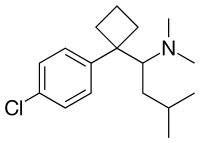
SIBUTRAMINE
- Molecular FormulaC17H26ClN
- Average mass279.848 Da
1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-a-(2-methylpropyl)cyclobutane methanamine
1-[1-(4-Chlorophenyl)cyclobutyl]-N,N,3-trimethyl-1-butanamine
106650-56-0[RN]
106650-56-0 (Sibutramine );
125494-59-9 (Sibutramine HCl Monohydrate);
84485-00-7 (Sibutramine HCl);
6124
UNII:WV5EC51866, WV5EC51866
сибутрамин[Russian]
سيبوترامين[Arabic]
西布曲明[Chinese]
Drug Name:Sibutramine Hydrochloride Hydrate
Research Code:BTS-54524
Trade Name:Meridia®
MOA:Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Indication:Obesity
Status:Withdrawn
Company:Abbott (Originator)
Sibutramine hydrochloride monohydrate, KES-524, BTS-54524, Meridia, Reductil
Sibutramine, formerly sold under the brand name Meridia among others, is an appetite suppressant which has been discontinued in many countries. Until 2010, it was widely marketed and prescribed as an adjunct in the treatment of obesity along with diet and exercise. It has been associated with increased cardiovascular events and strokes and has been withdrawn from the market in several countries and regions including Australia,[1] Canada,[2] China,[3] the European Union,[4] Hong Kong,[5] India,[6] Mexico, New Zealand,[7] the Philippines,[8] Thailand,[9] the United Kingdom,[10] and the United States.[11] However, the drug remains available in some countries.[12]
Sibutramine was originally developed in 1988 by Boots in Nottingham, UK,[13] and marketed by Knoll Pharmaceuticals after BASF/Knoll AG purchased the Boots Research Division in 1995, and was most recently manufactured and marketed by Abbott Laboratories before its withdrawal from most markets. It has been sold under a variety of brand names including Reductil, Meridia, Siredia, and Sibutrex. It is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance in the United States.
Sibutramine hydrochloride hydrate was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on Nov 16, 1997. It was developed and marketed as Meridia® by Abbott in the US.
Sibutramine hydrochloride hydrate is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, it produces its therapeutic effects by norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine reuptake inhibition. Meridia® is indicated for the management of obesity, including weight loss and maintenance of weight loss, and should be used in conjunction with a reduced calorie diet.
Meridia® is available as capsule for oral use, containing 5, 10 or 15 mg of Sibutramine hydrochloride hydrate. The recommended dose is initiated at 10 mg once daily with or without food and may increase to 15 mg once daily.
Sibutramine has been withdrawn from the market in several countries and regions since 2010, owning to its side effect that associated with increased cardiovascular events and strokes.Route 1
Reference:1. US4746680A / US4806570A.
2. US4929629A.
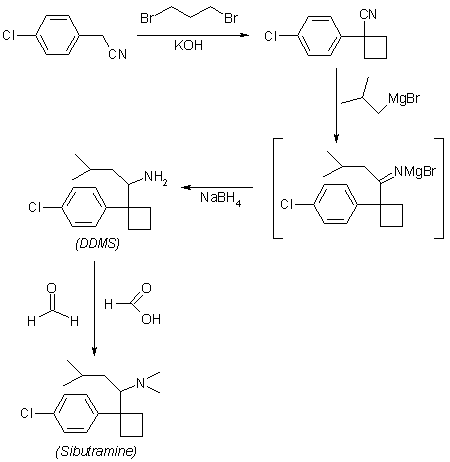
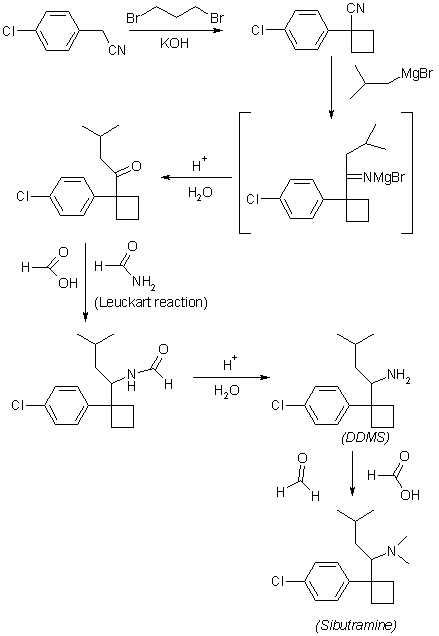
SYN

SYN

SYN
PAT
https://patents.google.com/patent/KR20060019351A/en
Sibutramine hydrochloride (Sibutramine HCl: C 17 H 26 CIN HCl) is a chemical name {1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutyl} -dimethylamine hydrochloride, and has the structure of Formula 1 .

