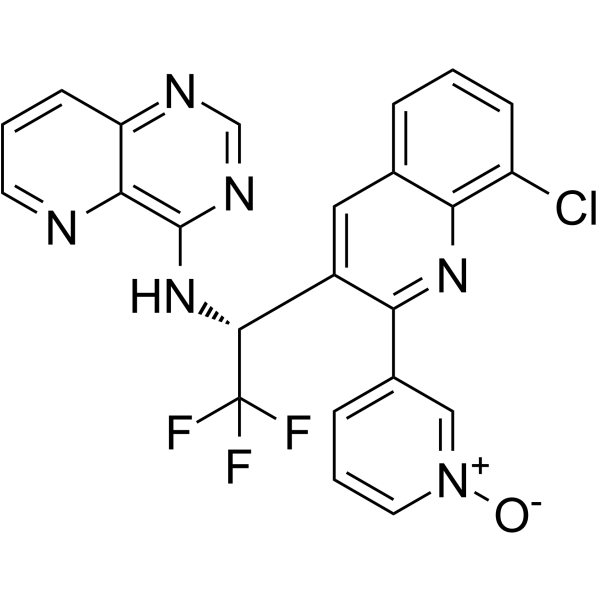
SELETALISIB
CAS 1362850-20-1
UCB-5857 , Plaque psoriasis,Sjoegren’s syndrome,Immunodeficiency disorders
PHASE 3 UCB
23H14ClF3N6O , 482.85
Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase delta (PI3Kδ) inhibitors
| Pyrido[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-amine, N-[(1R)-1-[8-chloro-2-(1-oxido-3-pyridinyl)-3-quinolinyl]-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl]- |
3-{8-chloro-3-[(1R)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-({pyrido[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-yl}amino)ethyl]quinolin-2-yl}pyridin-1-ium-1-olate
Seletalisib has been used in trials studying the treatment and basic science of Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome.
- Originator UCB
- Class Anti-inflammatories; Small molecules
- Mechanism of Action Immunomodulators; Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase delta inhibitors
- Phase III Immunodeficiency disorders
- Phase II Sjogren’s syndrome
- No development reported Plaque psoriasis
- 05 Dec 2017 UCB Celltech terminates a phase II trial in Sjogren’s syndrome in France, Spain, United Kingdom, Greece, Sweden, Italy, due to enrolment challenges (PO) (NCT02610543) (EudraCT2014-004523-51)
- 04 Nov 2017 No recent reports of development identified for phase-I development in Plaque-psoriasis in United Kingdom (PO, Capsule)
- 14 Jun 2017 Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics data from Preclinical and Clinical studies in Immunodeficiency disorders presented at the 18th Annual Congress of the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR-2017)
SYN
US 9029392
https://patents.google.com/patent/US9029392B2/en
Example 27 N—{(R)-1-[8-Chloro-2-(pyridin-3-yl)quinolin-3-yl]-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl}N-(1-oxypyrido-[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amine
A stirred solution of Example 1 (955 mg, 2.05 mmol) in DCM (40 mL) was cooled to 0° C. MCPBA (410 mg, 1.84 mmol) was added and the mixture was allowed to warm slowly to r.t. over 3 h. The reaction mixture was partitioned between DCM and saturated aqueous NaHCO3 solution. The aqueous phase was extracted with further DCM and the combined organic fractions were washed with brine, dried Na2SO4) and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was purified by column chromatography (SiO2, 3-60% MeOH in EtOAc) to give the title compound (39 mg, 4%) as a yellow solid. δH (DMSO-d6) 9.64-9.52 (m, 1H), 9.30 (s, 1H), 9.06 (dd, J 4.2, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 8.78-8.71 (m, 2H), 8.67 (dd, J 4.9, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 8.64 (s, 1H), 8.16-8.01 (m, 4H), 7.75-7.69 (m, 1H), 7.52 (ddd, J 7.8, 4.9, 0.7 Hz, 1H), 6.65-6.52 (m, 1H). LCMS (ES+) 483 (M+H)+, RT 1.87 minutes.

AND

PATENT
WO 2012032334
PATENT
WO 2015181053
WO 2015181055
WO 2016170014
PATENT
A SPECIFIC TRIFLUOROETHYL QUINOLINE ANALOGUE FOR USE IN THE TREATMENT OF APDS
The present invention relates to the new therapeutic use of a known chemical compound. More particularly, the present invention concerns the use of a specific substituted quinoline derivative comprising a fluorinated ethyl side-chain in the treatment of activated phosphoinositide 3 -kinase delta syndrome (APDS).
