granted orphan drug designation. Orphan drug designation provides incentives such as tax credits, user fee waivers, and eligibility for exclusivity to assist and encourage the development of drugs for rare diseases.
Uptravi is marketed by San Francisco-based Actelion Pharmaceuticals US, Inc.

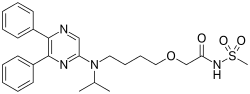
Selexipag, Uptravi
475086-01-2 CAS
(C26H32N4O4S, Mr = 496.6 g/mol)
A prostacyclin receptor (PGI2) agonist used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
NIPPON SHINYAKU….INNOVATOR
Selexipag (brand name Uptravi) is a drug developed by Actelion for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Selexipag and its active metabolite, ACT-333679 (MRE-269) (the free carboxylic acid), are agonists of the prostacyclin receptor, which leads to vasodilation in the pulmonary circulation.[1]
The US FDA granted it Orphan Drug status[2] (for PAH). It was approved by the U.S. FDA on 22 December 2015.[2]
ACT-333679 or MRE-269, the active metabolite of selexipag

PATENT
US2012/101276
http://www.google.st/patents/US20120101276?hl=pt-PT&cl=en
The present invention relates to a crystal of 2-{4-[N-(5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)-N-isopropylamino]butyloxy}-N-(methylsulfonyl)acetamide (hereinafter referred to as “compound A”).
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Compound A has an excellent PGI2 agonistic effect and shows a platelet aggregation inhibitory effect, a vasodilative effect, a bronchodilative effect, a lipid deposition inhibitory effect, a leukocyte activation inhibitory effect, etc. (see, for example, in WO 2002/088084 (“WO ‘084”)).
Specifically, compound A is useful as preventive or therapeutic agents for transient ischemic attack (TIA), diabetic neuropathy, diabetic gangrene, peripheral circulatory disturbance (e.g., chronic arterial occlusion, intermittent claudication, peripheral embolism, vibration syndrome, Raynaud’s disease), connective tissue disease (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, mixed connective tissue disease, vasculitic syndrome), reocclusion/restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA), arteriosclerosis, thrombosis (e.g., acute-phase cerebral thrombosis, pulmonary embolism), hypertension, pulmonary hypertension, ischemic disorder (e.g., cerebral infarction, myocardial infarction), angina (e.g., stable angina, unstable angina), glomerulonephritis, diabetic nephropathy, chronic renal failure, allergy, bronchial asthma, ulcer, pressure ulcer (bedsore), restenosis after coronary intervention such as atherectomy and stent implantation, thrombocytopenia by dialysis, the diseases in which fibrosis of organs or tissues is involved [e.g., Renal diseases (e.g., tuburointerstitial nephritis), respiratory diseases (e.g., interstitial pneumonia (pulmonary fibrosis), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), digestive diseases (e.g., hepatocirrhosis, viral hepatitis, chronic pancreatitis and scirrhous stomachic cancer), cardiovascular diseases (e.g, myocardial fibrosis), bone and articular diseases (e.g, bone marrow fibrosis and rheumatoid arthritis), skin diseases (e.g, cicatrix after operation, scalded cicatrix, keloid, and hypertrophic cicatrix), obstetric diseases (e.g., hysteromyoma), urinary diseases (e.g., prostatic hypertrophy), other diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, sclerosing peritonitis; type I diabetes and organ adhesion after operation)], erectile dysfunction (e.g., diabetic erectile dysfunction, psychogenic erectile dysfunction, psychotic erectile dysfunction, erectile dysfunction associated with chronic renal failure, erectile dysfunction after intrapelvic operation for removing prostata, and vascular erectile dysfunction associated with aging and arteriosclerosis), inflammatory bowel disease (e.g., ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, intestinal tuberculosis, ischemic colitis and intestinal ulcer associated with Behcet disease), gastritis, gastric ulcer, ischemic ophthalmopathy (e.g., retinal artery occlusion, retinal vein occlusion, ischemic optic neuropathy), sudden hearing loss, avascular necrosis of bone, intestinal damage caused by administration of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent (e.g., diclofenac, meloxicam, oxaprozin, nabumetone, indomethacin, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, naproxen, celecoxib) (there is no particular limitation for the intestinal damage so far as it is damage appearing in duodenum, small intestine and large intestine and examples thereof include mucosal damage such as erosion and ulcer generated in duodenum, small intestine and large intestine), and symptoms associated with lumbar spinal canal stenosis (e.g., paralysis, dullness in sensory perception, pain, numbness, lowering in walking ability, etc. associated with cervical spinal canal stenosis, thoracic spinal canal stenosis, lumbar spinal canal stenosis, diffuse spinal canal stenosis or sacral stenosis) etc. (see, for example, in WO ‘084, WO 2009/157396, WO 2009/107736, WO 2009/154246, WO 2009/157397, and WO 2009/157398).
