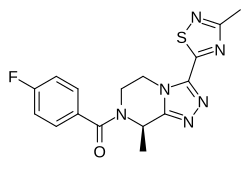
Fezolinetant ESN-364
- Molecular FormulaC16H15FN6OS
- Average mass358.393 Da
-
Methanone, [(8R)-5,6-dihydro-8-methyl-3-(3-methyl-1,2,4-thiadiazol-5-yl)-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl](4-fluorophenyl)-UNII:83VNE45KXXфезолинетант [Russian] [INN]فيزولينيتانت [Arabic] [INN]非唑奈坦 [Chinese] [INN]
- Originator Euroscreen
- Developer Ogeda
- Class Pyrazines; Small molecules; Triazoles
- Mechanism of Action Gonadal steroid hormone modulators; Neurokinin 3 receptor antagonists
- Phase II Hot flashes; Polycystic ovary syndrome; Uterine leiomyoma
- Preclinical Weight gain
- DiscontinuedBenign prostatic hyperplasia; Endometriosis
- 14 Sep 2018 Ogeda completes a phase II trial in Hot flashes (In the elderly, In adults) in USA (PO) (NCT03192176)
- 23 May 2018 Astellas Pharma completes a phase I trial in Polycystic ovary syndrome (In volunteers) in Japan (PO) (NCT03436849)
- 22 Feb 2018 Phase-I clinical trials in Polycystic ovary syndrome (In volunteers) in Japan (PO) (NCT03436849)
Fezolinetant (INN; former developmental code name ESN-364) is a small-molecule, orally active, selective neurokinin-3 (NK3) receptorantagonist which is under development by Ogeda (formerly Euroscreen) for the treatment of sex hormone-related disorders.[1][2] As of May 2017, it has completed phase I and phase IIa clinical trials for hot flashes in postmenopausal women.[1] Phase IIa trials in polycystic ovary syndrome patients are ongoing.[1] In April 2017, it was announced that Ogeda would be acquired by Astellas Pharma.[3]
Ogeda (formerly Euroscreen ) is developing fezolinetant, an NK3 antagonist, for treating endometriosis, benign prostate hyperplasia, polycystic ovary syndrome, uterine fibroids and hot flashes. In November 2018, drug was listed under phase II development for PCOS, uterine fibroids and hot flashes in company’s pipeline. In October 2018, the company was proceeding to phase III study preparation, and regulatory filings were expected in 2021 or later .
Fezolinetant shows high affinity for and potent inhibition of the NK3 receptor in vitro (Ki = 25 nM, IC50 = 20 nM).[2] Loss-of-function mutations in TACR and TACR3, the genes respectively encoding neurokinin B and its receptor, the NK3 receptor, have been found in patients with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.[2] In accordance, NK3 receptor antagonists like fezolinetant have been found to dose-dependently suppress luteinizing hormone (LH) secretion, though not that of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and consequently to dose-dependently decrease estradiol and progesterone levels in women and testosterone levels in men.[4] As such, they are similar to GnRH modulators, and present as a potential clinical alternative to them for use in the same kinds of indications.[5]However, the inhibition of sex hormone production by NK3 receptor inactivation tends to be less complete and “non-castrating” relative to that of GnRH modulators, and so they may have a reduced incidence of menopausal-like side effects such as loss of bone mineral density.[4][5]
Unlike GnRH modulators, but similarly to estrogens, NK3 receptor antagonists including fezolinetant and MLE-4901 (also known as AZD-4901, formerly AZD-2624) have been found to alleviate hot flashes in menopausal women.[6][7] This would seem to be independent of their actions on the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis and hence on sex hormone production.[6][7] NK3 receptor antagonists are anticipated as a useful clinical alternative to estrogens for management of hot flashes, but with potentially reduced risks and side effects.[6][7]
PATENT
WO2011121137
hold protection in most of the EU states until 2031 and expire in the US in 2031.