N- {(R)- 1 -[8-Chloro-2-(l -oxypyridin-3-yl)quinolin-3-yl]-2,2,2-trifiuoroethyl} -pyrido[3,2-JJpyrimidin-4-ylamine is specifically disclosed in WO 2012/032334. The compounds described in that publication are stated to be of benefit as pharmaceutical agents, especially in the treatment of adverse inflammatory, autoimmune, cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, metabolic, oncological, nociceptive and ophthalmic conditions.
There is no specific disclosure or suggestion in WO 2012/032334, however, that the compounds described therein might be beneficial in the treatment of APDS.
Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta syndrome (APDS), also known as
PASLI (pi ΙΟδ-activating mutation causing senescent T cells, lymphadenopathy and immunodeficiency), is a serious medical condition that impairs the immune system.
APDS patients generally have reduced numbers of white blood cells (lymphopenia), especially B cells and T cells, compromising their propensity to recognise and attack invading microorganisms, such as viruses and bacteria, and thereby prevent infection. Individuals affected with APDS develop recurrent infections, particularly in the lungs, sinuses and ears. Recurrent respiratory tract infections may gradually lead to bronchiectasis, a condition which damages the passages leading from the windpipe to the lungs (bronchi) and can cause breathing problems. APDS patients may also suffer from chronic active viral infections, including Epstein-Barr virus infections and cytomegalovirus infections.
APDS has also been associated with abnormal clumping of white blood cells, which can lead to enlarged lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy). Alternatively, the white blood cells can build up to form solid masses (nodular lymphoid hyperplasia), usually in the moist lining of the airways or intestines. Whilst lymphadenopathy and nodular lymphoid hyperplasia are benign (noncancerous), APDS also increases the risk of developing a form of cancer called B cell lymphoma.
APDS is a disorder of childhood, typically arising soon after birth. However, the precise prevalence of APDS is currently unknown.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta (ΡΒΚδ) is a lipid kinase which catalyses the generation of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). PI3K5 activates signalling pathways within cells, and is specifically found in white blood cells, including B cells and T cells. PI3K5 signalling is involved in the growth and division (proliferation) of white blood cells, and it helps direct B cells and T cells to mature (differentiate) into different types, each of which has a distinct function in the immune system.
APDS is known to occur in two variants, categorised as APDSl and APDS2.
APDSl is associated with a heterozygous gain-of- function mutation in the PIK3CD gene encoding the PI3K5 protein; whereas APDS2 is associated with loss-of-function frameshift mutations in the regulatory PIK3R1 gene encoding the p85a regulatory subunit of class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) peptides. Both mutations lead to hyperactivated PI3K signalling. See I. Angulo et ah, Science, 2013, 342, 866-871; C.L. Lucas et ah, Nature Immunol, 2014, 15, 88-97; and M-C. Deau et al, J. Clin. Invest., 2014, 124, 3923-3928.
There is currently no effective treatment available for APDS. Because of the seriousness of the condition, and the fact that it arises in infancy, the provision of an effective treatment for APDS would plainly be a highly desirable objective.
It has now been found that N-{(R)-l-[8-chloro-2-(l-oxypyridin-3-yl)quinolin-3-yl]- 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl}pyrido[3,2-(i]pyrimidin-4-ylamine is capable of inhibiting the elevation of PI3K signalling in T cells (lymphocytes) from both APDSl and APDS2 patients in the presence or absence of T cell receptor activation.
The present invention accordingly provides N-{(R)-l-[8-chloro-2-(l-oxypyridin-3-yl)quinolinB-yl]-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl}pyrido[3,2-JJpyrimidin-4-ylamine of formula (A):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment and/or prevention of APDS.
The present invention also provides a method for the treatment and/or prevention of APDS, which method comprises administering to a patient in need of such treatment an effective amount of N-{(R)-l-[8-chloro-2-(l-oxypyridin-3-yl)quinolin-3-yl]-2,2,2-trifluoro-ethyl}pyrido[3,2-(i]pyrimidin-4-ylamine of formula (A) as depicted above, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The present invention also provides the use of N-{(R)-l-[8-chloro-2-(l-oxypyridin-3-yl)quinolin-3-yl]-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl}pyrido[3,2-JJpyrimidin-4-ylamine of formula (A) as depicted above, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment and/or prevention of APDS.
PAPER
Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics (2017), 361(3), 429-440.
http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/content/361/3/429
///////////////SELETALISIB, PHASE 3, UCB, селеталисиб , سيلستاليسيب , 司来利塞 ,
[O-][N+]1=CC(=CC=C1)C1=NC2=C(Cl)C=CC=C2C=C1[C@@H](NC1=NC=NC2=CC=CN=C12)C(F)(F)F