In addition, compound A is useful as an accelerating agent for angiogenic therapy such as gene therapy or autologous bone marrow transplantation, an accelerating agent for angiogenesis in restoration of peripheral artery or angiogenic therapy, etc. (see, for example, in WO ‘084).
Production of Compound A
Compound A can be produced, for example, according to the method described in WO ‘084, and, it can also be produced according to the production method mentioned below.
Step 1:
6-Iodo-2,3-diphenylpyrazine can be produced from 6-chloro-2,3-diphenylpyrazine by reacting it with sodium iodide. The reaction is carried out in the presence of an acid in an organic solvent (e.g., ethyl acetate, acetonitrile, acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, or their mixed solvent). The acid to be used is, for example, acetic acid, sulfuric acid, or their mixed acid. The amount of sodium iodide to be used is generally within a range of from 1 to 10 molar ratio relative to 6-chloro-2,3-diphenylpyrazine, preferably within a range of from 2 to 3 molar ratio. The reaction temperature varies depending on the kinds of the solvent and the acid to be used, but may be generally within a range of from 60° C. to 90° C. The reaction time varies depending on the kinds of the solvent and the acid to be used and on the reaction temperature, but may be generally within a range of from 9 hours to 15 hours.
Step 2:
5,6-Diphenyl-2-[(4-hydroxybutyl(isopropyl)amino]pyrazine can be produced from 6-iodo-2,3-diphenylpyrazine by reacting it with 4-hydroxybutyl(isopropyl)amine. The reaction is carried out in the presence of a base in an organic solvent (e.g., sulfolane, N-methylpyrrolidone, N,N-dimethylimidazolidinone, dimethyl sulfoxide or their mixed solvent). The base to be used is, for example, sodium hydrogencarbonate, potassium hydrogencarbonate, potassium carbonate, sodium carbonate or their mixed base. The amount of 4-hydroxybutyl(isopropyl)amine to be used may be generally within a range of from 1.5 to 5.0 molar ratio relative to 6-iodo-2,3-diphenylpyrazine, preferably within a range of from 2 to 3 molar ratio. The reaction temperature varies depending on the kinds of the solvent and the base to be used, but may be generally within a range of from 170° C. to 200° C. The reaction time varies depending on the kinds of the solvent and the base to be used and on the reaction temperature, but may be generally within a range of from 5 hours to 9 hours.
Step 3:
Compound A can be produced from 5,6-diphenyl-2-[4-hydroxybutyl(isopropyl)amino]pyrazine by reacting it with N-(2-chloroacetyl)methanesulfonamide. The reaction is carried out in the presence of a base in a solvent (N-methylpyrrolidone, 2-methyl-2-propanol or their mixed solvent). The base to be used is, for example, potassium t-butoxide, sodium t-butoxide or their mixed base. The amount of N-(2-chloroacetyl)methanesulfonamide to be used may be generally within a range of from 2 to 4 molar ratio relative to 5,6-diphenyl-2-[4-hydroxybutyl(isopropyl)amino]pyrazine, preferably within a range of from 2 to 3 molar ratio. The reaction temperature varies depending on the kinds of the solvent and the base to be used, but may be generally within a range of from −20° C. to 20° C. The reaction time varies depending on the kinds of the solvent and the base to be used and on the reaction temperature, but may be generally within a range of from 0.5 hours to 2 hours.