PATENT
US 20170095472

PATENT
WO2016146712
PATENT
WO-2019012033
Novel deuterated analogs of fezolinetant , processes for their preparation and compositions comprising them are claimed. Also claims are their use for treating pain, convulsion, obesity, inflammatory disease including irritable bowel syndrome, emesis, asthma, cough, urinary incontinence, reproduction disorders, testicular cancer and breast cancer. Further claims are processes for the preparation of fezolinetant. claiming use of NK3R antagonist eg fezolinetant, for treating pathological excess body fat or prevention of obesity.
Fezolinetant was developed as selective antagonist of NK-3 receptor and is useful as therapeutic compound, particularly in the treatment and/or prevention of sex-hormone dependent diseases. Fezolinetant corresponds to (R)-(4-fluorophenyl)-(8-methyl-3-(3-memyl-l,2,4-miacMazol-5-yl)-5,6-dmy(ko-[l,2,4]trizolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl)methanone and is described in WO2014/154895.
Drug-drug interactions are the most common type of drug interactions. They can decrease how well the medications works, may cause serious unexpected side effects, or even increase the blood level and possible toxicity of a certain drug.
Drug interaction may occur by pharmacokinetic interaction, during which one drug affects another drug’s absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion. Regarding metabolism, it should be noted that drugs are usually eliminated from the body as either the unchanged drug or as a metabolite. Enzymes in the liver, usually the cytochrome P450s (CYPs) enzymes, are often responsible for metabolizing drugs. Therefore, determining the CYP profile of a drug is of high relevancy to determine if it will affect the activity of CYPs and thus if it may lead to drug-drug interactions.The five most relevant CYPs for drug-drug interaction are CYP3A4, 2C9, 2C19, 1A2 and 2D6, among which isoforms 3A4, 2C9 and 2C19 are the major ones. The less a drug inhibits these CYPs, the less drug-drug interactions would be expected.
Therefore, it is important to provide drugs that present the safest CYP profile in order to minimize as much as possible the potential risks of drug-drug interactions.Even if fezolinetant possesses a good CYP profile, providing analogs of fezolinetant with a further improved CYP profile would be valuable for patients.
In a completely unexpected way, the Applicant evidenced that deuteration of fezolinetant provides a further improved CYP profile, especially on isoforms CYP 2C9 and 2C19. This was evidenced for the deuterated form (R)-(4-fluorophenyl)-(8-methyl-3-(3-(memyl-d.?)-l,2,4-miacttazol-5-y ^yl)methanone, hereafter referred to as “deuterated fezolinetant”.
Importantly, deuterated fezolinetant retains the biological activity of fezolinetant as well as its lipophilic efficiency.
Deuterated fezolinetant also presents the advantage to enable improvement of the in vivo half -life of the drug. For example, half -life is increased by a factor 2 in castrated monkeys, compared to fezolinetant.
Synthetic scheme
Deuterated fezolinetant may be synthesized using the methodology described following schemes (Part A and Part B):
Part A: Preparation of deuterated key intermediate (ii)
Part B: Synthesis of deuterated fezolinetant using intermediate (ii)
Synthesis of deuterated fezolinetant was performed through key intermediate (ii). Part A corresponds to the synthesis of intermediate (ii). Part B leads to deuterated fezolinetant (d3-fezolinetant), using intermediate (ii), using procedures adapted from WO2014/154895.
Experimental details
Part A – Step 1): Formation of d3-acetamide (b)
To i¾-acetic acid (a) (10 g, 1 equiv.) in DCM (100 mL) CDI (25.3 g, 1 equiv.) was added and the resultant mixture stirred at RT for 30 min, thereupon ammonia gas was bubbled through the reaction mixture for 40 min at 0-5 °C. Thereafter the bubbling was stopped, the mixture was filtered and the filtrate was evaporated under reduced pressure to give 30.95 g crude product that was purified using flash chromatography on silica to furnish 6.65 g (yield: 73 %) deuterated acetamide (b) was obtained (GC (column RTX-1301 30 m x 0.32 mm x 0.5 μπι) Rt 7.4 min, 98 %).
