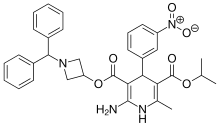

Azelnidipine
C33H34N4O6, 582.6 g/mol
CAS 123524-52-7
3-(1-Benzhydrylazetidin-3-yl) 5-isopropyl 2-amino-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
CS-905, RS-9054
Approved India cdsco 2020
SYN REF https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4245158/
MP 95-98 °C AND NMR WO 2004058745 . EP 266922
Azelnidipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It is marketed by Daiichi-Sankyo pharmaceuticals, Inc. in Japan. It has a gradual onset of action and produces a long-lasting decrease in blood pressure, with only a small increase in heart rate, unlike some other calcium channel blockers. It is currently being studied for post-ischemic stroke management.
Azelnidipine (INN; marketed under the brand name CalBlock — カルブロック) is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. Azelnidipine is L and T calcium channel blocker. It is sold in Japan by Daiichi-Sankyo pharmaceuticals, Inc. Unlike nicardipine, it has a gradual onset and has a long-lasting hypotensive effect, with little increase in heart rate. Drug Controller General Of India (DCGI) has approved the use of azelnipine in India. It is launched under the brand name Azusa (ajanta pharma ltd.)[1] In 2020.
Chemical Synthesis
A solution of benzhydrylamine (46) and epichlorohydrin (47) was mixed without adding solvent to give azetidinol 48 in 57% yield. DCC coupling between cyanoacetic acid (49) and azetidinol 48 in hot THF gave ester 50 in 93% yield. Cyanoester 50 was treated with ethanol and HCl gas in chloroform to give imidate HCl salt 51, which was treated with ammonia gas in chloroform and ammonium acetate in acetonitrile to give the corresponding amidinoacetate 52. A modified Hantzsch reaction was employed to construct the 2-amino-1,4- dihydropyridine core structure. Compound 52 was condensed with 2-(3-nitrobenzylidene)acetic acid isopropyl ester (55) in the presence of NaOMe in refluxing isopropanol to give the cyclized product, azelnidipine (V) in 74% yield. Benzylideneacetoacetate 55 was obtained through the Knoevenagel reaction employing 3-nitrobenzaldehyde (53) and isopropyl acetoacetate (54) in isopropanol containing a catalytic amount of piperidinium acetate at 45-55oC in 65% yield.

PATENT
EP 266922
IN 201621044802
CN 106279109
CN 107188885
CN 105461691
CN 103509003
CN 103183663
CN 102382104
JP 2012020970 A
PAPER
Bioanalysis (2019), 11(4), 251-266.
PAPER
Asian Journal of Chemistry (2014), 26(15), 4675-4678.
PAPER
http://www.asianjournalofchemistry.co.in/User/ViewFreeArticle.aspx?ArticleID=26_16_30

Azelnidipine is designated chemically as 3-(1-benzhydrylazetidin-3-yl)-5-isopropyl-2-amino-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate. Its literature synthesis (Scheme-I) involves 3-nitrobenzaldehyde 5 with isopropyl acetoacetate 6. The product of (Z)-isopropyl 2-(3- nitrobenzylidene)-3-oxobutanoate (7a, b, c), on treatment with piperidine and acetic acid, coupling of (7) and 1-benzhydrylazetidin-3-yl 3-amino-3-iminopropanoate acetate (8) gave azelnidipine (1).
PAPER
International Research Journal of Pharmacy (2012), 3(8), 191-192.
Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1995), 43(5), 797-817.
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2014139410A1/en
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and provides an important intermediate of dihydropyridine calcium antagonist adipine, 3-amino-3-iminopropionic acid-1-(diphenylhydrazinyl)-3-azetidine The synthesis process of ester acetate. Background technique
Azelnidipine is a new type of dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker developed by Sankyo and Ube Industries of Japan. It was approved for sale in Japan in late May 2003 under the trade name Calblock. Adipine has a selective blockade of calcium channels in arterial smooth muscle cells, it can dilate blood vessels, reduce peripheral vascular resistance and arterial pressure, and is widely used clinically for mild or moderate essential hypertension, renal disorders with hypertension And treatment of severe hypertension. Compared with nicardipine and nifedipine dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, adipine is superior in selectivity, long-lasting and long-lasting, and has little effect on the heart.