The compounds to be used as the starting materials in the above-mentioned production method for compound A are known compounds, or can be produced by known methods.
PATENT
WO 2002088084
and
http://www.google.fm/patents/WO2009157398A1?cl=en
PAPER
Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2007 , vol. 15, 21 p. 6692 – 6704
compd 31
PAPER
Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2007 , vol. 15, 24 p. 7720 – 7725
 2a isthe drug
2a isthe drug
N-Acylsulfonamide and N-acylsulfonylurea derivatives of the carboxylic acid prostacyclin receptor agonist 1 were synthesized and their potential as prodrug forms of the carboxylic acid was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. These compounds were converted to the active compound 1 by hepatic microsomes from rats, dogs, monkeys, and humans, and some of the compounds were shown to yield sustained plasma concentrations of 1 when they were orally administered to monkeys. These types of analogues, including NS-304 (2a), are potentially useful prodrugs of 1.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0968089607007614
PATENT
Example 1 t- butylamine Form I crystal of the salt
Compound A (40 mg) with 0.5mL dimethoxyethane (hereinafter, referred to as. “DME”) was dissolved in, and t- butylamine (1.1 eq) were added, 25 1 ° C. at 8 it was stirred for hours. Thereafter, the reaction solution was added t- butyl methyl ether (1mL), at -20 ° C. 3 and held hours. It was collected by filtration the precipitated crystals produced, under reduced pressure, and dried, I-form crystals of t- butylamine salt ( 3 to afford 9.9mg). B Powder X-ray diffraction spectrum of type I crystal obtained t- butylamine salt using the apparatus shown in Figure 1.
Melting point: 152.5 ℃
elemental analysis (C 3 0 H 4 3 N 5 O 4 S + 0.0 3 H 2 as O)
calculated value (%) C: 6 3 .1 8 H: 7 . 6 1 N: 12 .2 8 measured value (%) C: 6 2. 8 5 H: 7 . 6 4 N: 12.52 1 H-NMR (DMSO-D 6 ): delta 8 .15 (s, 1H), 7 .55 – 7 . 8 0 (M, 2H), 7 .10- 7 . .45 (M, 10H), 4 7 . 0-4 8 5 (M, 1H), 3 . 6 6 (s, 2H), 3 .4 7 (t, 2H), 3 .45 (t, 2H), 2. 7 3 (s, 3 H), 1.50-1. 7 5 (M, 4H), 1.2 3 (s, 9H), 1.22 (D, 6 H)
Example 2 I-form crystal of the potassium salt
Compound A tetrahydrofuran with (40mg) 12mL (hereinafter, referred to as. “THF”) was dissolved in, 0.1M aqueous potassium hydroxide solution (1.1 eq) was added, 40 ℃ It was heated and stirred in for 15 minutes. After that, it was evaporated under reduced pressure, the solvent. The residue it was added ethyl acetate (200μL). While shaking the mixture heated to 50 ° C. 8 was allowed to cool to 25 ℃ over hours. After repeated two more times this step, at -20 ° C. 3 and held hours. The resulting precipitated crystals were collected by filtration under reduced pressure, and dried to obtain Form I crystal of the potassium salt. B Powder X-ray diffraction spectrum of type I crystal of the obtained potassium salt using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1 H-NMR (DMSO-D 6 ): delta 8 .14 (s, 1H), 7 .1 8 – 7 . 3 8 . (M, 10H), 4 7 . 2-4 8 4 (M, 1H) , 3 . 6 5 (s, 2H), 3 .4 7 (t, 2H), 3 .45 (t, 2H), 2. 7 2 (s, 3 H), 1.55-1. 7 0 ( M, 4H), 1.2 3 (D, 6 H)
Example 3 II-form crystals of the potassium salt
Compound A with (40mg) was dissolved in THF and 12mL, 0.1M aqueous potassium hydroxide solution (1.1 eq) was added and heated with stirring for 15 min at 40 ℃. After that, it was evaporated under reduced pressure, the solvent. The residue it was added ethyl acetate (200μL). While shaking the mixture heated to 50 ° C. 8 was allowed to cool to 25 ℃ over hours. This operation was repeated two more times, at -20 ° C. 3 and held hours. It was collected by filtration the precipitated crystals produced, under reduced pressure, after drying, 40 ℃, relative humidity 7 while 5% of thermo-hygrostat 7 left for days to give crystalline Form II of the potassium salt. B Powder X-ray diffraction spectrum of crystalline Form II of the resulting potassium salt using the apparatus Fig 3 is shown in.