Part A – Step 2): Ring closure leading to compound (c)
<¾-Acetamide (b) (3.3 g, 1 equiv.) and chlorocarbonylsulfenyl chloride (CCSC) (8.4 g, 1.2 equiv.) were combined in 1,2-dichloroethane (63 mL), and refluxed for 4.5 h. CCSC can be prepared as per the procedure described in Adeppa et al. (Synth. Commun., 2012, Vol. 42, pp. 714-721). The volatiles were then removed to obtain 6.60 g (102 % yield) oxathiazolone (c) product as a yellow oil. The product was analyzed by GC (Rt= 7.8 min, 97 ). 13C NMR (CDC13): 16.0, 158.7, 174.4 ppm.
Part A – Step 3): formation of compound (d)
To oxathiazolone (c) (6.6 g, 1 equiv) in rn-xylene (231 mL) methyl cyanoformate (14.70 g, 3.2 equiv.) was added. The mixture was stirred at 130 °C for 19 h and thereafter the volatiles removed under reduced pressure at 50 °C to obtain 4.53 g brown oil (yield: 51 %). The product (d) was analyzed by GC (Rt = 11.8 min, 81 %) and mass spectrometry (M+H = 162).
Part A – Step 4): formation of intermediate (ii)
The ester (d) obtained above (3.65 g, lequiv.) was dissolved in ethanol (45 mL). The undissolved material was filtered off then hydrazine hydrate (2.3 mL, 1.15 equiv. 55w/w in H20) was added to the stirred solution. Thick suspension formed in minutes, the suspension was stirred for 45 min, filtered and washed with EtOH (3 mL) to furnish intermediate (ii) a pale yellow solid (2.43 g, 55 % yield). Mass spectrometry (M+H = 162, M+Na = 184); ¾ NMR (cfe-DMSO): 4.79 ppm (br s, 2H), 10.55 ppm (br s, 1H); 13C NMR (fife-DMSO): 17.4 ppm, 155.6 ppm, 173.4 ppm, 183.0 ppm.
Part B – Step a): formation of compound (iii)
Intermediate (i) was prepared as described in WO2014/154895.
Intermediate (ii) (490 mg, 3.04 mmol) and compound (i) (1.0 g (87 mol 1.3 content), 2.97 mmol) were taken up in MeOH and the reaction mixture was stirred at a temperature ranging from 55°C to 70°C for a period of time ranging from 6 hours to 8 hours. The reaction was deemed complete by TLC. The reaction mixture was evaporated and the crude product was purified by flash chromatography on silica in DCM : MeOH eluent to afford 1.13 g (97 % yield) of compound (iii) as a yellow oil. JH NMR (CDC13): δ (ppm) 7.26 (d, 1H), 6.48-6.49 (2H), 4.50 (m, 1H), 4.30 (m, 1H), 4.09 (m, 1H), 3.94 (d, 1H), 3.80 (s, 6H), 3.61 (d, 1H), 3.22 (m, 1H), 2.75 (m, 1H), 1.72 (d, 3H); Mass spectrometry (M+H = 390, 2M+Na = 801). Chiral LC (column: Chiralpak IC, 250 x 4.6 mm – eluent: MTBE MeOH DEA 98/2/0.1) 99.84 .
Part B – Step b): deprotection leading to compound (iv)
Intermediate (iii) prepared above (1.05 g, 2.7 mmol) was dissolved in DCM and washed with aq. NaOH. The organic phase was dried, then TFA (1.56 mL, 2.3 g, 7.5 equiv.) was added at RT. The resulting solution was stirred at RT for 2 h. The reaction was monitored by TLC. After completion of the reaction water was added to the reaction mixture, and the precipitate filtered and washed with water. The phases were separated, the pH of the aq. phase was adjusted to pH 13 by addition of 20 % aq. NaOH. NaCl was then added to the aqueous solution that was then extracted with DCM. The organic phase was evaporated under reduced pressure to give 504 mg of compound (iv) (78 % yield). ¾ NMR (cfe-DMSO): δ (ppm) 4.42 (m, 1H), 4.10 (m, 2H), 3.0 (m, 1H), 2.82 (m, 1H), 1.46 (d, 3H). 13C NMR (rf6-DMSO): δ (ppm) 174.8, 173.4, 156.2, 145.0, 48.1, 45.7, 40.7, 19.1. Mass spectrometry (M+H = 240, 2M+Na = 501).