Sibutramine was originally developed as a drug for the treatment of depression and was found to give weight to patients taking this drug. It was developed as an anti-obesity drug. Let your appetite decrease.
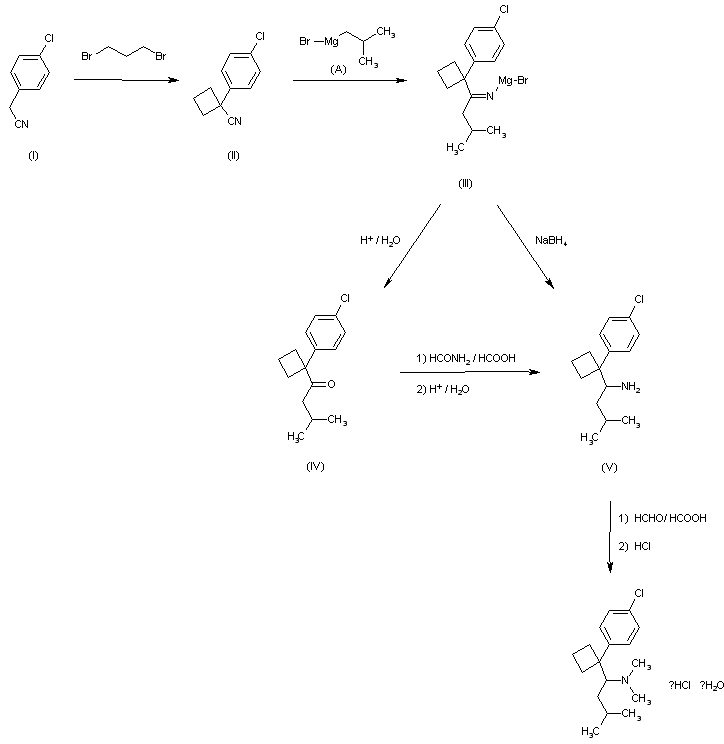
Korean Patent Publication No. 1990-274 (corresponding patent DE3212682 (Boots), filed Oct. 21, 1982; priority GB 1981.4.6.) For the preparation of 1- (1-arylcyclobutyl) alkylamine derivative comprising sibutramine It is described. The method for synthesizing sibutramine described in this document proceeds in a total of five steps as follows.
Step A

1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide is obtained from 4-Chlorobenzyl cyanide. Examples of the actual synthesis method described in this document are as follows.
After dissolving 25 g of 4-chlorobenzyl cyanide and 15 ml of 1,3-dibromopropane in 150 ml of DMSO, the solution was dissolved in nitrogen at room temperature (20-35 ° C.) and 7.5 g of NaH dispersed in mineral oil. And 200 ml of DMSO was added dropwise. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, 8 ml of IPA was added dropwise, and 110 ml of water was added dropwise. The mixture is filtered through CELITE  and the solid residue is washed with ether. The ether layer is separated, washed with water, dried, evaporated and vacuum distilled at high temperature to separate the desired 1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide. The total reaction time of this step is 5 hours and the yield from the starting material is 78%.
and the solid residue is washed with ether. The ether layer is separated, washed with water, dried, evaporated and vacuum distilled at high temperature to separate the desired 1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide. The total reaction time of this step is 5 hours and the yield from the starting material is 78%.
Step B

1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyanobutyl] -3-methyl-butan-1-one is obtained from 1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide. Specific synthesis examples are as follows. 35.2 g of 1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide are dissolved in 100 ml of ether and this solution is added to the product prepared by the reaction of 32 g of propylbromide and 6.36 g of magnesium. The ether is replaced with toluene and the mixture is heated under reflux for 1 hour. After adding water, concentrated hydrochloric acid is added, and the mixture is heated under reflux for 1 hour. The mixture obtained in the same manner as in the previous step was treated with ether, water, dried and evaporated and then vacuum distilled to give the desired 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyanobutyl] -3-methyl-butan-1-one. To separate. The reaction time of this step is a total of 22 hours, the yield is 81%. The target product is bp 100-120 ° C / 0.2 mm / Hg.
Step C

N- {1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutyl from 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyanobutyl] -3-methyl-butan-1-one } Formamide is obtained. Specific synthesis examples are as follows. To 23.5 ml of formamide, 37 g (0.14 mol) of 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyanobutyl] -3-methyl-butan-1-one and 9 ml of HCOOH were added dropwise at 160-170 ° C. The temperature is maintained at 175 ° C. to 180 ° C. for 24 hours. The mixture is extracted with ether and concentrated to afford an oil, which crystallizes the desired N- {1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutyl} formamide from petroleum ether. The reaction time of this step is a total of 24 hours, the yield is 39%. The target is mp 110-112 ° C.