阿折地平的结构式

A flat floor structure
At present, references to the preparation of agdipine include: European patents EP0266922; Chinese patent CN201010516967.7; Chinese Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2010, 20 (3): 192-194; Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Industry, 2008, 39 (3): 163-165; Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2009, 26 ( 1 ): 15-18; Qilu Pharmacy, 2005, 24 (6): 365-366. The preparation method of adipine in these literatures is based on the reaction of epichlorohydrin and diphenylamine with N-alkylation, cyclization, esterification, Pinner synthesis, neutralization, and oxime reaction. The intermediate 3-amino-3-iminopropionic acid-1-(diphenylfluorenyl)-3-azetidinyl acetate is prepared first, followed by 2-(3-nitrobenzylidene)acetyl Acepinedipine was obtained by the Hantzsch condensation of isopropyl acetate.
The control of the solvent and reaction conditions in the esterification, Pinner synthesis and neutralization three-step reaction in this route is critical. Using the preparation methods provided by these documents, we found that the operation was cumbersome and the yield and purity were not satisfactory.
In the esterification reaction, according to the method specifically reported in the above literature, the highest yield of the obtained product is only 85%, and the purity is poor, it is difficult to purify, and it is difficult to obtain a solid product.

副产物 (7 )和(8 )结构式 发明内容 We have found that 3-amino-3-iminopropionic acid-1- (3) is prepared by a three-step reaction from cyanoacetate-1-diphenylhydrazin-3-azetidinyl ester (3) according to the method specifically reported in the above literature. Diphenylhydrazino)-3-azetidinyl acetate (6), the reaction operation is cumbersome, and it is easy to produce by-products of hydrolysis of ester bonds and hydrolysis of imid bonds (7) and (8), three-step reaction. The total yield is only 20~30%, and the purification of the product is difficult, which seriously affects the quality of the final product and greatly increases the production cost.

Byproducts (7) and (8) structural formula Summary of the invention
It is an object of the present invention to provide a process for the preparation of the key intermediate of adipine, 3-amino-3-iminopropionic acid-1-(diphenylhydrazinyl)-3-azetidinyl acetate. The adipine intermediate of the present invention 3-amino-3-iminopropionic acid-1-(diphenylhydrazinyl)-3-azetidinyl acetate acetate has the following structural formula:


The preparation method of 3-amino-3-iminopropionic acid-1-(diphenylindenyl)-3-azetidinyl acetate of the present invention comprises the following steps: 1) Esterification: 1-diphenylhydrazin-3-azetidinol (2), cyanoacetic acid (1) and N,N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) in organic solvent at 0~ Reacting at 80 ° C, to obtain 7-diphenylindolyl-3-azetidinyl cyanoacetate (3);
2) Pinner reaction: Add intermediate (3), absolute ethanol to dichlorosilane, stir and cool
To -20~25 °C, dry hydrogen chloride gas is passed, and then the reaction solution is kept sealed at -20~25 °C to obtain 3-imino-3-ethoxypropionic acid-1-(diphenylfluorenyl) -3-azetidinyl ester hydrochloride (4);
3) Neutralization reaction: The intermediate (4) is dissolved in dichloromethane, and the base is added at -5 to 25 ° C to obtain 3-imino-3-ethoxypropionic acid-1-(diphenylhydrazine). Benzyl-3-azetidinyl ester (5);
4) Formation reaction: The intermediate (5) is dissolved in acetonitrile, ammonium acetate is added, and the temperature is raised to 40 to 60 ° C to obtain 3-amino-3-iminopropionic acid-1-(diphenylfluorenyl)-3. – azetidinium acetate compound (6). detailed description
Example
1. Preparation of cyanoacetic acid-1-diphenylhydrazine-3-azetidine (esterification)


Method 1: Add 1-diphenylhydrazin-3-azetidinol (2, 235 g, 0.983 mol) and cyanoacetic acid (1, 100 g, 1.18 mol) to 1.5 mL of dichloromethane, and stir until fully dissolved. Ν, Ν-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC, 243 g, 1.18 mol) was added at 0-10 ° C and allowed to react at room temperature for 3 h. After the completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was cooled to 0 to 5 ° C, and filtered, filtered, washed with a small portion of dichloromethane. The organic solvent was evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure and dried to give 275 g of white solid.
Method 2: chloroform was used as the reaction solvent, and the operation was the same as above, and the reaction was carried out at 55 ° C for 5 hours, the HPLC purity was 98.7%, and the product yield was 95.3%.
Method 3: Ethyl acetate was used as the reaction solvent, and the operation was the same as above, and the reaction was carried out at 55 ° C for 2 h, the HPLC purity was 98.9%, and the product yield was 96.1%.

