Clik here to view.

Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.
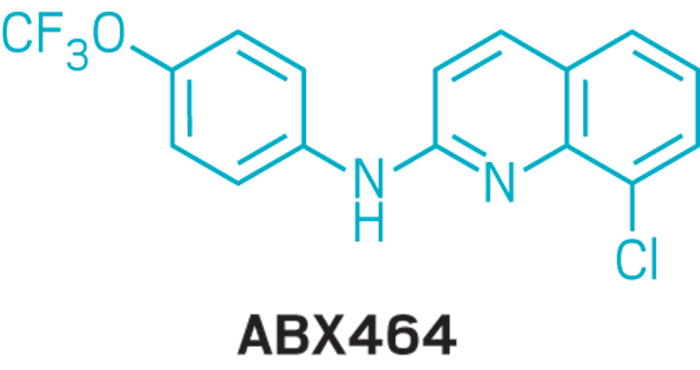
ABX-464
- Molecular FormulaC16H10ClF3N2O
- Averrage mass338.712 Da
SPL-4641258453-75-6[RN]26RU378B9V2-Quinolinamine, 8-chloro-N-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-8-Chloro-N-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-2-quinolinamine
EX-A3322, DB14828, SB18690, BS-14770
Abivax is developing ABX464 a lead from HIV-1 splicing inhibitors, which modulates biogenesis of viral RNA, and acts by targeting the Rev protein, for treating HIV infection, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis and COVID-19 infection.
In August 2021, ABX464 was reported to be in phase 3 clinical development.
ABX464 is an oral, first-in-class, small molecule that has demonstrated safety and profound anti-inflammatory activity in preclinical trials and in Phase 2a and Phase 2b induction trials to treat ulcerative colitis (UC). Patients who completed the induction studies had the option to roll over into the respective open-label extension studies.
In May 2021, Abivax communicated the top-line results of its randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled Phase 2b induction trial conducted in 15 European countries, the US and Canada in 254 patients. The primary endpoint (statistically significant reduction of Modified Mayo Score) was met with once-daily ABX464 (25mg, 50mg, 100mg) at week 8.
Further, all key secondary endpoints, including endoscopic improvement, clinical remission, clinical response and the reduction of fecal calprotectin showed significant difference in patients dosed with ABX464 compared to placebo. Importantly, ABX464 also showed rapid efficacy in patients who were previously exposed to biologics and/or JAK inhibitors treatment.
In addition to the top-line induction results, preliminary data from the first 51 patients treated with 50mg ABX464 in the Phase 2b open-label maintenance study showed increased and durable clinical remission and endoscopic improvement after 48 weeks of treatment.
Based on the positive results from the Phase 2a and Phase 2b studies, Abivax plans to advance ABX464 into a Phase 3 clinical program by the end of 2021.
- Originator Splicos
- Developer Abivax
- Class Anti-inflammatories; Antirheumatics; Antivirals; Small molecules
- Mechanism of Action MicroRNA stimulants; Rev gene product inhibitors; RNA cap-binding protein modulators
- Phase II/III COVID 2019 infections
- Phase II Crohn’s disease; Rheumatoid arthritis; Ulcerative colitis
- DiscontinuedHIV infections
- 24 Jun 2021 Discontinued – Phase-II for HIV infections (Adjunctive treatment, Treatment-experienced) in France (PO) (Abivax pipeline, June 2021)
- 24 Jun 2021 Discontinued – Phase-II for HIV infections (Treatment-experienced, Adjunctive treatment) in Belgium (PO) (Abivax pipeline, June 2021)
- 24 Jun 2021
- Discontinued – Phase-II for HIV infections (Treatment-experienced, Adjunctive treatment) in Spain (PO) (Abivax pipeline, June 2021)
Evotec and Abivax in small-molecule pact
by Michael McCoy
September 18, 2017 | A version of this story appeared in Volume 95, Issue 37
Clik here to view.
The contract research firm Evotec will work with Abivax, a French biotech company, to develop new treatments for viral diseases. Abivax has developed a library of more than 1,000 small molecules designed to inhibit mRNA biogenesis. At its facility in Toulouse, France, Evotec will optimize Abivax’s drug candidates and help develop new drugs for influenza, Dengue, and other viral infections. Abivax’s lead candidate, ABX464, is in Phase II clinical trials as an HIV/AIDS treatment.
PATENT
WO 2010143170
WO 2010143168
WO 2010143169
EP 2974729
WO 2016009065
WO 2017158201
PATENT
WO2016009065
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2016009065
Clik here to view.