Step D

1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutylamine hydrochloride from N- {1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutyl} formamide Get Specific synthesis examples are as follows. 4 g of N- {1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutyl} formamide, 25 ml of 2-methoxyethyl ether, 10 ml of water and 22 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid were refluxed for 18 hours. Stir under. Dilute with water, wash with ether, and add 35 ml of 5M aqueous NaOH solution. After completion of the process by treatment with ether, water and brine, treated with magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The concentrated crude product is saturated with hydrochloric acid dissolved in 20 ml of ether. The resulting solid is filtered, concentrated and crystallized with petroleum ether to give the desired product 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutylamine hydrochloride. The reaction time of this step is a total of 20 hours, the yield is 96% oil, 46% hydrochloride. The target product is mp 163-165 ° C.
Step E

The final target from 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutylamine hydrochloride {1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutyl} -dimethyl Amine hydrochloride, ie sibutramine hydrochloride, is obtained. Specific synthesis examples are as follows. 3.3 g of 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutylamine hydrochloride, 2.99 g of HCOOH and 1 ml of water are mixed while cooling. 3.93 ml of 37% aqueous formaldehyde is added and heated at 85-95 ° C. for 18 hours. Excess hydrochloric acid is added and the solution is evaporated to dryness. 5N NaOH solution is added, extracted with ether and concentrated to give a pale yellow oil. This oil is dissolved in a mixture of 4 mL IPA, 20 mL ether and 2 mL hydrochloric acid is added dropwise. Concentrate, repeatedly dissolve in ethanol and concentrate again. Polishing with petroleum ether gives a yellow solid and recrystallizes with acetone to give the final target sibutramine hydrochloride. The reaction time of this step is a total of 18 hours, the yield is 80%. The target product is mp 195-197 ° C. The yield in 5 steps (A to E) is 18.9%.
As described above, the conventional sibutramine synthesis method has a total of five steps, which is complicated and takes a long time, and requires high temperature vacuum distillation (step A). Since the reaction proceeds at the high temperature of the raw material there was a problem that the yield is reduced. In fact, the synthesis was performed by applying the conventional sibutramine synthesis method, the total yield was very low as 18.9%.
First step
4-Chlorobenzyl cyanide is reacted with 1,3-dibromopropane to give 1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide.

In a flask at room temperature (20-35 ° C.), 14.1 g (352 mmol) of NaH dispersed in mineral oil (200%) and 200 ml of DMSO were added. 25 g (160 mmol) of 4-chlorobenzyl cyanide and 1,3- A solution of 36 g (176 mmol) of dibromopropane dissolved in 200 ml of DMSO was added dropwise. The mixture is stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, 10 ml of IPA is added dropwise and 200 ml of water is added dropwise. The mixture is filtered through a CELITE  filter and the solid residue is washed with ether. The ether layer is separated, washed with water, filtered, concentrated and dried to give 34.72 g of crude product of 1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide. The yield of crude product is 109.8%.
filter and the solid residue is washed with ether. The ether layer is separated, washed with water, filtered, concentrated and dried to give 34.72 g of crude product of 1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide. The yield of crude product is 109.8%.
2nd step
1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide isobutyl magnesium bromide is reacted to obtain 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutylamine.

10 g (52 mmol) of 1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide was dissolved in 25 ml of toluene at room temperature, followed by addition of a 2.0 M solution of isobutyl magnesium bromide dissolved in 40 ml of diethyl ether. The mixture is heated at reflux at a temperature of at least 105 ° C. for 2 hours. After completion of the reaction at 0 ° C. with methanol, 2.4 g of NaBH 4 was added to the mixture at 0-25 ° C. and stirred for 1 hour or more. Concentrate, treat with ether, water, concentrate again, and vacuum dry. The yield of crude product is 91.6%.
3rd step
The amine group of 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutylamine was dimethylated to obtain {1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl]-which is the final object of the present invention. 3-methylbutyl} -dimethylamine hydrochloride, ie sibutramine hydrochloride, is obtained.