Method 4: Using hydrazine as the reaction solvent, the operation was the same as above, and the reaction was carried out at 55 ° C for 7 h, the HPLC purity was 98.5%, and the product yield was 94.7%. 2. Preparation of 3-imino-3-ethoxypropionic acid-1-(diphenylfluorenyl)-3-azetidinyl ester hydrochloride (Pinner reaction)

Intermediate 3 (270 g, 0.882 mol), absolute ethanol (61.8 mL, 1.06 mol) was added to 1.5 L of dry dichloromethane, cooled to -5 to 0 ° C in a water salt bath, and dried. HC1 gas for 2.5 h, after the completion of the aeration, the reaction solution was kept under stirring at 0 ° C for 6 h.
Allow to stand overnight at 0-4 °C. After completion of the reaction, the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to give an oily viscous intermediate 4 .
3. Preparation of 3-imino-3-ethoxypropionic acid-1-(diphenylfluorenyl)-3-azetidinyl ester


Method 1: Add 1.4 L of dichloromethane to Intermediate 4, cool to 0-5 ° C, add dry diethylamine (182 mL, 1.76 mol) to the solution, adjust pH 7-8, continue to stir after the dropwise addition. 2h. The mixture was suction filtered, and the filtrate was evaporated to dryness vacuo.
Method 2: Diamine is used for neutralization, and the operation is the same as above.
Method 3: Triethylamine is used for neutralization, and the operation is the same as above.
Method 4: Ethylenediamine is used for neutralization, and the operation is the same as above.
Method 5: Add 1.4 L of dichloromethane to Intermediate 4, cool to 0-5 ° C, add potassium carbonate (242.88 g, 1.76 mol) to the solution in portions, adjust pH 7-8, continue stirring for 2 h. . The mixture was suction filtered, and the filtrate was evaporated to dryness vacuo. Method 6: Neutralize with sodium carbonate, and operate as above.
Method 7: Neutralize with sodium hydroxide, and operate as above.

4. Preparation of 3-amino-3-iminopropionic acid-1-(diphenylindenyl)-3-azetidinyl acetate (formed into 脒)

To the intermediate 5, 1.2 L of acetonitrile was added, and after dissolution, ammonium acetate (68.0 g, 0.882 mol) was added, and the mixture was heated to 55 ° C for 6 h. After the reaction, it was naturally cooled, crystallization, suction filtration, acetonitrile washing cake, and dried to give 236 g of a white solid. The total yield of the three-step reaction was 69.9 73.1%.
PAPER
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/cc/c4cc09337b#!divAbstract
Abstract
A protocol for the coupling of 3-iodoazetidines with Grignard reagents in the presence of an iron catalyst has been developed. A variety of aryl, heteroaryl, vinyl and alkyl Grignards were shown to participate in the coupling process to give the products in good to excellent yields. Furthermore, a short formal synthesis towards a pharmacologically active molecule was shown.

http://www.rsc.org/suppdata/cc/c4/c4cc09337b/c4cc09337b1.pdfPATENThttps://patents.google.com/patent/CN103509003A/zhAzelnidipine, whose chemical name is 3-(1-diphenylmethylazetidin-3-yl) 5-isopropyl 2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl 4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, developed by Japan Sankyo Co., Ltd. and approved to be marketed in Japan in late May 2003. The existing synthesis method of azedipine is cumbersome, and the preparation of intermediate (VI) adopts column chromatography method, and the purification of product (I) also uses column chromatography method, which is not suitable for industrial production.
A method for preparing azeldipine, which is characterized in that it is prepared by the following steps.
[0006]