Part B – Step c): acylation and recrystallization to form deuterated fezolinetant
Intermediate (iv) (450 mg, 1.88 mmol) was dissolved in DCM, then sat. aq. NaHC03 was added and the mixture was stirred for 30 min. To this mixture 4-fluorobenzoyl chloride (v) (220 1 equiv.) was added dropwise at RT. The reaction was stirred for a period of time ranging from about 20 min to overnight at RT and reaction progress monitored by TLC. After completion the phases were separated, the organic phase was washed with water, dried over MgS04, filtered and evaporated under reduced pressure to give 745 mg crude <i3-fezolinetant (110 % yield). The crude product was purified by flash chromatography using MeOH : DCM together with a second batch, then
crystallized (EtOH H20) before final analysis. ¾ NMR (d6-DMSO): δ (ppm) 7.60 (m, 2H), 7.33 (m, 2H), 5.73 (m, 1H), 4.68 (dd, 1H), 4.31 (m, 1H), 4.06 (m, 1H), 3.65 (m, 1H), 1.61 (d, 3H). 13C NMR (d6-DMSO): δ (ppm) 174.4, 173.5, 168.7, 163.7, 161.8, 154.1, 144.9, 131.6, 129.5, 115.5, 44.7, 18.7. Isotopic purity based on an intense molecular ion observed at m/z = 362.2 Da is estimated as approximately 100 % isotopic purity. Chiral purity (LC) (column: Chiralpak IC, 250 x 4.6 mm – eluent: n-hexane/EtOH DEA 80/20/0.1) >99.9 %. A single crystal X-ray structure of the deuterated fezolinetant final product was obtained (Figure 1) that confirmed the structure of the compound as well as the stereochemistry.
References
- ^ Jump up to:a b c http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800039455
- ^ Jump up to:a b c Hoveyda, Hamid R.; Fraser, Graeme L.; Dutheuil, Guillaume; El Bousmaqui, Mohamed; Korac, Julien; Lenoir, François; Lapin, Alexey; Noël, Sophie (2015). “Optimization of Novel Antagonists to the Neurokinin‑3 Receptor for the Treatment of Sex-Hormone Disorders (Part II)”. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters (6): 736-740. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00117.
- ^ http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/astellas-to-acquire-ogeda-sa-300433141.html
- ^ Jump up to:a b Fraser GL, Ramael S, Hoveyda HR, Gheyle L, Combalbert J (2016). “The NK3 Receptor Antagonist ESN364 Suppresses Sex Hormones in Men and Women”. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 101 (2): 417–26. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-3621. PMID 26653113.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Fraser GL, Hoveyda HR, Clarke IJ, Ramaswamy S, Plant TM, Rose C, Millar RP (2015). “The NK3 Receptor Antagonist ESN364 Interrupts Pulsatile LH Secretion and Moderates Levels of Ovarian Hormones Throughout the Menstrual Cycle”. Endocrinology. 156 (11): 4214–25. doi:10.1210/en.2015-1409. PMID 26305889.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/878262
- ^ Jump up to:a b c https://www.clinicalleader.com/doc/ogeda-announces-positive-fezolinetant-treatment-menopausal-flashes-0001
External links
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ESN-364 |
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H15FN6OS |
| Molar mass | 358.40 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
////////////////Fezolinetant, ESN-364, фезолинетант , فيزولينيتانت , 非唑奈坦 , Phase II, Hot flashes, Polycystic ovary syndrome, Uterine leiomyoma, Euroscreen, Ogeda
Smiles
C[C@H]1N(CCn2c1nnc2c3nc(C)ns3)C(=O)c4ccc(F)cc4
“ALL FOR DRUGS” CATERS TO EDUCATION GLOBALLY, No commercial exploits are done or advertisements added by me. This is a compilation for educational purposes only. P.S. : The views expressed are my personal and in no-way suggest the views of the professional body or the company that I represent
READ
ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO
 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
![]() amcrasto@gmail.com
amcrasto@gmail.com
CALL +919323115463 INDIA
//////////////






 amcrasto@gmail.com
amcrasto@gmail.com