5.02 g of 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutylamine and 10 ml of HCOOH are mixed with cooling. 6 ml of 37% aqueous formaldehyde is added and heated at 85-95 ° C. for 18 hours. Excess 2M HCl is added and the solution is evaporated to dryness. 5N NaOH solution is added, extracted with ether and concentrated to give a pale yellow oil. After dissolving in a small amount of ether, ether saturated with HCl gas is slowly added dropwise at 0 ° C. The solid obtained was filtered and dried in vacuo to give 5.12 g of sibutramine hydrochloride as the final target. Yield of the product is 92%, mp 193.5-194.8 ° C. The total yield of the first to third stages is 52.7%. The H 1 NMR results of the final product are as follows: H 1 NMR (CDCl 3 ) 1.058 (6H, dd), 1.400 (2H, m), 1.508 (2H, m), 2.193 (3H, d), 2.316 (2H , m), 2.784 (2H, m), 2.910 (3H, d), 2.967 (1H, m), 3.568 (1H, m), 7.386 (2H, d), 7.638 (2H, d), 10.771 (1H, s)
The present invention is to shorten the process that was conventionally carried out in five steps to three steps to greatly shorten the process as well as to eliminate the difficult and time-consuming high-temperature vacuum distillation process to enable mass production In addition, it is possible to greatly reduce production time and production costs by improving the process step by step, and to reduce the production cost by showing a yield improvement effect nearly three times that of the conventional synthesis method in terms of overall yield.
Claims (3)
Hide Dependent
- In the method for synthesizing {1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutyl} -dimethylamine from 4-chlorobenzyl cyanide,(a) reacting 4-chlorobenzyl cyanide with 1,3-dibromopropane to obtain 1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide;(b) To isobutyl magnesium bromide dissolved in diethyl ether is added to 1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide dissolved in toluene, and the mixture is refluxed at a temperature of 105 ° C. or higher at 1-3 ° C. Heating and cooling for a period of time, followed by addition of NaBH 4 at 0-25 ° C., followed by stirring for at least 1 hour to obtain 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutylamine;(c) Dimethylating the amine group of 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutylamine to yield {1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methyl Improved synthesis method of sibutramine consisting of a three-step reaction comprising the step of obtaining butyl} -dimethylamine.
- The method according to claim 1,In step (a), the solution of 4-chlorobenzyl cyanide and 1,3-dibromopropane dissolved in DMSO is added dropwise to the mixture of NaH and DMSO dispersed in mineral oil, followed by filtration. , Washing, concentrating and drying to obtain a crude product of 1- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-cyclobutyl cyanide, and proceeding to the next step (b) as it is without distillation at high temperature. Improved Synthesis of Sibutramine.
- The method according to claim 1,In step (c), 1- [1- (4-chlorophenyl) -cyclobutyl] -3-methylbutylamine is mixed with formaldehyde in a free base state, and 37% aqueous formaldehyde is added thereto, and 85 An improved method for synthesizing sibutramine, characterized in that sibutramine hydrochloride is obtained by heating at -95 ° C for 15-22 hours followed by addition of hydrochloric acid.
SYN
DE 3212682; GB 2098602; US 4806570
4-Chlorobenzyl cyanide (I) is cycloalkylated with 1,3-dibromopropane to yield 1-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclobutyl cyanide (II). The cyclobutyl cyanide (II) is treated with 2-methylpropyl magnesium bromide te give the imine salt (III), which may be either hydrolyzed to the ketone (IV), which is then formylaminated with formamide and formic acid and subsequently hydrolyzed, or reduced with sodium borohydride in ethanol to give 1-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclobutyl]-3-methylbutylamine (V). Eschweiler-Clarke methylation and hydrochloride formation yield N-[1-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclo butyl]-3-methylbutyl]-N,N-dimethylamine hydrochloride monohydrate
//////////

AS ON DEC2021 3,491,869 VIEWS ON BLOG WORLDREACH AVAILABLEFOR YOUR ADVERTISEMENT

join me on Linkedin
Anthony Melvin Crasto Ph.D – India | LinkedIn
join me on Researchgate
RESEARCHGATE

join me on Facebook
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | Facebook
join me on twitter
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | twitter
+919321316780 call whatsaapp
EMAIL. amcrasto@amcrasto
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Medical uses
Sibutramine has been used to produce appetite suppression for the purpose of attaining weight loss in the treatment of patients with obesity.