Description of the drawings:
Figure 1 is a flow chart of the synthesis process of azeldipine.
[0025] Example 12-Preparation of (3-nitrobenzylidene) isopropyl acetoacetate (III)
[0026] Add 2.1kg of 3-nitrobenzaldehyde and 5L of isopropanol to the reaction kettle, start stirring, add 3kg of isopropyl acetoacetate, and stir. Add 43ml of anhydrous piperidine and 12ml of glacial acetic acid, and continue to stir until the solid is completely dissolved. Heat the temperature to 45°C and keep the reaction for 6h, then lower the temperature, stir and crystallize for 16h. Filter and collect the resulting filter cake. Put the obtained filter cake and 16L ethanol (industrial) into the reaction kettle, start stirring, beating, filtering, and collecting the filter cake. Put the filter cake in the baking tray, put it in the oven, and dry at 70-80°C. Collect the product 2-(3-nitrobenzylidene) isopropyl acetoacetate (III), about 2.7 kg.
[0027] Example 21-Preparation of benzhydryl-3-hydroxyazetidine (Intermediate V)
[0028] 9.6L of methanol, 5.4kg of benzhydrylamine (IV) and 3.33kg of epichlorohydrin were added to the reaction kettle, stirred at room temperature for 48 hours, the reaction was completed, the temperature was raised to 68°C, and the reaction was refluxed for 72h. Cool to room temperature. Concentrate under reduced pressure to remove methanol, and collect the filter cake by filtration. The filter cake was put into the reaction kettle, 19.2L of ether and 13.75L of 3mol/L NaOH solution were added, stirred, and the water layer was released after standing still. The ether layer was washed with water and saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and the filtrate was collected. The ether was recovered under reduced pressure to dryness to obtain about 3.05 kg of 1-benzyl-3-hydroxyazetidine (Intermediate V).
[0029] Example 3 Preparation of cyanoacetic acid (1-diphenylmethylazetidin-3-yl) ester (Intermediate VI)
[0030] Put about 3.05g of intermediate (V), 27L of tetrahydrofuran and 1.7kg of cyanoacetic acid into the reactor, start stirring, turn on the chilled water of the reactor to cool down, and slowly add 3.1kgN, N’-dicyclohexyl to the reactor Diimine, control the temperature at IO0C -15°C, after the addition, close the chilled water in the reactor. Turn on the heating system, slowly increase the temperature to 55-60°C, and react for 10 hours. The material liquid was cooled to room temperature, filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated to dryness. Put 16.8L of ethyl acetate into the reaction kettle, stir to dissolve, then wash with water, dry with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filter, and collect the filtrate. Ethyl acetate was recovered under reduced pressure, petroleum ether was added to the solid residue, stirred, and filtered to obtain cyanoacetic acid (1-diphenylmethylazetidin-3-yl) ester (Intermediate VI), about 3.19 kg.
[0031] Example 4 Preparation of amidinoacetic acid (1-diphenylmethylazetidin-3-yl) ester acetate (VII)
[0032] Put 25L of dichloromethane, about 3.19kg of intermediate (VI), and 430g of ethanol into the reactor, start stirring, cool to below 0°C, and pass in hydrogen chloride gas until the temperature stabilizes below 0°C, at 0°C Let stand for 14 hours at °C. Concentrate under reduced pressure to remove most of the hydrogen chloride gas and recover the solvent dichloromethane. Add 25L of dichloromethane to the residue of the reaction kettle, stir, cool to below 0°C, and pass in ammonia until the temperature stabilizes below 0°C, and filter . The filtrate was poured into the reactor, concentrated under reduced pressure to recover the solvent to obtain a colorless liquid, added 22.8L of acetonitrile and 905g of amine acetate, heated to 55-60°C for 1.5 hours, stopped the reaction, filtered while hot, and recovered the filtrate under reduced pressure Solvent to dryness, add 3L of ether to the residue to crystallize, filter, and dry to obtain amidinoacetic acid (1-diphenylmethylazetidin-3-yl) ester acetate (Intermediate VII) about 3.2kg .
[0033] Example 5. Add about 3.2kg of Intermediate (VII), about 2.7kg of Intermediate (III), 21L of isopropanol and 585g of sodium methoxide to the reaction kettle, start stirring, heat to reflux and react for 4 hours, and cool to Below 10°C, filter, the filtrate is decompressed to recover the solvent to dryness, add 35L ethyl acetate to the residue to dissolve, wash with 6.5LX3 water, release the water layer, add anhydrous sodium sulfate to the ethyl acetate layer to dry, filter , Collect the filtrate, recover ethyl acetate under reduced pressure, add 4.2L of toluene to the residue,
3.4L of n-hexane was heated to dissolve, filtered, the filtrate was stirred to room temperature to crystallize, filtered and collected and dried, and the product was placed in an oven at 45-55°C to dry to obtain the crude azedipine (I), about 2.3kg.
[0034] Example 6, Refining
[0035] Put 8.8L ethyl acetate and 8.8L n-hexane into the reaction kettle, turn on the stirring, put about 2.3kg of the crude azeldipine into the reaction kettle, slowly heat up until the material is dissolved, add 180g of activated carbon and stir for 0.5h, while it is hot Filter, hydraulically filter the material to the crystallization dad, wash the filter cake with 5.5L ethyl acetate and 4.5L n-hexane solution, combine with the filtrate, cool to 0~5°C to crystallize, filter, collect the product, and place it in a hot air circulating oven After drying at 45-55°C, 2.2 g of azeldipine is obtained. The purity is 99.6% as measured by high performance liquid chromatography. The refined yield is 96.0%.
[0036] Example 7 Azedipin Refining
[0037] The mixed solvent was prepared according to the volume ratio of ethyl acetate and n-hexane of 2:1, 22L of the mixed solvent was put into the reactor, about 2.3kg of azedipine crude product was put into the reactor, and the temperature was slowly heated until the material was dissolved, Add 180g of activated carbon and stir for 0.5h, filter while hot, filter the material hydraulically into a crystallization kettle, wash the filter cake with a mixed solvent, combine the washing liquid with the filtrate, cool to 0~5°C for crystallization, filter, collect the product, and circulate the hot air Dry in an oven at a temperature of 45-55°C to obtain 2.2 g of azeldipine fine product, with a purity of 99.7% measured by high performance liquid chromatography.
[0038] Example 8 prepared a mixed solvent at a volume ratio of ethyl acetate and n-hexane of 1.5:1, put 22L of the mixed solvent into the reactor, put about 2.3kg of crude azeldipine into the reactor, and slowly heated to Dissolve the material, add 180g of activated carbon and stir for 0.5h, filter while it is hot, filter the material hydraulically into a crystallization kettle, wash the filter cake with a mixed solvent, combine the washing liquid and the filtrate, cool to 0~5°C to crystallize, filter, and collect the product. Dry in a hot air circulating oven at a temperature of 45-55°C to obtain
2.2g azeldipine is a fine product with a purity of 99.6% measured by high performance liquid chromatography.
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/CN103183663B/zh
Azelnidipine (Azelnidipine) is a new type of dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker jointly developed by Sankyo Co., Ltd. and Ube Industries Co., Ltd., which inhibits the entry of calcium ions into excitable tissues and causes peripheral blood vessels And coronary artery vasodilation plays a role in lowering blood pressure. Clinically, it is widely used in patients with mild or moderate symptoms of primary hypertension, hypertension with renal dysfunction, and severe hypertension. Compared with similar antihypertensive drugs, azeldipine has a slow and long-lasting antihypertensive effect.
[0004] The chemical structure of azeldipine is similar to that of nifedipine:

[0006] The Chinese patent CN87107150.9 reported the compound earlier and gave a detailed introduction to its synthesis; afterwards, most of the synthesis of azeldipine adopts this route:

[0008] The reaction takes o-nitrobenzaldehyde and isopropyl acetoacetate as raw materials to prepare intermediate compound 5; takes benzhydrylamine and epichlorohydrin as raw materials to prepare compound 2, compound 2 and cyanoacetic acid act in DCC Compound 3 is prepared by the next reaction. Compound 3 is added with ethanol under the action of hydrogen chloride gas, ammonia gas ammonolysis, and acetate anion exchange to obtain compound 4. Compound 4 and compound 5 are under the action of sodium methoxide to obtain compound 1, namely azeldipine.
[0009] Wherein: Compound 3 can be purchased as an industrial product, or can be prepared according to the traditional method reported in the literature; Compound 5 is prepared according to the traditional method reported in the literature.
[0010] In the process of preparing amidine 4 in the traditional reaction route, hydrogen chloride gas and ammonia gas need to be passed in successively. Therefore, the reaction requires anhydrous reagents. According to literature reports, the reaction yield is about 70%. From the perspective of industrial synthesis, The application of anhydrous reagents will undoubtedly increase the cost, while the use of gas will increase the difficulty of operation and require the use of high-pressure equipment. At the same time, post-reaction processing is difficult and industrial production is difficult. Therefore, this step of the reaction requires further improvement.
With acetonitrile as a solvent, the crude product of reaction 2) was stirred until dissolved, ammonium acetate was added, and acetate anion exchange was performed to obtain the amidine compound 4;

