

Berdazimer
CAS NA SALT, 1846565-00-1
FDA APPROVE 1 /5/2024, To treat molluscum contagiosum
Drug Trials Snapshot
- NVN-1000 free acid
- NVN1000 free acid
- Silsesquioxanes, 3-(2-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-nitrosohydrazinyl)propyl 3-(methylamino)propyl, polymers with silicic acid (h4sio4) tetra-et ester, hydroxy-terminated
Berdazimer sodium, sold under the brand name Zelsuvmi, is a medication used for the treatment for molluscum contagiosum.[1] Berdazimer sodium is a nitric oxide releasing agent.[1] It is a polymer formed from sodium 1-hydroxy-3-methyl-3-(3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl)-1-triazene-2-oxide and tetraethyl silicate.[2]
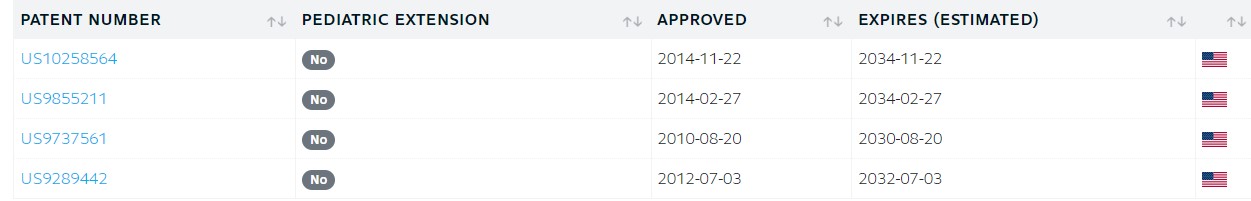
Berdazimer sodium was approved for medical use in the United States in January 2024.[3][4][5]
Medical uses
Berdazimer sodium is indicated for the topical treatment of molluscum contagiosum.[1]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Berdazimer sodium is a nitric oxide releasing agent.[1] The mechanism of action for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum is unknown.[1]
Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of berdazimer sodium are unknown.[1]
Society and culture
Legal status
Berdazimer sodium was approved for medical use in the United States in January 2024.[4]
Names
Berdazimer sodium is the international nonproprietary name.[6]
Berdazimer is a polymeric substance consisting of a polysiloxane backbone (Si-O-Si bonds) with covalently bound N-diazeniumdiolate nitric oxide (NO) donors. It releases NO through exposure to proton donors like water, which will degrade the N-diazeniumdiolate entity.2 Berdazimer was previously investigated as a potential treatment for molluscum contagiosum, a viral cutaneous infection mainly affecting children, sexually active adults, and immunocompromised patients. It is one of the 5 most prevalent skin diseases in the world and the third-most common viral skin infection in children.3 Previously, the first line treatment for molluscum contagiosum was surgical excision, although it poses challenges such as repeated doctor visits, post-surgical scarring and skin discoloration, and fear and anxiety in the pediatric population.3
On Jan 05, 2024, the FDA approved berdazimer under the brand name ZELSUVMI for the treatment of adult and pediatric molluscum contagiosum, and it is the first drug to be approved for this condition. This decision is based on positive results demonstrated in 2 Phase 3 trials, B-SIMPLE 4 and B-SIMPLE 2, where reduced lesion counts were observed with once-a-day uses of berdazimer.5



![]() References
References
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e f g h i “Zelsuvmi (berdazimer) topical gel” (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 January 2024. Retrieved 9 January 2024.
- ^ “GSRS”. gsrs.ncats.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 8 January 2024. Retrieved 8 January 2024.
- ^ “Drug Approval Package: Zelsuvmi”. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 2 February 2024. Archived from the original on 11 March 2024. Retrieved 11 March 2024.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Novel Drug Approvals for 2024”. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 29 April 2024. Archived from the original on 30 April 2024. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ^ “U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approves Zelsuvmi as a First-in-Class Medication for the Treatment of Molluscum Contagiosum”. Ligand Pharmaceuticals. 5 January 2024. Archived from the original on 8 January 2024. Retrieved 8 January 2024 – via Business Wire.
- ^ World Health Organization (2018). “International nonproprietary names for pharmaceutical substances (INN): recommended INN: list 79”. WHO Drug Information. 32 (1). hdl:10665/330941.
Further reading
- Pera Calvi I, R Marques I, Cruz SA, Mesquita YL, Padrao EM, Souza RM, et al. (2023). “Safety and efficacy of topical nitric oxide-releasing berdazimer gel for molluscum contagiosum clearance: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials”. Pediatric Dermatology. 40 (6): 1060–1063. doi:10.1111/pde.15419. PMID 37721050. S2CID 262045499.
- Han H, Smythe C, Yousefian F, Berman B (February 2023). “Molluscum Contagiosum Virus Evasion of Immune Surveillance: A Review”. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology. 22 (2): 182–189. doi:10.36849/JDD.7230. PMID 36745361. S2CID 256613906.
- Lacarrubba F, Micali G, Trecarichi AC, Quattrocchi E, Monfrecola G, Verzì AE (December 2022). “New Developing Treatments for Molluscum Contagiosum”. Dermatology and Therapy. 12 (12): 2669–2678. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00826-7. PMC 9674806. PMID 36239905.
- Ward BM, Riccio DA, Cartwright M, Maeda-Chubachi T (November 2023). “The Antiviral Effect of Berdazimer Sodium on Molluscum Contagiosum Virus Using a Novel In Vitro Methodology”. Viruses. 15 (12): 2360. doi:10.3390/v15122360. PMC 10747301. PMID 38140601.
External links
- “Berdazimer Sodium (Code C174810)”. NCI Thesaurus.
- Clinical trial number NCT04535531 for “A Phase 3 Molluscum Contagiosum Efficacy and Safety Study (B-SIMPLE4)” at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT03927703 for “A Phase 3 Efficacy & Safety of SB206 & Vehicle Gel for the Treatment of MC (B-SIMPLE2)” at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT03927716 for “A Phase 3 Randomized Parallel Group Study Comparing the Efficacy & Safety of SB206 & Vehicle Gel in the Treatment of MC (B-SIMPLE1)” at ClinicalTrials.gov
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Zelsuvmi |
| Other names | SB206 |
| License data | US DailyMed: Berdazimer sodium |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code | None |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | US: ℞-only[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 1846565-00-1 |
| DrugBank | DBSALT003491DB18712 |
| UNII | ORT9SID4QYB23P7SM943 |
| KEGG | D12758 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL4298064 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | Indeterminate[1] |
| Molar mass | Indeterminate[1] |
/////Berdazimer, Zelsuvmi, FDA 2024, APPROVALS 2024, NVN-1000 free acid, NVN1000 free acid
 References
References

