Buchwald-Hartwig coupling of 2,8-dichloroquinoline (I) with 4-(trifluoromethoxy)aniline (II) using Pd(OAc)2, Cs2CO3 and xantphos or Pd2dba3, K2CO3 and xphos in t-BuOH
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/US10253020B2/en
US 20170226095
COMPD 90
- (90) 8-chloro-N-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]quinolin-2-amine
Example 5: Compound (90) of the Table IAccording to route (A), a mixture of 2,8-dichloroquinoline (984 mg) and 4-(trifluoromethoxy)aniline (743 μL), Pd(OAc)2 (22 mg), XantPhos (58 mg) and Cs2CO3 (4.6 g) in 20 mL of t-BuOH gave compound (90) (1.1 g).1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.84 (d, J=9.1, 2H), 7.79 (d, J=8.9, 1H), 7.67 (dd, J=1.2, 7.6, 1H), 7.48 (dd, J=1.1, 8.0, 1H), 7.18 (s, 3H), 6.89 (s, 1H), 6.75 (d, J=8.9, 1H).13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ 153.88, 144.30, 143.91, 139.00, 138.25, 131.13, 130.13, 126.55, 125.42, 123.45, 122.50, 122.17, 120.49, 119.10, 113.24.
| 90 | 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.84 (d, J = 9.1, 2H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.9, 1H), 7.67 (dd, J = 1.2, |
| 7.6, 1H), 7.48 (dd, J = 1.1, 8.0, 1H), 7.18 (s, 3H), 6.89 (s, 1H), 6.75 (d, J = 8.9, | |
| 1H) | |
| 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ 153.88, 144.30, 143.91, 139.00, 138.25, 131.13, | |
| 130.13, 126.55, 125.42, 123.45, 122.50, 122.17, 120.49, 119.10, 113.24. | |
| MS (ESI) [M + H]+ = 339 |
PAPER
Tetrahedron Letters (2018), 59(23), 2277-2280.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0040403918305641
Abstract
A solvent-free Buchwald-Hartwig amination had been developed under high-speed ball-milling conditions, which afforded the desired products with moderate to high yields. The addition of sodium sulfate was found to be crucial for improving both the performance and the reproducibility. Comparative solvent-free stirring experiments implicated the importance of mechanical interaction for the transformation, and the inert gas was proved to be unnecessary for this amination.
Graphical abstract
Clik here to view.

PATENT
WO2015001518
COMPD 90
Clik here to view.
PATENT
WO-2021152131
Novel co-crystalline polymorphic forms and salts of ABX464 , useful for treating inflammatory diseases, cancer, and diseases caused by viruses eg HIV, severe acute respiratory syndrome caused by SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-2 infection including strains responsible for COVID-19 and their mutants.
W02010/143169 application describes the preparation and use of compounds, and in particular quinoline derivatives including certain pharmaceutically acceptable salts useful in the treatment of HIV infection. Said application in particular discloses 8-Chloro-N-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)quinolin-2-amine also named (8-chloro-quinoline-2-yl)-(4-trifluoromethoxy-phenyl) -amine which is currently under clinical development. The inventors have stated that ABX464 is naturally highly crystalliferous and thus is spontaneously present under a specific unique stable and crystalline form named “crystalline form I”.
W02017/158201 application deals with certain mineral acid or sulfonic acid salts of ABX464.
ABX464 has a poor solubility in aqueous solutions. The main drawback of said poor solubility is that the active ingredient cannot entirely reach their targets in the body if the drug remains undissolved in the gastrointestinal system.
PATENT
WO2021152129 ,
amorphous solid dispersion (eg tablet) comprising ABX464.
PATENT
WO2020127839
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2020127839
use of quinoline derivatives (ie ABX464) for treating cancer and dysplasia.
///////////ABX464, ABX 464, phase 3 , SPL 464, EX A3322, DB14828, SB18690, BS 14770
Clik here to view.