[0018] The second step: use toluene as a solvent, compound 4 and compound 5 in the use of sodium amide to obtain compound 1, namely azedipine

[0020] The preferred technical solution of the present invention is characterized in that the temperature of reaction 1) is controlled below _5°C
Example 1: Preparation of azeldipine
[0030] Add 50 g of compound 3, 1500 mL of dichloromethane, and 16.64 mL of absolute ethanol to a 5L three-necked flask, and under mechanical stirring, pass HC1 gas below -5 °C to saturation, and after saturation, keep the reaction at -5 °C for 24 hours. Protect from light and nitrogen, slowly add the above reaction system to 1665ml of ammonia water with a concentration of 2.5-3.0% under the control of 0-5°C. After the addition, stir for 0.5h, stand for 0.5h, and separate the liquids. The dichloromethane layer was washed once with 2000 mL of saturated brine, left standing for 1.0 h, separated, and the dichloromethane layer was drained under reduced pressure to obtain a white solid. Without drying, it was directly added to 2000 mL of acetonitrile, and the temperature was slowly heated to dissolve. Add 11.7g of ammonium acetate, control the temperature at 55°C -60°C, and react for 2h under mechanical stirring. After cooling, the solid precipitated, filtered, and dried to obtain 57.55 g of amidine 4, the yield was 91.2%, the HPLC purity was 99.63%, and the melting point was 130-132.3°C.
[0031] 50g amidine 4, 43.5g compound 5, 1000mL toluene, and 7.7g sodium amide were added into a 1000mL three-necked flask, mechanically stirred, heated to reflux, and reacted for 4 hours. TLC detects that the reaction is complete and cools to room temperature to crystallize. Filter, put the solid directly into the mixed solution of toluene and n-hexane (1:1.2-1.5) without drying, heat up to reflux to clear, cool to 56°C naturally, add seed crystals, stop stirring, and cool to 25° C, filter. The solid was purified once more according to the above method, and dried under reduced pressure at 40°C for 48 hours to obtain 66.87g of α-crystal form of Azedipine, yield 88.2%, melting point: 121-123°C.
[0032] Example 2; Preparation of Azeldipine
[0033] Add 50g of compound 3, 1500mL of dichloromethane, 16·64mL of absolute ethanol into a 5L three-necked flask, and under mechanical stirring, pass HC1 gas below -5°C to saturation, and after saturation, -6°C to -8°C Incubate the reaction for 24h. Under the control of 0-5 °C, slowly add the above reaction system to ammonia water with a concentration of 2.5-3.0%, adjust the pH to 7.8-8.5, after adding, stir for 0.5h, stand for 0.5h, and separate. The dichloromethane layer was washed once with 2000 mL of saturated brine, left standing for 1.0 h, separated, and the dichloromethane layer was drained under reduced pressure to obtain a white solid. Without drying, it was directly added to 2000 mL of acetonitrile, and the temperature was slowly heated to dissolve. Add 11.7g of ammonium acetate, control the temperature at 55°C-60°C, and react for 2h under mechanical stirring. After cooling, the solid precipitated, filtered, and dried to obtain 59.0 lg of amidine 4 with a yield of 93.5%, an HPLC purity of 99.52%, and a melting point of 130.1-132.0°C.
[0034] 50g amidine 4, 43.5g compound 5, 1000mL toluene and 7.7g sodium amide were added to a 1000mL three-necked flask, mechanically stirred, heated to reflux, and reacted for 4 hours. TLC detects that the reaction is complete and cools to room temperature to crystallize. Filter, put the solid directly into the mixed solution of toluene and n-hexane (1:1.2-1.5) without drying, heat up to reflux to clear, cool to 56°C naturally, add seed crystals, stop stirring, and cool to 25° C, filter. The solid was refined once more according to the above method, and dried under reduced pressure at 40°C for 48 hours to obtain 68.31 g of α-crystal azedipine, yield 90.01%, melting point: 121 -123 °C.
[0035] Example 3: Preparation of Amidine 4
[0036] Add 50g of compound 3, 1500mL of dichloromethane, 16·64mL of absolute ethanol into a 5L three-necked flask, and under mechanical stirring, pass HC1 gas below -5°C to saturation, and after saturation, -7°C to -9°C Incubate the reaction for 24h. Under the control of 0-5 °C, slowly add the above reaction system to the ammonia water with a concentration of 2.5-3.0%, adjust the pH to 8.5-9.5, after adding, stir for 0.5h, stand for 0.5h, and separate. The dichloromethane layer was washed once with 2000 mL of saturated brine, left standing for 1.0 h, separated, and the dichloromethane layer was drained under reduced pressure to obtain a white solid. Without drying, it was directly added to 2000 mL of acetonitrile, and the temperature was slowly heated to dissolve. Add 11.7g of ammonium acetate, control the temperature at 55°C-60°C, and react for 2h under mechanical stirring. After cooling, the solid precipitated, filtered, and dried to obtain 59.5 g of amidine 4, HPLC purity 99.78%, melting point: 130.7-132·2°C.