Example 4 III type crystal of the potassium salt
Compound A , in addition to (100mg) acetonitrile (1mL), and stirred with heating, Compound A was dissolved, followed by cooling to 20 ℃. To a solution 3 .5M potassium hydroxide / ethanol solution (1.1 eq) was added and stirred for 200 minutes at 20 ℃. While stirring the mixture 7 after a heated stirring for 1 hour to 0 ° C., and then cooled to 10 ℃ over 10 hours. Further heated while the mixture 6 is heated to 0 ℃, t- butyl methyl ether (0. 3 after adding mL), cooled to 20 ℃ over 10 hours. It was collected by filtration the precipitated crystals produced, under reduced pressure, and dried, III type crystal of the potassium salt ( 7 to afford 5mg). The powder X-ray diffraction spectrum of the type III crystal of the obtained potassium salt using R unit is shown in FIG. Furthermore, in differential scanning calorimetry, of about 7 endothermic peak was observed at around 4 ° C..
Elemental analysis (C 2 6 H 3 1 N 4 O 4 . SK + 0 7 8 H 2 as O)
calculated value (%) C: 5 6 .91 H: 5.9 8 N: 10.21
measured value (%) C: 5 6 . 6 1 H: 5.55 N:. 10 3 6
EXAMPLE 5 IV-type crystal of the potassium salt
Compound A , in addition to (50mg) and ethyl acetate (1mL), and stirred with heating, Compound A was dissolved, followed by cooling to 20 ℃. To a solution 3 .5M potassium hydroxide / ethanol solution (2.2 eq) was added and 2 at 20 ° C. 3 and stirred for hours. It was collected by filtration the precipitated crystals produced, under reduced pressure, and dried to obtain Form IV crystal of the potassium salt (41mg). The powder X-ray diffraction spectrum of crystalline Form IV of the resulting potassium salt using R unit is shown in FIG. Furthermore, in differential scanning calorimetry, an endothermic peak was observed at around approximately 91 ℃.
Selexipag (C26H32N4O4S, Mr = 496.6 g/mol) ist ein Diphenylpyrazin-Derivat. Es wird in der Leber zum aktiven Metaboliten ACT-333679 (MRE-269) biotransformiert. Selexipag unterscheidet sich strukturell von Prostazyklin und anderen Prostazylin-Rezeptor-Agonisten.

References
- 1 Sitbon, O.; Morrell, N. (2012). “Pathways in pulmonary arterial hypertension: The future is here”. European Respiratory Review 21 (126): 321–327. doi:10.1183/09059180.00004812. PMID 23204120.
- 2 New Drug Approved for Rare Lung Disorder. PPN. 23 Dec 2015 Has link to GRIPHON study results
- Kuwano et al. NS-304, an orally available and long-acting prostacyclin receptor agonist prodrug. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007;322:1181-1188.
- Kuwano et al. A long-acting and highly selective prostacyclin receptor agonist prodrug, NS-304, ameliorates rat pulmonary hypertension with unique relaxant responses of its active form MRE-269 on rat pulmonary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2008;326:691-699.
- Simonneau G, Lang I, Torbicki A, Hoeper MM, Delcroix M, Karlocai K, Galie N. Selexipag, an oral, selective IP receptor agonist for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension Eur Respir J 2012; 40: 874-880
- Mubarak KK. A review of prostaglandin analogs in the management of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respir Med 2010;104:9-21.