Contraindications
Sibutramine is contraindicated in patients with:
- Psychiatric conditions as bulimia nervosa, anorexia nervosa, serious depression or pre-existing mania
- Patients with a history of or a predisposition to drug or alcohol abuse
- Hypersensitivity to the drug or any of the inactive ingredients
- Patients below 18 and above 65 years of age[14]
- Concomitant treatment with a MAO inhibitor, antidepressant or other centrally active drugs, particularly other anoretics
- History of peripheral arterial disease
- Hypertension that is not sufficiently controlled (e.g., >145/90 mmHg), caution in controlled hypertension
- Existing pulmonary hypertension
- Existing damage on heart valves, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, serious arrhythmias, previous myocardial infarction
- A history of coronary artery disease (e.g., angina, history of myocardial infarction), congestive heart failure, tachycardia, peripheral arterial occlusive disease, arrhythmia or cerebrovascular disease (stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA))[14]
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid gland)
- Closed angle glaucoma
- Seizure disorders
- Enlargement of the prostate gland with urinary retention (relative contraindication)
- Pheochromocytoma
- Pregnant and lactating women (relative contraindication)
Side effects
A higher number of cardiovascular events has been observed in people taking sibutramine versus control (11.4% vs. 10.0%).[15] In 2010 the FDA noted the concerns that sibutramine increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes in patients with a history of cardiovascular disease.[15]
Frequently encountered side effects are: dry mouth, paradoxically increased appetite, nausea, strange taste in the mouth, upset stomach, constipation, trouble sleeping, dizziness, drowsiness, menstrual cramps/pain, headache, flushing, or joint/muscle pain.
In a 2016 Cochrane review sibutramine was found to substantially increase blood pressure and heart rate in some patients, in the updated review in 2021 sibutramine was not included since the drug had been withdrawn from the market.[16] When used, regular blood pressure monitoring needed to be performed.
The following side effects are infrequent but serious and require immediate medical attention: cardiac arrhythmias, paresthesia, mental/mood changes (e.g., excitement, restlessness, confusion, depression, rare thoughts of suicide).
Symptoms that require urgent medical attention are seizures, problems urinating, abnormal bruising or bleeding, melena, hematemesis, jaundice, fever and rigors, chest pain, hemiplegia, abnormal vision, dyspnea and edema.
Currently, no case of pulmonary hypertension has been noted. (Fenfluramine, of the 1990s “Fen-Phen” combo, forced excess release of neurotransmitters—a different action. Phentermine was uninvolved in the rare—but clinically significant—heart issues of fenfluramine.)
Interactions
Sibutramine has a number of clinically significant interactions. The concomitant use of sibutramine and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs, such as selegiline) is not indicated, as it may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, a somewhat rare but serious adverse drug reaction.[17] Sibutramine should not be taken within two weeks of stopping or starting an MAOI. Taking both sibutramine and certain medications used in the treatment of migraines—such as ergolines and triptans—as well as opioids, may also increase the risk for serotonin syndrome, as may the use of more than one serotonin reuptake inhibitor at the same time.[17]
The concomitant use of sibutramine and drugs which inhibit CYP3A4, such as ketoconazole and erythromycin, may increase plasma levels of sibutramine.[18] Sibutramine does not affect the efficacy of hormonal contraception.[17]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
| Compound | SERT | NET | DAT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sibutramine | 298–2,800 | 350–5,451 | 943–1,200 |
| Desmethylsibutramine | 15 | 20 | 49 |
| (R)-Desmethylsibutramine | 44 | 4 | 12 |
| (S)-Desmethylsibutramine | 9,200 | 870 | 180 |
| Didesmethylsibutramine | 20 | 15 | 45 |
| (R)-Didesmethylsibutramine | 140 | 13 | 8.9 |
| (S)-Didesmethylsibutramine | 4,300 | 62 | 12 |
| Values are Ki (nM). |
Sibutramine is a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) that, in humans, reduces the reuptake of norepinephrine (by ~73%), serotonin (by ~54%), and dopamine (by ~16%),[21] thereby increasing the levels of these substances in synaptic clefts and helping enhance satiety; the serotonergic action, in particular, is thought to influence appetite. Older anorectic agents such as amphetamine and fenfluramine force the release of these neurotransmitters rather than affecting their reuptake.[22]
Despite having a mechanism of action similar to tricyclic antidepressants, sibutramine has failed to demonstrate antidepressant properties in animal studies. It was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in November 1997[23] for the treatment of obesity.
Sibutramine is reported to be a prodrug to two active metabolites, desmethylsibutramine (M1; BTS-54354) and didesmethylsibutramine (M2; BTS-54505), with much greater potency as MRIs.[24][25]
Unlike other serotonergic appetite suppressants like fenfluramine, sibutramine and its metabolites have only low and likely inconsequential affinity for the 5-HT2B receptor.[21]
Pharmacokinetics
Sibutramine is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (77%), but undergoes considerable first-pass metabolism, reducing its bioavailability. The drug itself reaches its peak plasma level after 1 hour and has also a half-life of 1 hour. Sibutramine is metabolized by cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP3A4 into two pharmacologically-active primary and secondary amines (called active metabolites 1 and 2) with half-lives of 14 and 16 hours, respectively. Peak plasma concentrations of active metabolites 1 and 2 are reached after three to four hours. The following metabolic pathway mainly results in two inactive conjugated and hydroxylated metabolites (called metabolites 5 and 6). Metabolites 5 and 6 are mainly excreted in the urine.