Step 2: Using toluene as a solvent, compound 4 and compound 5 under the action of sodium amide to obtain compound 1, namely azeldipine

PATENThttps://patents.google.com/patent/CN102453023A/zh
detailed description
[0007] In the synthesis workshop, benzhydrylamine is used as a raw material to be synthesized by addition, cyclization, esterification, acidification, ammoniation, condensation and other reactions. The crude azeodipine is refined, dried, mixed and packaged in a clean area. Fold the ground. The specific response is as follows:
[0008] 1. Addition and cyclization reaction
[0009] Methanol, benzhydrylamine, and epichlorohydrin were added to the reaction kettle, stirred at room temperature for 24hr, the reaction was completed, the reaction was heated to reflux for 24hr, cooled, filtered to collect the precipitated solid, and then the mother liquor was concentrated to recover the raw materials, and the heating was continued to reflux 18 After hours, collect the product, add dichloromethane and H2O to the obtained solid, adjust the pH to 10-11 with 40% NaOH while stirring in an ice bath, stand still, separate the organic layer, dry with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and recover the dichloromethane under reduced pressure To dryness, a colorless solid compound III (1-benzyl-3-hydroxyazetidine) is obtained. After improvement, the raw materials are fully reacted, and the reaction yield of this step is improved. The mass yield is 75%. % Mentioned 85%.
[0010]

[0011] 2. Esterification reaction
[0012] Add THF, compound (III), and cyanoacetic acid to the reaction kettle, stir evenly, add DCC in batches under ice bath stirring, control the temperature at 10°C~15°C, after the addition, remove the ice water bath, and slowly heat up React at 55°C~60°C for 18h. After the reaction is complete, cool, filter to remove insoluble materials, concentrate the filtrate to dryness, add ethyl acetate to the residue to dissolve, wash with water, dry with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and recover ethyl acetate under reduced pressure. The residue was added with petroleum ether and stirred for crystallization, and the solid was collected by filtration to obtain compound IV (1-diphenylmethyl-3-azetidinyl cyanoacetate).
[0013]

[0014] 3. Acidification and amination reaction
[0015] Dichloromethane, ethanol and intermediate (IV) were added to the reaction kettle respectively, mixed and stirred, cooled to about _5 ° C in an ice salt bath, and dried hydrogen chloride gas was introduced until saturation (about 1.5 hours) after . Let stand overnight at about -5°C, recover the solvent under reduced pressure at room temperature, add dichloromethane to the residue and stir, cool to about _5°C in an ice-salt bath, pass in the dried ammonia gas until saturation (about 3 hours) , Filtration to remove the insoluble matter, and the filtrate was decompressed to recover solvent at room temperature. Acetonitrile and ammonium acetate were added to the residue respectively, and the temperature was raised to 55~60°C for 2 hours with stirring. After the reaction was completed, it was cooled and filtered. 3-Azacyclobutanylamidinoacetate acetate), the reaction in this step is controlled at about _5°C, and the transesterification
The side reaction is reduced, and the reaction yield is improved.
[0016]

[0017] 4. Condensation reaction
[0018] Add isopropanol, intermediate (III’), sodium methoxide and compound V to the reaction kettle, mix and stir, heat to reflux and react for 5 hours. After the reaction is complete, cool and filter, and the filtrate is decompressed to recover the solvent to dryness, leaving residue Add ethyl acetate to dissolve, wash with water, dry with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, recover ethyl acetate under reduced pressure to 1/4 of the total volume, add n-hexane, and stir at 50°C for 30 min. After cooling and crystallization, the solid was collected by filtration, and air-dried at 45°C to obtain the crude azedipine (I). After the crude product was dissolved in ethyl acetate-n-hexane mixed solvent, activated carbon was added for decolorization and impurity removal to achieve the purpose of purification.