- Sitbon, O.; Morrell, N. (2012). “Pathways in pulmonary arterial hypertension: The future is here”. European Respiratory Review 21 (126): 321–327. doi:10.1183/09059180.00004812. PMID 23204120.
| Patent | Submitted | Granted |
|---|---|---|
| Methods of identifying critically ill patients at increased risk of development of organ failure and compounds for the treatment hereof [US8877710] | 2009-12-30 | 2014-11-04 |
| Form-I crystal of 2-{4-[N-(5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)-N-isopropylamino]butyloxy}-N-(methylsulfonyl)acetamide and method for producing the same [US8791122] | 2010-06-25 | 2014-07-29 |
| COMPOUNDS CAPABLE OF MODULATING/PRESERVING ENDOTHELIAL INTEGRITY FOR USE IN PREVENTION OR TREATMENT OF ACUTE TRAUMATIC COAGULOPATHY AND RESUSCITATED CARDIAC ARREST [US2015057325] | 2013-03-26 | 2015-02-26 |
| INHIBITION OF NEOVASCULARIZATION BY SIMULTANEOUS INHIBITION OF PROSTANOID IP AND EP4 RECEPTORS [US2014275200] | 2014-03-05 | 2014-09-18 |
| INHIBITION OF NEOVASCULARIZATION BY INHIBITION OF PROSTANOID IP RECEPTORS [US2014275238] | 2014-03-05 | 2014-09-18 |
| Fibrosis inhibitor [US8889693] | 2014-04-10 | 20 |
| Patent | Submitted | Granted |
|---|---|---|
| Heterocyclic compound derivatives and medicines [US7205302] | 2004-05-27 | 2007-04-17 |
| METHODS OF IDENTIFYING CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS AT INCREASED RISK OF DEVELOPMENT OF ORGAN FAILURE AND COMPOUNDS FOR THE TREATMENT HEREOF [US2014322207] | 2014-07-11 | 2014-10-30 |
| THERAPEUTIC COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING MACITENTAN [US2014329824] | 2014-07-18 | 2014-11-06 |
| Sustained Release Composition of Prostacyclin [US2014303245] | 2012-08-10 | 2014-10-09 |
| COMPOUNDS CAPABLE OF MODULATING/PRESERVING ENDOTHELIAL INTEGRITY FOR USE IN PREVENTION OR TREATMENT OF ACUTE TRAUMATIC COAGULOPATHY AND RESUSCITATED CARDIAC ARREST [US2013261177] | 2011-09-30 | 2013-10-03 |
| METHODS OF TREATMENT OF PATIENTS AT INCREASED RISK OF DEVELOPMENT OF ISCHEMIC EVENTS AND COMPOUNDS HEREOF [US2013040898] | 2011-04-29 | 2013-02-14 |
| Substituted Diphenylpyrazine Derivatives [US2013005742] | 2010-08-06 | 2013-01-03 |
| USE OF FORM-I CRYSTAL OF 2–N-(METHYLSULFONYL)ACETAMIDE [US2014148469] | 2014-01-22 | 2014-05-29 |
| CRYSTALS OF 2- {4- [N- (5,6-DIPHENYLPYRAZIN-2-YL) -N-ISOPROPYLAMINO]BUTYLOXY}-N- (METHYLSULFONYL) ACETAMIDE [US2014155414] | 2014-01-22 | 2014-06-05 |
| PROSTACYCLIN AND ANALOGS THEREOF ADMINISTERED DURING SURGERY FOR PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF CAPILLARY LEAKAGE [US2014044797] | 2012-03-30 | 2014-02-13 |
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-{4-[(5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)(propan-2-yl)amino]butoxy}-N-(methanesulfonyl)acetamide
|
|
| Other names
ACT-293987, NS-304
|
|
| Identifiers | |
475086-01-2  |
|
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL238804  |
| ChemSpider | 8089417  |
| 7552 | |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image |
| KEGG | D09994  |
| PubChem | 9913767 |
| UNII | P7T269PR6S  |
| Properties | |
| C26H32N4O4S | |
| Molar mass | 496.6 g·mol−1 |
SEE……….http://apisynthesisint.blogspot.in/2015/12/fda-approves-new-orphan-drug-uptravi.html
//////////
CC(C)N(CCCCOCC(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C)C1=CN=C(C(=N1)C2=CC=CC=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3
Filed under: 0rphan drug status, FDA 2015 Tagged: FDA 2015, NS-304, Orphan Drug, Selexipag, Uptravi