Chemistry
Sibutramine has usually been used in the form of the hydrochloride monohydrate salt.
Detection in body fluids
Sibutramine and its two active N-demethylated metabolites may be measured in biofluids by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Plasma levels of these three species are usually in the 1–10 μg/L range in persons undergoing therapy with the drug. The parent compound and norsibutramine are often not detectable in urine, but dinorsibutramine is generally present at concentrations of >200 μg/L.[26][27][28]
Society and culture
Regulatory approval
Studies are ongoing into reports of sudden death, heart failure, renal failure and gastrointestinal problems. Despite a 2002 petition by Ralph Nader-founded NGO Public Citizen,[29] the FDA made no attempts to withdraw the drug, but was part of a Senate hearing in 2005.[30] Similarly, David Graham, FDA “whistleblower”, testified before a Senate Finance Committee hearing that sibutramine may be more dangerous than the conditions it is used for.[31]
Between January 2003 and November 2005, a large randomized-controlled “Sibutramine Cardiovascular OUTcomes” (SCOUT) study with 10,742 patients examined whether or not sibutramine administered within a weight management program reduces the risk for cardiovascular complications in people at high risk for heart disease and concluded that use of silbutramine had a RR 1.16 for the primary outcome (composit of nonfatal MI, nonfatal CVA, cardiac arrest, and CV death).[32]
In a dissenting article, “Sibutramine: gone, but not forgotten”, David Haslam (chairman of the National Obesity Forum) says that the SCOUT study is flawed as it only covered high-risk patients and did not consider obese patients who do not have cardiovascular complications or similar contraindications [33]
On January 21, 2010, the European Medicines Agency recommended suspension of marketing authorizations for sibutramine based on the SCOUT study results.[34]
In August 2010 the FDA added a new contraindication for patients over 65 years of age due to the fact that clinical studies of sibutramine did not include sufficient numbers of such patients.[14]
Abbott Laboratories announced on October 8, 2010 that it is withdrawing sibutramine from the US market under pressure from the FDA, citing concerns over minimal efficacy coupled with increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events.[35]
Counterfeit weight-loss products
On December 22, 2008, the United States Food and Drug Administration issued an alert to consumers naming 27 different products marketed as “dietary supplements” for weight loss, that illegally contain undisclosed amounts of sibutramine.[36][37] In March 2009, Dieter Müller et al. published a study of sibutramine poisoning cases from similar Chinese “herbal supplements” sold in Europe, containing as much as twice the dosage of the legally licensed drug.[38]
An additional 34 products were recalled by the FDA on April 22, 2009, further underscoring the risks associated with unregulated “herbal supplements” to unsuspecting persons. This concern is especially relevant to those with underlying medical conditions incompatible with undeclared pharmaceutical adulterants.[39] In January 2010, a similar alert was issued for counterfeit versions of the over-the-counter weight loss drug Alli sold over the Internet. Instead of the active ingredient orlistat, the counterfeit drugs contain sibutramine, and at concentrations at least twice the amount recommended for weight loss.[40]
In March 2010 Health Canada advised the public that illegal “Herbal Diet Natural” had been found on the market, containing sibutramine, which is a prescription drug in Canada, without listing sibutramine as an ingredient.[41] In October 2010 FDA notified consumers that “Slimming Beauty Bitter Orange Slimming Capsules contain the active pharmaceutical ingredient sibutramine, a prescription-only drug which is a stimulant. Sibutramine is not listed on the product label.”[42]
In October 2010 the MHRA in the UK issued a warning regarding “Payouji tea” and “Pai You Guo Slim Capsules” which were found to contain undeclared quantities of sibutramine.[43]
On December 30, 2010 the FDA released a warning regarding “Fruta Planta” dietary products, which were found to contain undeclared amounts of sibutramine. The recall stated that “there is NO SAFE formula on the US market and that all versions of Fruta Planta contain sibutramine. All versions of the formula are UNSAFE and should not be purchased from any source.”[44]
Some illegal weight loss products imported into Ireland have been found to contain sibutramine.[45][46] Similar concerns have been raised in Australia, where illegal imported supplements have been found to contain sibutramine, resulting in public alerts from Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration.[47]
In October 2011, the FDA warned that 20 brands of dietary supplements were tainted with sibutramine.[48] In a 2018 study FDA has found synthetic additives including sibutramine in over 700 diet supplements marketed as “natural”, “traditional” or “herbal remedies”.[49]
References
- ^ “Sibutramine (Reductil) – withdrawal in Australia”. Therapeutic Goods Administration (Tga). Therapeutic Goods Administration, Department of Health, Australian Government. 2010. Retrieved 2014-10-06.