[0020] The refined product is dissolved in dioxane, refluxed with n-hexane, cooled and crystallized, and dried to obtain a solid that is boiled in cyclohexane, cooled and filtered, and dried to obtain α-crystalline form Azedipine.
Patent
Publication numberPriority datePublication dateAssigneeTitleCN102453023A *2010-10-212012-05-16大丰市天生药业有限公司Process for producing azelnidipineCN103130700A *2013-03-142013-06-05沈阳中海药业有限公司Preparation method of azelnidipine intermediateCN103509003A *2012-06-272014-01-15威海威太医药技术开发有限公司Preparation method of azelnidipine
JP3491506B2 *1997-10-142004-01-26宇部興産株式会社Method for producing dihydropyridine derivativeCN101475521B *2008-11-132010-11-10青岛黄海制药有限责任公司Method for synthesizing acetate of 1-benzhydryl-3-azetidine amidino acetic ester
TitleLIU, JIAN-FENG ET AL.: “Improved Synthesis of Azelnidipine”, CHINESE JOURNAL OF MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY, vol. 20, no. 3, 30 June 2010 (2010-06-30), pages 192 – 194 *ZHANG, KAI ET AL.: “Synthesis of Azelnidipine”, CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICALS, vol. 39, no. 3, 31 March 2008 (2008-03-31), pages 163 – 165, XP025959789, DOI: doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.12.041 *
CN103130700B *2013-03-142015-04-29沈阳中海药业有限公司Preparation method of azelnidipine intermediateCN104860855B *2014-12-082017-06-16宁夏紫光天化蛋氨酸有限责任公司A kind of preparation method of the methylmercapto butyric acid ester of 2 hydroxyl of the D of high-purity, L 4CN105949102A *2016-06-202016-09-21许昌豪丰化学科技有限公司Production method of azelnidipine intermediatePublication numberPriority datePublication dateAssigneeTitleWO2014139410A1 *2013-03-142014-09-18Shenyang Zhonghai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.A kind of preparation method of azeldipine intermediateCN105461691A *2015-12-312016-04-06Weihai Disu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.A kind of preparation method of azeldipineCN106279109A *2016-08-182017-01-04Weihai Disu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.A kind of preparation method of azeldipineCN106543061A *2016-10-202017-03-29Weihai Disu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.Preparation method of N-diphenylmethylcyclobutane-3-alcohol
References
- ^ Oizumi K, Nishino H, Koike H, Sada T, Miyamoto M, Kimura T (September 1989). “Antihypertensive effects of CS-905, a novel dihydropyridine Ca++ channel blocker”. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 51 (1): 57–64. doi:10.1254/jjp.51.57. PMID 2810942.
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | CalBlock,AZUSA,Azovas |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | In general: ℞ (Prescription only) |
| Identifiers | |
| showIUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 123524-52-7 |
| PubChem CID | 65948 |
| ChemSpider | 59352 |
| UNII | PV23P19YUG |
| KEGG | D01145 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1275868 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID3020120 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.162.151 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C33H34N4O6 |
| Molar mass | 582.657 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| hideSMILES[O-][N+](=O)c1cccc(c1)C5C(/C(=O)OC(C)C)=C(\NC(\N)=C5\C(=O)OC4CN(C(c2ccccc2)c3ccccc3)C4)C | |
| hideInChIInChI=1S/C33H34N4O6/c1-20(2)42-32(38)27-21(3)35-31(34)29(28(27)24-15-10-16-25(17-24)37(40)41)33(39)43-26-18-36(19-26)30(22-11-6-4-7-12-22)23-13-8-5-9-14-23/h4-17,20,26,28,30,35H,18-19,34H2,1-3H3 Key:ZKFQEACEUNWPMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
/////////Azelnidipine, CS-905, RS-9054, INDIA 2020, APPROVALS 2020
#Azelnidipine, #CS-905, #RS-9054, #INDIA 2020, #APPROVALS 2020
CC1=C(C(C(=C(N1)N)C(=O)OC2CN(C2)C(C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4)C5=CC(=CC=C5)[N+](=O)[O-])C(=O)OC(C)C