- ^ Health Canada Endorsed Important Safety Information on MERIDIA (Sibutramine Hydrochloride Monohydrate): Subject: Voluntary withdrawal of Meridia (sibutramine) capsules from the Canadian market.
- ^ “Notification of Termination of Production, Sale, and Usage of Sibutramine Preparations and Their Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient”. sda.gov in People’s Republic of China. October 30, 2010. Retrieved 2011-05-21.
- ^ (in German) Sibutramin-Vertrieb in der Europäischen Union ausgesetzt [1]. Abbott Laboratories in Germany. Press Release 2010-01-21. Retrieved 2010-01-27
- ^ “De-registration of pharmaceutical products containing sibutramine” (Press release). info.gov in Hong Kong. November 2, 2010. Retrieved 2010-11-08.
- ^ “Banned Medicines” (Press release). Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. February 10, 2011. Retrieved 2011-03-15.
- ^ “Withdrawal of Sibutramine (Reductil) in New Zealand” (Press release). MedSafe in New Zealand. October 11, 2010. Retrieved 2012-11-06.
- ^ “FDA warns online sellers of banned slimming pills”. January 12, 2014. Retrieved February 20, 2014.
- ^ “Thai FDA reveals voluntary withdrawal of sibutramine from the Thai market” (PDF) (Press release). Food and Drug Administration of Thailand. October 20, 2010. Retrieved 2010-12-22.
- ^ “Top obesity drug sibutramine being suspended”. BBC News. 2010-01-22. Retrieved 2010-01-22.
- ^ Rockoff JD, Dooren JC (October 8, 2010). “Abbott Pulls Diet Drug Meridia Off US Shelves”. The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ^ “Sibutramine – Drugs.com”. drugs.com.
- ^ Buckett WR, Thomas PC, Luscombe GP (1988). “The pharmacology of sibutramine hydrochloride (BTS 54 524), a new antidepressant which induces rapid noradrenergic down-regulation”. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry. 12 (5): 575–84. doi:10.1016/0278-5846(88)90003-6. PMID 2851857. S2CID 24787523.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c “The FDA August 2010 drug safety update”. fda.gov.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Early Communication about an Ongoing Safety Review of Meridia (sibutramine hydrochloride)”. United States Food and Drug Administration. 1 February 2010. Archived from the original on 6 January 2012.
- ^ Siebenhofer, Andrea; Winterholer, Sebastian; Jeitler, Klaus; Horvath, Karl; Berghold, Andrea; Krenn, Cornelia; Semlitsch, Thomas (2021-01-17). “Long-term effects of weight-reducing drugs in people with hypertension”. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1: CD007654. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007654.pub5. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 8094237. PMID 33454957.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c “Meridia Side Effects, and Drug Interactions”. RxList.com. 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ (in Portuguese) Cloridrato de sibutramina monoidratado. Bula. [Sibutramine hydrochloride monohydrate—label information]. Medley (2007).
- ^ Nisoli E, Carruba MO (October 2000). “An assessment of the safety and efficacy of sibutramine, an anti-obesity drug with a novel mechanism of action”. Obesity Reviews. 1 (2): 127–39. doi:10.1046/j.1467-789x.2000.00020.x. PMID 12119986. S2CID 20553857.
- ^ Rothman RB, Baumann MH (May 2009). “Serotonergic drugs and valvular heart disease”. Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 8 (3): 317–29. doi:10.1517/14740330902931524. PMC 2695569. PMID 19505264.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Meridia (sibutramine hydrochloride monohydrate) Capsules CIV. Full Prescribing Information” (PDF). Abbott Laboratories, North Chicago, IL 60064, U.S.A. Retrieved 6 February 2016.
- ^ Heal DJ, Aspley S, Prow MR, Jackson HC, Martin KF, Cheetham SC (August 1998). “Sibutramine: a novel anti-obesity drug. A review of the pharmacological evidence to differentiate it from d-amphetamine and d-fenfluramine”. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 22 Suppl 1: S18–28, discussion S29. PMID 9758240.
- ^ “FDA APPROVES SIBUTRAMINE TO TREAT OBESITY” (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration. November 24, 1997. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ Kim KA, Song WK, Park JY (November 2009). “Association of CYP2B6, CYP3A5, and CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms with sibutramine pharmacokinetics in healthy Korean subjects”. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 86 (5): 511–8. doi:10.1038/clpt.2009.145. PMID 19693007. S2CID 24789264.
- ^ Hofbauer K (2004). Pharmacotherapy of obesity : options and alternatives. Boca Raton, Fla: CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-415-30321-7.
- ^ Jain DS, Subbaiah G, Sanyal M, et al. Liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry validated method for the simultaneous quantification of sibutramine and its primary and secondary amine metabolites in human plasma and its application to a bioequivalence study. Rapid Comm. Mass Spec. 20: 3509-3521, 2006.
- ^ Thevis M, Sigmund G, Schiffer AK, Schänzer W. Determination of N-desmethyl- and N-bisdesmethyl metabolites of Sibutramine in doping control analysis using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Eur. J. Mass Spec. 12: 129-136, 2006.
- ^ R. Baselt, Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 8th edition, Biomedical Publications, Foster City, CA, 2008, pp. 1426–1427.
- ^ Wolfe SM, Sasich LD, Barbehenn E (March 19, 2002). “Petition to FDA to ban the diet drug sibutramine (MERIDIA) (HRG Publication #1613)”. Public Citizen. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ Japsen B (13 March 2005). “FDA weighs decision on Meridia; Health advisory likely for Abbott obesity drug”. Chicago Tribune. Chicago, Illinois. p. 1.
- ^ Hearing of 17 November 2004. Related CBS news item 19 November 2004.
- ^ James WP, Caterson ID, Coutinho W, Finer N, Van Gaal LF, Maggioni AP, Torp-Pedersen C, Sharma AM, Shepherd GM, Rode RA, Renz CL (September 2010). “Effect of sibutramine on cardiovascular outcomes in overweight and obese subjects” (PDF). The New England Journal of Medicine. 363 (10): 905–17. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1003114. hdl:2437/111825. PMID 20818901.
- ^ Haslam D (April 2010). “Sibutramine: gone, but not forgotten” (PDF). Pract Diab Int. 27 (3): 96–97. doi:10.1002/pdi.1453. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 July 2015.
- ^ “European Medicines Agency recommends suspension of marketing authorisations for sibutramine” (PDF). European Medicines Agency. January 21, 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-04-01.
- ^ Pollack A (October 8, 2010). “Abbott Labs Withdraws Meridia From Market”. The New York Times.
- ^ “FDA warns consumers about tainted weight loss pills” (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 22 December 2008.
- ^ “Consumer directed questions and answers about FDA’s initiative against contaminated weight loss products”. U.S. Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. 22 December 2008.
- ^ Müller D, Weinmann W, Hermanns-Clausen M (March 2009). “Chinese slimming capsules containing sibutramine sold over the Internet: a case series”. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. 106 (13): 218–22. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2009.0218. PMC 2680571. PMID 19471631.
- ^ 34 weight loss products recalled, WebMD, 22 April 2009.
- ^ “Fake Alli diet pills can pose health risks”. CNN.com. January 23, 2010. Retrieved 2010-01-24.
- ^ “Herbal diet product poses heart risk”. CBC News. March 26, 2010.
- ^ “FDA Alert: Slimming Beauty Bitter Orange Slimming Capsules: Undeclared Drug Ingredient”. drugs.com.
- ^ “Press release: Warning over unlicensed herbal Payouji tea and Pai You Guo Slim Capsules”. United Kingdom Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. 20 October 2010. Archived from the original on 9 February 2012.
- ^ “PRock Marketing, LLC Issues a Voluntary Nationwide Recall of All weight loss formulas and variation of formulas of Reduce Weight Fruta Planta/Reduce Weight Dietary Supplement”. United States Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on 23 March 2012.
- ^ Pope C. “Seizures of illegal medicines rise”. The Irish Times.
- ^ “FDA Alert: Slim Xtreme Herbal Slimming Capsule: Undeclared Drug Ingredient”. drugs.com.
- ^ “Majestic slimming capsules: Safety advisory”. Therapeutic Goods Administration. Australian Government. 9 November 2012.
- ^ Carroll L (19 October 2011). “‘Natural’ diet pills tainted with banned prescription drug”. MSNBC. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012.
- ^ Cohen, Ronnie (12 October 2018). “No Wonder It Works So Well: There May Be Viagra In That Herbal Supplement”. NPR.org. Retrieved 2018-10-14.
External links
- Abbott Press Release on Meridia Withdrawal
- Sibutramine drug information from Merck Manual. Includes dosage information and a comprehensive list of international brand names
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) product safety website
/////////////SIBUTRAMINE, UNII:WV5EC51866, WV5EC51866, сибутрамин , سيبوترامين , 西布曲明 , ABOTT, OBESITY
